Recently updated on February 8th, 2023 at 06:41 am
If you have always thought that hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, or diabetes are the same, or that hypoglycemia can only occur in diabetic patients – both are not true.
Though hypoglycemia is more common in diabetic patients, it can also occur in non-diabetics due to a receding glucose level in the bloodstream. The differences between hypoglycemia and diabetes are quite significant and will help you understand how they are dissimilar.
Comparison Table
| Factor | Hypoglycemia | Diabetes |
| Definition | Decreased blood sugar | Increased blood sugar |
| Indicator (Fasting) | <70 mg/ dL | >100mg/dL |
| Types | Two | Three |
| Nature | Reversible | Irreversible |
| Causes | Excess insulin, and less food intake | Insensitivity to insulin, or sedentary lifestyle |
| Symptoms | Sweating, shivering, etc, | Increased thirst, more urination, etc. |
| Diagnosis | Fasting blood sugar | Fasting blood sugar, and glucose tolerance |
| Treatment | Quick carb dose | Insulin/lifestyle changes |
| Complications | Brain damage, coma | Limb amputations |
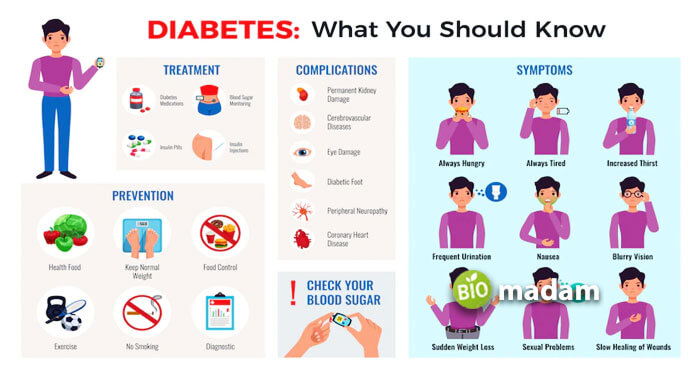
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic, untreatable condition in which your blood sugar levels are very high. When you intake food, it is broken down into carbs, proteins, saturated, and unsaturated fats to provide energy to the body for bodily functions. When the sugar levels in your blood levels rise due to high carbohydrate content in the body, insulin helps consume the sugar to generate energy. In diabetes, either your body does not produce enough insulin or is not used properly, resulting in higher blood glucose levels.
The normal glucose range in the blood before taking a meal is <100mg/dL.
It is reported that diabetes is the seventh most prominent cause of death in the United States, with over 37 million people having any one of the two diabetes types. Diabetes is classified as Diabetes type 1 and Diabetes type 2. Gestational diabetes is a third type of diabetes that presents itself during pregnancy.
Causes of Diabetes
The three types of diabetes are defined on the basis of their cause. The most common causes of diabetes include your body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use it in the right way.
- Diabetes type 1 occurs as a result of an autoimmune reaction that reduces or diminishes your body’s ability to produce enough insulin.
- Diabetes type 2 is caused mostly by unhealthy eating habits and lifestyles causing insulin resistance.
- Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy as the placenta produces hormones to maintain pregnancy. These hormones sometimes cause your cells to develop insulin resistance.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes presents itself through many signs or symptoms, some of which are common in most diabetic patients. Some of the signs of diabetes include
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Sores
- Frequent infections
- Ketones in the urine
Treatment of Diabetes
As the causes of diabetes type 1 and 2 are different, their treatment is also disease-specific.
Type 1 diabetes is usually managed by continuously monitoring the amount of blood glucose levels and keeping them in range with insulin.
Type 2 diabetes is more related to lifestyle changes. Reducing the number of carbs through total calories in your diet and adopting an active lifestyle can help you live a healthy life.
What is Hypoglycemia?
The normal value of fasting blood glucose is between 70mg/dL and 100 mg/dL. If the glucose levels in your bloodstream drop below 70 mg/ dL, it is called hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is common in people with diabetes who do not take care of their meals or forget to monitor their glucose levels. It also happens when they take too much insulin. If you do not have diabetes and have experienced hypoglycemia, it is possible to occur when you do not take enough food during the day.
