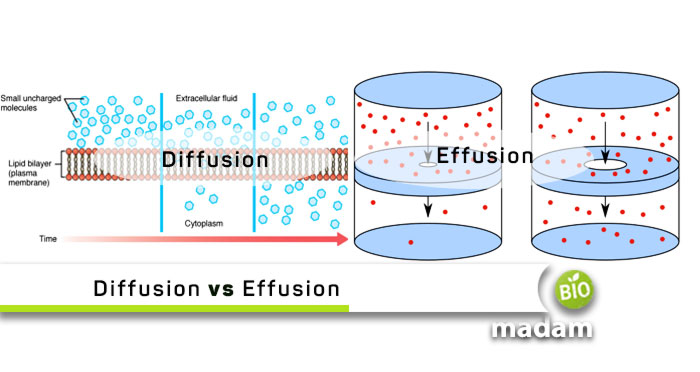
Our biomes and ecosystems comprise different processes like photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, osmosis, evaporation, transpiration in plants, etc. Diffusion and effusion are two such processes occurring within biotic and abiotic components around us. Diffusion in body cells allows them to intake nutrition and get rid of waste products. It also plays a major role in photosynthesis in plants. On the other hand, effusion plays a significant role in maintaining normal body physiology, especially in the lungs.
Keep reading to learn all the differences between diffusion and effusion.
Comparison Table
| Factors | Diffusion | Effusion |
| Definition | Movement of molecules from higher to lower conc. | Gas-molecule movement across several small holes |
| Origin Word | Diffundre | Effundo |
| Type of Molecule | Solid, liquid, gas | Gas |
| Occurrence | Conc. gradient | Pressure difference |
| Movement of Molecule | Freely moving | Across small holes |
| Collision | Present | Absent |
| Efficiency | Less | More |
| Example | Spread of fragrance, and exchange of gases | Balloon deflation, entry of water in lungs |
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is defined as the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. It is also known as the movement of particles down the concentration gradient. The concentration gradient is the difference in the concentration of molecules.
In simple words, diffusion refers to mixing gas molecules with each other. The collision of gas molecules in space releases the gas’s molecular energy. This mechanism will then result in the reduction of the efficiency of diffusion. Diffusion is of two types, usually occurring inside the human body, such as exchanging oxygen between cells. The main reason for the occurrence of distribution is the concentration gradient of molecules. It is the random thermal motion of particles in a gaseous state. However, diffusion depends on the size and kinetic energy of those molecules. Gasses have a rapid diffusion due to the rapid movement of particles in a gas. The particles will move even faster if it is a hot gas. Diffusion is often confused with osmosis because of a similar mechanism. However, osmosis is water movement across a semipermeable membrane compared to diffusion.

Examples of Diffusion
- The smell of perfume spreading through the room
- Food inside a packed room
- Movement of oxygen or carbon dioxide gas between cells
What is Effusion?
Effusion refers to the movement of gas molecules from one place to another through a small hole or small aperture. The concentration gradient of the gas molecules generates a pressure gradient around the opening which works as a driving force that makes gas molecules move from gasses of high concentration to gasses of low concentration through the opening. The opening in the effusion should be small.
It is explained as the movement of molecules or compounds through a barrier with one or many small holes preventing gas expansion into the new volume. The diameter of the holes in the barrier is typically less than the mean free path of the gas molecules. The mean free path refers to the average distance traveled by a gas molecule before the collision with another molecule.
Example of Effusion
To understand effusion, consider the example of a balloon. However, gas or air cannot enter a balloon. But effusion shows that it contains a hole in it. Such as, if helium gas is filled inside a balloon and left aside for a few days, the balloon will collapse. In other cases, if hydrogen gas is filled inside a balloon, it would collapse even faster. Because of the smaller size of hydrogen molecules, they will escape easily, resulting in the balloon’s collapse.
