Recently updated on October 5th, 2023 at 09:28 am
Every living cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane that protects its inner structures. Microvilli and cilia are kinds of projections naturally grown on the plasma membranes. Both are pretty different. Microvilli are primarily present on intestinal villi and egg cell surfaces, whereas the cilia are eukaryotic motile structures. Another differentiating feature is that the former is a non-motile structure, and the latter promotes movements.
We will talk in detail about both microvilli and cilia, but for now, know that they have the main variation in functioning. Microvilli increase a cell’s surface area to promote nutrient absorption. On the other hand, cilia help a body move rhythmically from one point to another. Let’s step ahead to understand their different features through a table.
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | Microvilli | Cilia |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Finger-like projections | Eyelash-shaped filaments |
| Composition | Microfilaments | Microtubules |
| Function | Enhances Absorption | Helps in Movements |
| Glycocalyx Layer | Present | Absent |
| Thickness | Thicker | Thinner |
| Length | Short | Long |
| 9 + 2 Arrangement | Absent | Present |
| Motility | Non-Motile | Motile & Non-Motile |
| Endings | Blunt Endings | Tapered Endings |
| Basal Granules | Absent | Source of Arousal |
| Quantity | Numerous | Can be fewer to many |
What are Microvilli?
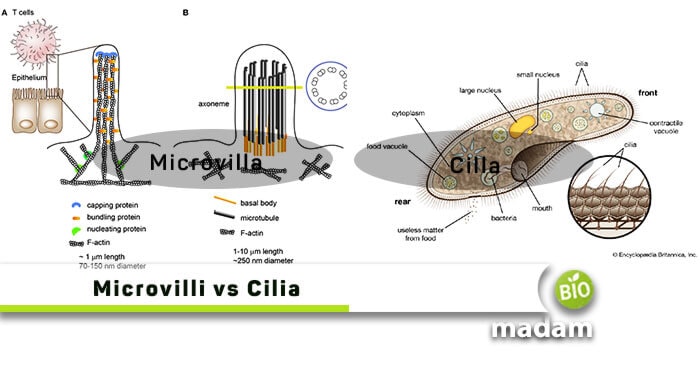
Microvilli are tiny, and microscopic projections are present everywhere in and around the cells. They consist of tiny protein fibers called actin filaments parallel along the microvillus length through interconnections. These structures are referred to as finger-like plasma membrane extensions located on the top of a wide cell variety. Moreover, microvilli are seen most abundant on epithelial tissues, for example, intestinal lining and the outer surface of the proximal kidney tubule. Even though they are cellular extensions, sometimes few or no cellular organelles are present in the microvilli.
Structure
Microvilli are encased in the cell membrane, surrounding the cytoplasm and microfilaments. They are often almost 0.1 µm in diameter and vary in length from a few micrometers to approximately 2 µm. Every microvillus has a tightly packed pile of inter-connected actin filaments, representing its structural core.
Location
They are present at the surface of many cell types but are huge on the small intestine, on the exterior of egg cells, and on leukocytes (White Blood Cells).
Functions
These tiny structures play different essential roles in a body, such as:
- Microvilli increase the cell’s surface area, helping in absorption, adhesion, secretion, and mechanotransduction functions.
- Furthermore, they contribute to easier fertilization as they help the sperm reach the egg easily.
- Inside the intestine, they work together with villi to take in a large number of nutrients and various materials because they increase the intestine’s surface area.
What is Cilia?
On the contrasting side, Cilia are thin, tiny, short eyelash-shaped filaments that are very abundant on animal tissues and usually present on the top of all mammalian cells. These structures are hollow tubes, also called microtubules. Furthermore, we consider these entities as ancient, one or many. Ciliates belong to protozoans that have cilia.
