All animals and most plants consist of millions of complex cells, known as eukaryotic cells. These organisms perform several functions through different organelles, such as nucleus, ribosomes, smooth and rough ER, etc. One such is the mitochondria having functions in plant and animal cells.
What is a Mitochondrion?
This word is extracted from the Greek language, meaning threadlike granules. A German Pathologist named Richard Altmann explained this organelle in 1890. He came up with the following idea about mitochondria:

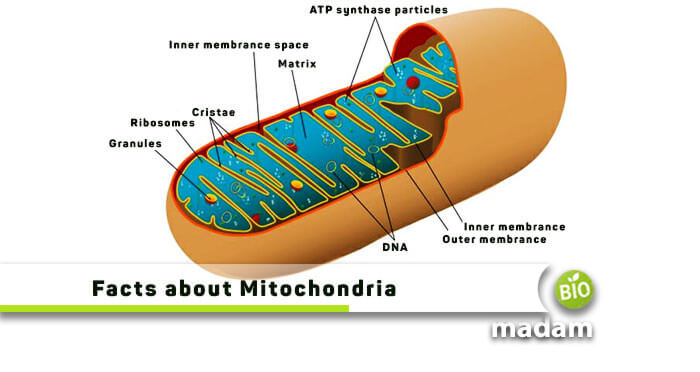
It is a double-membrane bounded organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. A mitochondrion has multiple inner folding, called cristae. This colorless substance appears to be bean-shaped, which is being surrounded by cytosol and is floating in the cytoplasm. A mitochondrion is responsible for breaking essential nutrients into energy that a cell further consumes. A lot of biochemical mechanisms concerning cellular respiration occur in mitochondria.
Basic Facts About Mitochondria
Let’s talk about the facts of Mitochondria:
- There is a considerable number of this organelle present within an organism, also called as the powerhouse of the cell. On average, a cell consists of about ten to twenty lac mitochondria to generate everyday energy.
- A mitochondrial structure is double membranous, which is composed of a thick outer membrane, an inner membrane that is folded inside, called cristae, and a matrix.
- The inner folding of a mitochondrion helps increase its surface area, promoting it to perform maximum cellular mechanisms.
- The fluid part of the organelle is the matrix, containing water and proteins.
- Mitochondria have the same property as ribosomes that function to manufacture proteins, which makes them a semi-autonomous organelle. These proteins help the organelle in producing ATP (energy needed for the disintegration of glucose.
- Mitochondria are essentially present where there is more requirement of energy. Hence, muscle cells have the maximum mitochondria for their regular activities.
- The amount of mitochondrion cells varies according to cell requirement. A human body contains numerous mitochondria but lacks this organelle in red blood cells.
- All organs have their specified function with a set number of mitochondria in them. For example, a liver functions through almost 1600 mitochondria, while a kidney has approximately 1000 such organelles.
- A mitochondrion can alter its shape and even die if required.
- Furthermore, apoptosis initiates from mitochondria, which is programmed cell death. There are multiple other functions of this organelle, such as it helps in cell growth, detoxification of the liver, cell cycle management, etc.
Functions of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are involved in many processes like heme, synthesis of phospholipids, apoptotic activation, and cell death. It takes part in the cellular respiratory processes, providing energy during the entire procedure. A respiratory process occurs in oxygen, known as Krebs’s Cycle or Citric Acid cycle because the cycle starts with citrate and ends on it. This cycle forms ATP and NADH+ molecules through the help of mitochondria.
Furthermore, this organelle follows a fusion process called mitochondrial fusion. When a cell is in stress condition, the outer and inner mitochondrial membrane fuses to maintain the cell’s health.
Complex Enzymes in Mitochondrial Matrix

There are four different complex enzymes present in a mitochondrial matrix, aiding in its functioning. These are:
- Combination of NADH-Q-reductase, helping protons to cross the membrane
- Combination of Succinate-Q-reductase
- QH2-Cytochrome-C-reductase
- Cytochrome-C-oxidase
Such enzymes enhance ATP production, which is used in oxidative phosphorylation.
What Happens When a Mitochondrion Fails?
According to research, a child with mitochondrial dysfunction is born every thirty minutes. 1 out of 4300 people gets affected by mitochondria diseases and respective infections around the globe. When this organelle fails, it stops producing sufficient energy needed for the cell, damaging or destroying it. The initial problem with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s patients is that they have improper mitochondrial functioning. It can be inherited from parents to children, so do a regular checkup every six months.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.