Graham’s Law of Diffusion and Effusion
Thomas Graham devised ‘Graham’s law of effusion’ in 1848 when he discovered that lighter molecules travel faster than heavy ones. Graham’s law of effusion states:
“Rate of effusion or diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight.”
He mentions that the atoms or molecules with lower molecular mass will effuse faster than heavier atoms at constant temperature and pressure. Mathematically, it states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular mass.
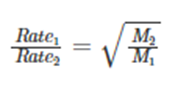
Similarities between Diffusion and Effusion
- Diffusion and effusion help in the movement of different molecules from one place to another.
- The motion of molecules in both diffusion and effusion mechanisms is continuous and random.
- Both take place via a concentration gradient.
- They both do not need the energy to move molecules in space
Differences between Diffusion and Effusion
Definition
Diffusion
It refers to the movement of molecules from a high-concentration region to a low-concentration region.
Effusion
Whereas effusion refers to the movement of gas particles through a small aperture.
Origin Word
Diffusion
The English word ‘diffusion’ comes from the Latin word ‘Diffundre,’ translating to ‘spread out.’
Effusion
On the other hand, effusion originates from another Latin word, ‘effundo,’ meaning ‘pour out.’
Type of Molecules
Diffusion
Diffusion occurs in all three states, i.e., solid, liquid, and gas.
Effusion
Conversely, effusion occurs in a gaseous state, and not in the aqueous or liquid state.
Occurrence
Diffusion
Diffusion occurs when gas particles are spread all over the tube. They do not require a membrane for the movement of molecules.
Effusion
At the same time, effusion occurs when gas particles move from a small area, known as the mean free path. In other words, it appears when there is a pressure difference.
Movement of Molecules
Diffusion
In diffusion, molecules roam around freely in space.
Effusion
However, in effusion, molecules move only through tiny holes.
Driving Force
Diffusion
The concentration gradient acts as the driving force in simple and facilitated diffusion.
Effusion
On the contrary, the concentration gradient generates a pressure gradient in effusion which works as a driving force of molecules.
Collision
Diffusion
There are many collisions of molecules in diffusion.
Effusion
Alternatively, they are no chances of collision of molecules in effusion.
Efficiency
Diffusion
It is a less efficient method compared to others.
Effusion
On the other hand, effusion is more efficient due to the pressure difference.
Examples
Diffusion
The exchange of gasses between blood vessels, especially capillaries, and the environment occurs through diffusion.
Effusion
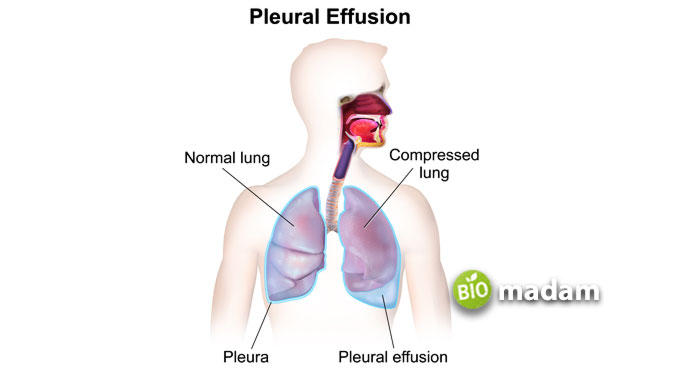
Pleural effusion, also known as water in the lungs, is an example of effusion affecting the right and left lungs. Such as, when there is a perfume spray in the room, the particles spread all over the area and get mixed within the air. In other words, it occurs when there are no holes or the holes are more significant than the mean free path.
The Bottom Line
Diffusion and effusion are critical processes essential to maintaining normal bodily function. Diffusion allows the exchange of molecules between cells, tissues, and organs. On the other hand, uncontrolled effusion may lead to a pathological condition called pleural effusion, which is a result of any underlying disease. The main difference between diffusion and effusion is the passage of molecules through small holes in effusion.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.