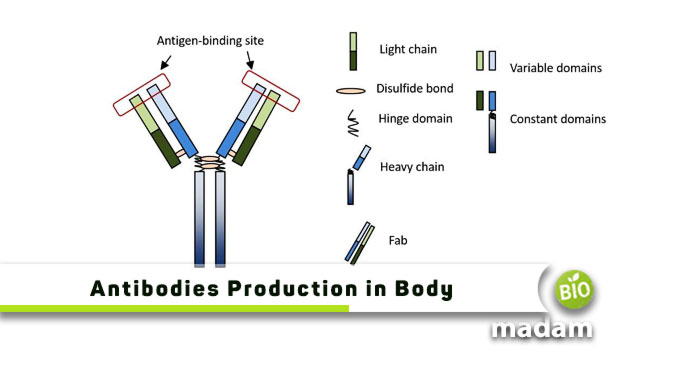
The immune system is an important component of our body that protects us from antigens and pathogens that may cause diseases. It comprises different types of cells, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. Each type of immune cell contains different further components, such as B cells and T cells. They both are a type of lymphocyte and protect the body from elements that may be harmful but in different ways. Students often wonder, “Do T cells produce antibodies?”
T-cells do not produce antibodies. Instead, B cells produce antibodies.
But what do T cells produce, then? And how do they fight potential damage to bodily cells? This article answers all these questions. Keep reading to learn more.
B & T Cells in Immunity
B cells and T cells are not the first line of action when an antigen enters the body. Any pathogen or foreign body is first greeted and attacked by macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, or dendritic cells. However, T and B cells come into action when the body requires an advanced and more sophisticated attack. They use past interactions and behaviors of the pathogen to destroy them.
T cells and B cells are types of lymphatic cells in the body. Just like antibodies, lymphocytes play a critical role in your immune system by fighting off pathogens, antigens, and cancer cells.
Do T Cells Produce Antibodies?
Now, it’s time for the big question: “Do T-cells produce antibodies?” As mentioned earlier, T cells do not produce antibodies. They help B cells eliminate pathogens and directly attack infected or cancerous cells to protect the body. Meanwhile, T cells may also contribute to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
The bone marrow produces the T cells, which mature, multiply, and differentiate in the thymus. T cells differentiate into cytotoxic, helper, memory, and regulatory T cells. After differentiation, the cells move to the peripheral tissues or circulate in the lymphatic or blood-circulatory system.
Other Cells Producing Antibodies
Opposed to T cells, B cells produce antibodies called B lymphocytes. These antibodies bind to pathogens to kill them. B cells also prevent the pathogens from entering a normal cell to cause infection and help other cells destroy infected cells.
Mechanism of Action of T Cells
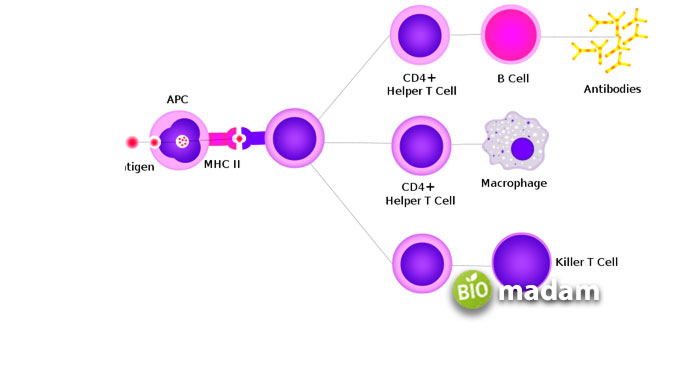
T cells are a component of your adaptive immune system that builds a customized attack plan to fight a foreign body. Every T cell fights only one type of antigen and remembers it. Your immune system locates and identifies the foreign entity, and the specific T cells multiply to attack the intruder. Later they become memory cells and remember the invader to protect your body against that foreign entity.
Here’s how the T cells in the body activate and fight against antigens:
- The antigen-presenting cells locate the invader and attach it to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Attaching to MHC allows the T cells to recognize the pathogen or infected cell.
- Next, the T cell binds to one of the major histocompatibility complexes depending on the receptor on the T cell. Cytotoxic T cells have CD8 receptors that bind to MHC-I, while the helper T cells bind to MHC-II.
- The T cells activate after binding with the correct MHC and are ready to fight the infected or cancerous cell or foreign body.
The activated T cells send signals to other cells (helper T cells) or fight the intruder (cytotoxic T cells) to protect your body from harm.
Types of T Cells
The three types of T cells are helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells:
Helper T Cells
Helper T cells signal other cells in the immune system to coordinate and produce an attack against antigens. They signal macrophages and cytotoxic T cells to prepare for the attack. They do so due to the presence of the CD4 receptor on their membranes.
Cytotoxic T Cells
Cytotoxic T cells are the other type of T cells that translate to “harmful to cells.” They have a CD8 receptor on their membranes, which enables them to destroy infectious and tumor cells besides invaders. Cytokines allow the activation of cytotoxic T cells.
Regulatory T Cells
Regulatory T cells are also known as suppressor cells and play a vital role in the immune system by suppressing the activity of other T cells when needed. In easier words, they control the activity of the T cells and prevent them from attacking your body’s healthy cells.
Difference between T Cells and Antibodies
T cells and antibodies contribute to a healthier body by protecting you from pathogens and tumor cells in different ways.
T cells attach to specific antigens to destroy and remember them for the next time. On the other hand, B cells manufacture different types of antibodies to kill harmful cells. B cells use antibodies to produce immune action, while T cells attack directly.
The Bottom Line
T cells and B cells are two types of lymphocytes that are a part of the lymphatic system, and the answer to “Do T cells produce antibodies” is no. T cells do not produce antibodies and attack the harmful cells directly. Contrarily, B cells produce antibodies that help kill antigens. T cells can be helper or cytotoxic depending on their function in the immune process. They both work together to save the body from pathogen attacks.
FAQs
How does cancer treatment affect T cells and B cells?
Cancer treatment, primarily chemotherapy, produces action by acting on cells multiplying fast. Besides tumor cells, B and T cells multiply fast to fight antigens. Thus chemotherapy and radiation therapy may kill B and T cells as well. However, most people gain their B and T cells after treatment.
What is the difference between B and T cells?
B cells and T cells are white blood cells belonging to the lymphatic system. They contribute to the adaptive immune system by fighting off the cells based on previous memory and interaction. B cells produce antibodies, while T cells attack directly.
Do T cells activate B cells?
Helper T cells activate B cells when they recognize the MHC class II complex on the B cell. It allows them to understand the type of cell depending on the type of major histocompatibility complex.
What proteins are produced by T cells?
While B cells produce antibodies, T cells create another protein called perforin. It is a pore-forming protein homologous to the complement component C9 and helps form transmembrane channels.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.