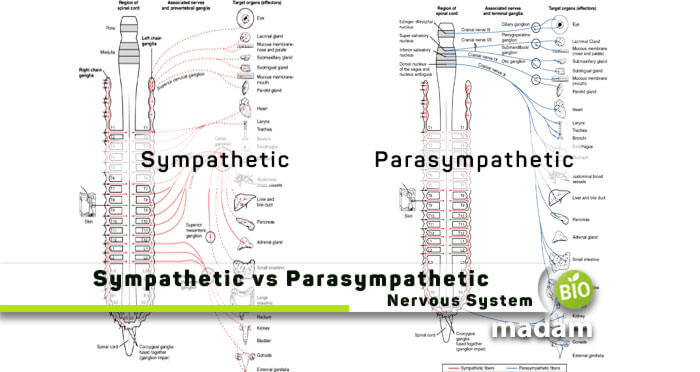
Before grabbing the differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, understand what an autonomic nervous system is. It is the primary controlling mechanism of our body that specifically involves blood circulation, breathing, digestion, urination, etc. The reason behind naming it autonomic is due to its autonomous functioning, which means it works involuntarily. Unlike the autonomic, there is another called the somatic nervous system which controls involuntary movements.
Besides the functions mentioned above, homeostasis is also considered a fundamental role of the ANS. It is the ability to maintain an internal environment despite several changes in the surrounding. Today, we’ll discuss the differences between the two major types of the autonomic nervous system, i.e., sympathetic and parasympathetic.
Let’s first glance at their comparison table below!
Comparison Table
| Parameters | Sympathetic Nervous System | Parasympathetic Nervous System |
| Outflow | Thoracolumbar Outflow | Craniosacral Outflow |
| Ganglion Position | Away from Effector & Close to Spinal Cord | Close to Effector & Away from Spinal Cord |
| Pre-Ganglionic Fiber Size | Short | Long |
| Post-Ganglionic Fiber Size | Long | Short |
| Activation of Responses | Fight & Flight | Rest & Digest |
| Neuron Pathways | Fast System, Very Short Neurons | Slow System, Longer Pathways |
| Nerves | Adrenergic | Cholinergic |
| Response Time | Quick Response | Slow Response |
| Coverage | Large Body Area | Small Body Area |
| Effect Type | Diffused | Localized |
| Released Neurotransmitter | Noradrenaline | Acetylcholine |
| Homeostatic Effect | Excitatory | Inhibitory |
Sympathetic Nervous System – Brief Explanation
The part of ANS that controls the “fight and flight” responses in the body is called the sympathetic nervous system. As this system arises from the spinal cord, particularly the lumbar and thoracic regions, it deals with external danger. The pre-ganglionic nerve fibers produce a response that secretes acetylcholine. This neurotransmitter through the adrenal gland is responsible for activating adrenaline and noradrenaline. Adrenaline further prepares the body for emergencies, such as increased heart rate, decreasing GIT motility, breakdown of glycogen, etc.
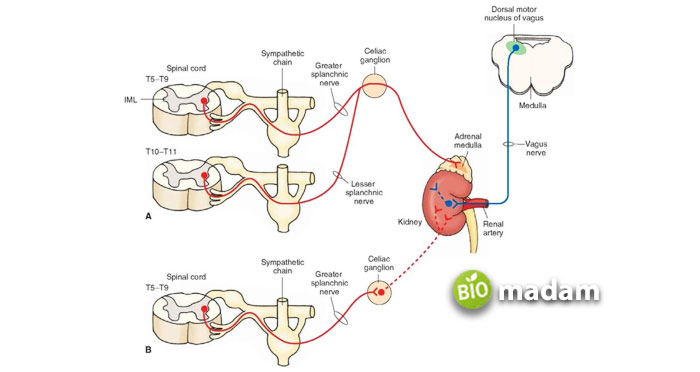
SNS (Sympathetic Nervous System) covers a large portion of the body as its nerve fibers innervate almost all body organs. Moreover, sympathetic activity broadens the bronchial passageways for rapid breathing. It also dilates eye pupils and constricts blood vessels (veins and arteries).