Causes of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia could be reactive or non-reactive depending on the cause of the condition. Reactive hypoglycemia typically occurs when you do not take food on time or fail to eat enough for your body’s needs. It may be an indicator of prediabetes. Non-reactive hypoglycemia may occur due to another underlying condition or a side effect of some specific medicines. The main reasons behind non-reactive hypoglycemia include:
- Anorexia, Bulimia, or Binge-Eating disorder
- Excessive alcohol drinking leads to liver damage
- Pituitary gland or adrenal gland issues
- Kidney, heart, or liver diseases
- Pregnancy
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is usually indicated by nausea and palpitations along with other symptoms of low blood sugar like
- Headache
- Pale skin
- Short-term anxiety
- Sweating
- Shaking
- Blurred vision
- Faintness
- Stuttered speech
- Mental confusion
Sometimes untreated long-term hypoglycemia may also lead to coma. Also, hypoglycemia may be present without any symptoms. This condition is known as hypoglycemia unawareness.
Treatment of Hypoglycemia
As multiple different reasons and factors cause hypoglycemia, the treatment is also specific to the cause. Your doctor will first diagnose the condition and decide on the treatment accordingly. The first-line therapy is to provide instant carbohydrates to the hypoglycemic person.
Typically 15 grams of carbohydrates are given as the initial management of hypoglycemia.
You can take carbohydrates in the form of a quick energizer like fruit juice or complex carbohydrates like whole grains or pasta. You may experience another episode of hypoglycemia on quick management with a sugary drink. However, complex carbohydrates help sustain glucose levels in the long run.

Difference between Hypoglycemia and Diabetes
Definition
Hypoglycemia
When your blood glucose level falls below 70mg/dL, it is termed hypoglycemia.
Diabetes
Conversely, diabetes is a condition in which glucose levels in the bloodstream are higher than standard.
Types
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can be categorized into mild, moderate, and severe conditions.
Diabetes
On the other hand, there are three types of diabetes; Type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Nature
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is a temporary condition that can be reversed with the right treatment.
Diabetes
Alternatively, diabetes is an ongoing condition that can be managed yet not cured or reversed.
Causes
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is mainly caused in diabetic patients by excess insulin intake or skipping meals. Non-diabetics may experience hypoglycemia during pregnancy or due to an underlying health issue.
Diabetes
Whereas diabetes is either caused by a sedentary lifestyle leading to obesity or the body’s under-reactivity to insulin.
Symptoms
Hypoglycemia
The common symptoms of hypoglycemia include sweating, confusion, palpitations, shivering, etc.
Diabetes
Yet, common symptoms presented in diabetes are frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, etc.
Diagnosis
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is diagnosed by observing the signals and taking a fasting blood glucose test.
Diabetes
In contrast, the diagnosis of diabetes involves a fasting blood sugar test, random blood sugar test, or glucose tolerance test.
Treatment
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is typically treated by giving 15 grams of carbohydrates in the form of a sugary drink or complex carbohydrates to maintain glucose levels.
Diabetes
While diabetes is managed by taking insulin as directed by the doctor. Type 2 diabetes requires lifestyle modifications like exercise.
Complications
Hypoglycemia
Untreated hypoglycemia may cause complications like brain damage, seizures, or coma.
Diabetes
In comparison, the complications that arise from improper management of diabetes are ketoacidosis, limb amputation, blindness, or heart failure.
FAQs
Is diabetes hereditary?
Diabetes type 1 and type 2 have been seen to be influenced by genes, yet receiving type 2 diabetes from parents is more common than type 1. Having Type 1 diabetes in the family does not necessarily mean you will have it.
How quickly can you treat hypoglycemia?
It takes you around 15 minutes to recover from mild hypoglycemia. Monitoring your blood glucose levels after 15-20 minutes can help decide if you should take more carbs.
Can you treat diabetes?
While diabetes is not curable, you can manage the disease and save yourself from further infections or other complications.
Can hypoglycemia cause diabetes?
No, hypoglycemia cannot cause diabetes. Yet, some people having diabetes reduce their intake of insulin to prevent hypoglycemia from causing uncontrolled diabetes. Hypoglycemia should be managed appropriately after consulting the doctor instead of reducing the insulin dose by yourself.
Does keto help with diabetes?
Yes, a ketogenic diet can help manage diabetes type 2 as it reduces the intake of carbohydrates in your meals. Eventually, you adopt a healthy lifestyle by reducing the number of carbs and increasing activity.
The Bottom Line
Hypoglycemia and diabetes are different, yet they both need immediate attention and proper care to prevent complications. Checking your fasting blood glucose can help determine if you have any of these conditions. Do not reduce the insulin dose to avoid the chances of hypoglycemia without consulting your doctor. While hypoglycemia can be reversed by offering immediate treatment, diabetes is irreversible and should be managed properly.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.

