Golgi body, also known as the Golgi apparatus, is an organelle with a layered structure that transports material throughout the body in the form of sacs. They are named after the scientist who discovered them, Camillo Golgi. Besides the packing of materials into vesicles, they also transport proteins and lipids. They are located next to the endoplasmic reticulum near the cell membrane. Sometimes Golgi Bodies are mistaken as an extension of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Let’s talk about Golgi bodies in detail.
What are Golgi Bodies?
Golgi bodies are membrane-bound organelles present in the cytosol of the eukaryotic cell. They are mainly involved in transporting materials in packets or vesicles to different parts of the cell. The products transported by Golgi bodies are typically produced in the rough ER, however, the smooth ER has no function in it.
The Golgi apparatus is also involved in the production of lipids and fibrous or globular proteins. When the products from the ER reach the Golgi apparatus, they are modified and labeled by other proteins. The Golgi apparatus location of the release of these vesicles in the cytosol or cytoplasm depends on their labels and tags.
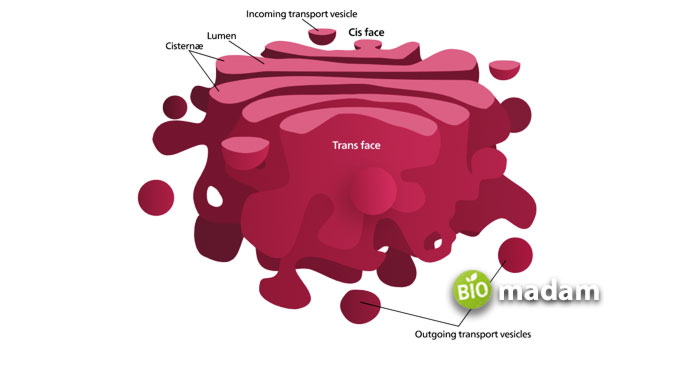
Structure of Golgi Body
Golgi bodies appear in layered structures under a compound or student microscope. It comprises 5 to 8 compartments called cisternae and lumen that look like flattened sacs stacked on each other similar to the ER. The Golgi body has two sides, the trans face, and the cis face. The trans face of the ER is away from the nucleus and secretes vesicles to different cell parts. On the other hand, the Cis face is towards the ER.
Function of Golgi Bodies
As the Golgi apparatus is involved in transporting material in vesicles, some other functions are associated with them that facilitate the process. The three most essential functions of Golgi bodies are:
Synthesis and Metabolism
The Golgi apparatus is involved in post-translational modification near the Golgi bodies, including glycosylation and phosphorylation. These processes are vital for body functioning and also cause enzymatic processing. The Golgi Bodies are a site for synthesizing numerous products like sphingomyelin and glycolipids, further having functions in the cell membrane.
Cellular Product Finalization
Sometimes the products are produced in one part of the cell and have to be used in another part of the cell. Before sending them to their destination, some changes have to be made to the product for proper utilization. The smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes and stores products, like lipids, calcium, steroids, etc. While some are meant for these organelles themselves, others have to move to various cell parts. One such example is the stomach acid produced in the Endoplasmic reticulum that later attaches to the cell membrane and releases the acid into the stomach.
Tagging
As mentioned before, one of the important functions of the Golgi apparatus is tagging the vesicles. Once the product’s structure is modified and packaged into vesicles, they are tagged to indicate where the vesicle needs to go. Markers like proteins or phosphate groups tag them. Once the vesicle is tagged, it is exited from the Golgi body and moves to the targeted area.
Is Golgi Apparatus in Plant and Animal Cells?
All eukaryotic cells, including plants and animals have Golgi bodies. While animals have a small number of Golgi bodies; plant cells have multiples of them. The Golgi apparatus in plants helps in the synthesis of polysaccharides which form the cell wall and process the oligosaccharide side chains of glycoproteins.
The Bottom Line
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle present in eukaryotes and performs various plant and animal cell functions. Besides the difference in their number in animal and plant cells, they perform specific functions in both. They are involved in synthesizing materials, finalizing, tagging, and transporting them to their target sites.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.