Types of Cilia
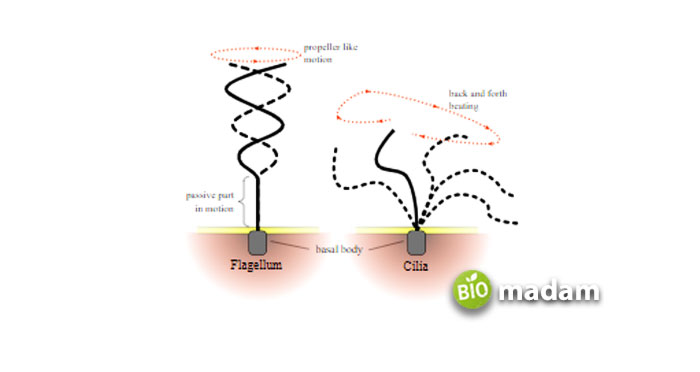
Motile Cilia
Many eukaryotes, e.g., mammals, possess motile cilia. Motile cilia are tiny, lash-like organelles whose beating generates an oriented fluid flow. Motile cilia are essentially needed in several physiological activities.
Non-Motile Cilia
These are also named primary cilia and serve as sensory organelles. They protrude from the apical membrane of numerous cells. Formerly, these structures were considered to be vestigial organelles. But current findings demonstrate the biological position of non-motile cilia that they work as a sensory cellular antenna that synchronizes many cellular signaling passageways.
Structure
A cilium is built from a central core comprising two microtubules covered in the plasma membrane. The microtubules are compact vacant rods made of tubulin (globular protein) bordered by an outer ring of nine microtubules, known as an axoneme. The nine exterior pairs are manufactured from a motor protein called dynein. The two middle microtubules end before entering the basal body.
Location
Some motile cilia are present on the epithelial cells of many inner organs, for example, left & right lungs, trachea, esophagus, digestive system, etc. They are observed on the protozoans, too, like paramecium, assisting them in locomotion.
Whereas the non-motile cilia are present in the dendritic protrusion of the olfactory neuron.
Functions
Cilia are equally crucial for a body as microvilli with the following essential functions:
- They play an essential role in the locomotion of protozoans of the phylum Ciliophora.
- Cilia are involved in discarding impurities from organs or tissues by providing help to the fluids to move over the cells.
- Moreover, they also take part in mechanoreception.
Differences between Microvilli and Cilia
There are prominent differences between the two terminologies. Let’s head towards them one by one.
Brief Description
Microvilli
The tiny projections bulging from epithelial cells in a body are microvilli.
Cilia
On the other hand, cilia are the narrow, long, hair-like filaments existing on the top of mammalian cells.
Location
Microvilli
These structures are generally observed in the columnar epithelium of kidney tubules and small intestines.
Cilia
Similarly, cilia are present in the epithelial walls of uterine tubes and the respiratory tract.
Structure
Microvilli
All microvilli structures are composed of microfilaments, thus, lack the 9 + 2 formation.
Cilia
On the contrary, these are composed of hollow structures known as microtubules. Moreover, cilia are arranged through the 9 + 2 ultrastructure.
Primary Function
Microvilli
These microfilaments help a body improve and increase absorption mechanisms.
Cilia
On the other side, cilia entirely assist in a body’s motility (movement).
Motility
Microvilli
These are fixed structures; thus, they show no motility.
Cilia
In contrast, cilia can be motile or non-motile structures based on their functioning.
Typical Shape
Both of them are typically cylindrical, but:
Microvilli
All microvilli have abrupt endings of their cylindrical shapes.
Cilia
On the contrary, cilia show tapering ends of their cylindrical structure.
Abundancy
Microvilli
These are abundantly present in a body. In short, microvilli are uncountable.
Cilia
On the contrasting side, cilia can be few in numbers.
Role of Basal Granules
Microvilli
There is no specific role of basal granules seen in microvilli.
Cilia
But on the other hand, these granules help cilia arise and perform their functions.
Final Verdict
When we compare the two terms, it appears that both microvilli and cilia are the projections in the plasma membrane. It’s just that they are involved in different functions and possess variable structures. Microvilli are the microfilaments that facilitate absorption. On the other side, cilia help a body move from one location to another. So, the critical difference turns out to be their role and functioning.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.