Parasympathetic Nervous System – Brief Explanation
The part of ANS that controls the “rest and digest” systems in the body is called the parasympathetic nervous system. This system originates from the medulla and spinal cord to control internal homeostasis maintenance. The neurotransmitter involved in parasympathetic activity is Acetylcholine, which directly acts on nicotinic receptors to produce its effect. The parasympathetic nervous system is the exact opposite of SNS, covering a small body portion. It produces a localized effect in the body at slow response.
As the cycle activates in rest and digestion conditions, so it promotes salivation, urination, digestion, defecation, and lacrimation. The inhibitory homeostatic effect of PSNS restores sensory awareness to a normal body level.
Similarities between the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
- Despite being opposite in managing a body’s internal system, both of them have a few similarities that are discussed below:
- Both are the main parts of the autonomic nervous system’s sympathetic or parasympathetic system.
- Both nervous systems commonly originate from the spinal cord.
- sympathetic and Parasympathetic nervous systems consist of pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic neurons.
- Whether SNS or PSNS, both significantly affect the body’s physiological processes, such as reproduction, circulation, respiration, digestion, urination, etc.
- Both systems play a major part in maintaining homeostasis, an internal temperature of the body.
Differences between the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
Both nervous systems have a major role in maintaining different body situations. While the sympathetic system controls emergencies, the other functions are balancing and restoring them. Let us discuss a few more common differences between the two.
How Do These Systems Respond?

Sympathetic Nervous System
- SNS accelerates and tenses up a living body. Here are the primary responses by a sympathetic nervous system:
- Increase in heart rate
- Constriction of the heart
- Contraction of smooth muscles
- Contraction of sphincters
- Dilation of the eye pupils and bronchial tubes in the lungs
- The decrease in urination
- Freeing up adrenaline from adrenal glands
- Shutting down all the unimportant processes of survival
- Breakdown of glycogen to produce energy
- Reduction in salivation
Parasympathetic Nervous System
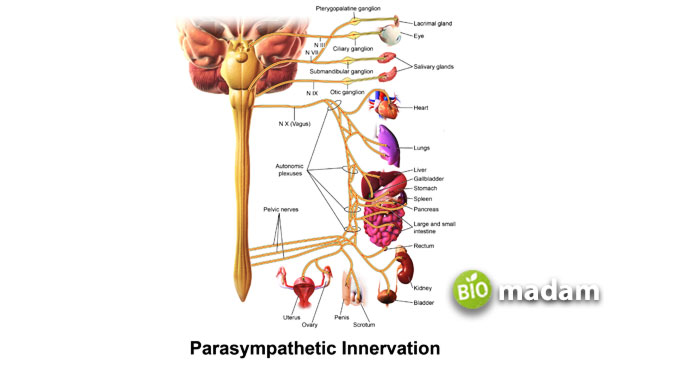
On the other hand, the parasympathetic system balances the sympathetic nervous system. It contributes to maintaining the calm state of the body. Below are the primary responses by this system:
- Reduction in heart rate
- Relaxation of smooth muscles
- Relaxation of sphincters
- Constriction of eye pupils and bronchial tubes in the lungs
- Increase in urination
- More saliva production for increased digestion
Working on the Nervous Systems
Sympathetic Nervous System
SNS is a rapid system with movements along the short neurons in the body. The sympathetic system triggers the adrenal medulla to discharge chemical receptors and hormones (for instance, estrogen and progesterone) into the bloodstream. Moreover, the targeted muscles and different glands get excited too. Soon after the danger is all gone, the other autonomic nervous system takes over to balance the body’s working.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
As discussed above, this system works to counterbalance the sympathetic system. Parasympathetic is a slower mechanism with movements along the higher pathways. This system usually activates the preganglionic fibers from the spinal cord or medulla that works near the target unit. They are set to produce a synapse that helps in activating the desired response.
Conclusion
The overall differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems make them two distinct types of the autonomic nervous system. Both methods work one after the other. If the former activates the fight and flight situation of the body, the latter counterbalances these activities to the rest and digestion condition. Whether it’s a sympathetic or parasympathetic system, both hold their own significance for the daily working of a body.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.