Recently updated on December 31st, 2025 at 07:08 pm
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes comprise cells with various organelles that perform specific functions. Prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane and vacuoles, but mitochondria are only found in eukaryotic cells. Let’s tell you the function of the plasma membrane, mitochondria, and vacuoles in detail.
Plasma Membrane
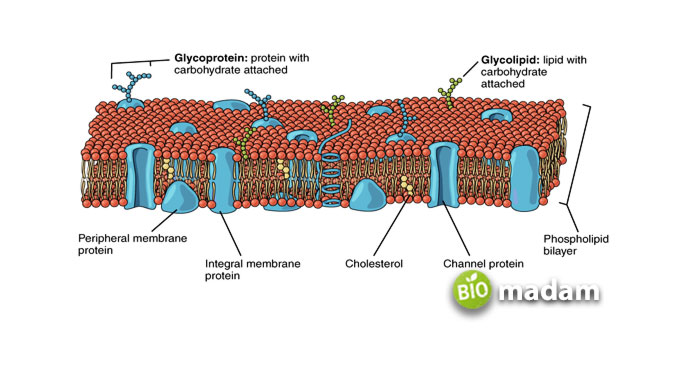
The plasma membrane, or cell membrane, is a thin layer surrounding the cell. It is composed of a double layer of lipids, known as a lipid bilayer. This bilayer acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The plasma membrane plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall function of the cell and is essential for the organism’s survival.
The structure of the cell membrane in animal or plant cell is important for its function. The lipid bilayer is made up of two layers of phospholipid molecules, with the hydrophobic tails facing inward and the hydrophilic heads facing outward. It creates a selectively permeable barrier, allowing certain molecules to pass through while preventing others. Embedded within the lipid bilayer are various types of proteins that also play a role in the membrane’s function.
Selective Permeability
One of the most important functions of the plasma membrane is regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This is known as selective permeability. The membrane is selectively permeable because it allows certain molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, to pass through while preventing others, such as large molecules or toxins, from entering the cell. The presence of different types of protein channels and pumps in the membrane allows this. Some proteins act as channels, which allow specific molecules to pass through, while others act as pumps that actively transport molecules across the membrane.
Structural Support
The lipid bilayer is flexible and strong, which helps to maintain the shape of the cell. Additionally, the presence of various types of proteins in the membrane, such as the cytoskeleton, provides additional support for the cell.
Protection from Environment
The membrane acts as a barrier against harmful bacteria or other parasites, and physical stress. This is achieved through enzymes and proteins that recognize and neutralize harmful substances.
Cell-to-Cell Communication
The plasma membrane in plants and animals also plays a role in cell-to-cell communication and cell signaling. Proteins in the membrane, such as receptors and signaling molecules, allow cells to communicate with each other and respond to environmental signals.
Mitochondria
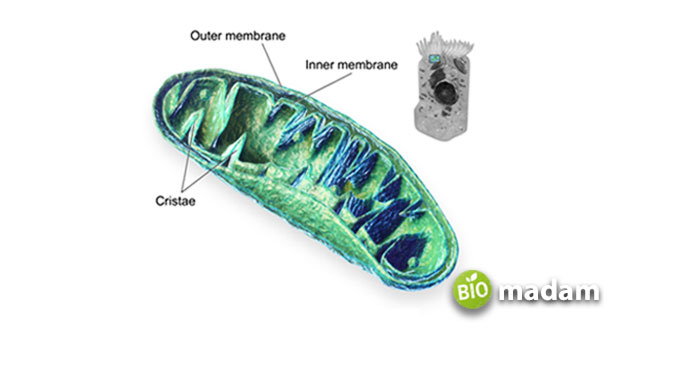
Mitochondria are organelles in almost all eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells. They are known as the powerhouses of the cell because they play a crucial role in the cell’s metabolism and overall function. Mitochondria are composed of a double membrane, the outer membrane, and the inner membrane. The inner membrane is folded into several cristae, which increases its surface area.
ATP Production
One of the most well-known functions of mitochondria is the production of ATP through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy in the form of ATP.
The inner membrane of the mitochondria is where most of this process takes place, specifically within the cristae. The inner membrane contains enzymes that catalyze the chemical reactions of cellular respiration, including the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. These reactions generate a proton gradient used to power the production of ATP through a process known as oxidative phosphorylation.
Cell Metabolism
They are involved in the breakdown of fatty acids, the synthesis of certain amino acids, and the regulation of the cell cycle.
Apoptosis
Mitochondria have a role in programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis. In response to certain signals, the mitochondria can release molecules that trigger apoptosis, leading to the death of the cell.
Cell Signaling
They can release reactive oxygen species (ROS), which act as signaling molecules that can communicate with other cells and activate an immune response. Mitochondria can also communicate with the nucleus of the cell to regulate gene expression and cell survival.
Ion Regulation
Mitochondria are involved in the regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) in the cell. They store calcium ions and release them upon demand. This is important for various cellular processes such as muscle contraction, cell division through mitosis and meiosis, and cell signaling.
Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis is the production of heat by burning calories. This is primarily seen in brown fat cells, specialized cells abundant in newborns and hibernating mammals.
Aging
They are thought to play a role in aging by generating more ROS over time which can cause damage to cellular components.
Vacuoles
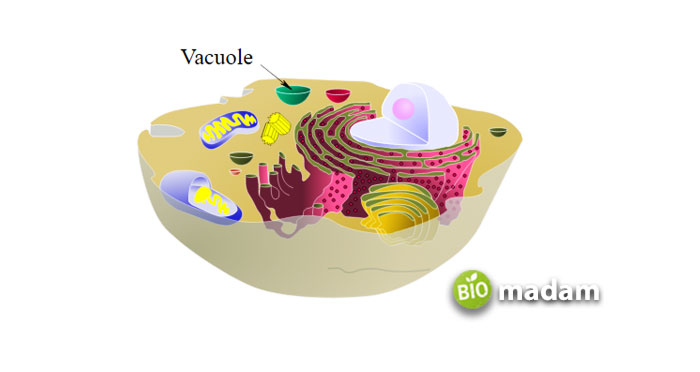
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles found in most eukaryotic cells. They are large, fluid-filled structures with various functions, including storage, regulation of water balance, and maintenance of the cell’s shape.
The structure of a vacuole is relatively simple. It is composed of a single membrane, called the tonoplast, that encloses the fluid-filled space inside. Vacuoles can be found in many different sizes and shapes, depending on the cell type and its specific function. Plant cells, for example, have large central vacuoles that can make up to 90% of the cell’s volume and are responsible for storage, while animal cells have small, temporary vacuoles.
Storage
Vacuoles, like lysosomes, can store a variety of molecules and ions, including proteins, carbohydrates, and inorganic ions, such as calcium and potassium. These molecules and ions are important for the cell’s metabolism and growth. In plant cells, vacuoles store pigments, enzymes, and waste products and also regulate turgor pressure, which helps maintain the shape of the cell.
Water Regulation
They can take in water, which can help to maintain the turgor pressure and shape of the cell. They can also release water, which can help to prevent the cell from bursting in an environment with high water pressure.
Degradation
Some vacuoles contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down macromolecules like proteins and polysaccharides. These enzymes are important for the recycling of nutrients and the removal of waste products.
Signaling
Vacuoles also play a role in cell signaling and communication. They release molecules that act as signaling molecules, which can communicate with other cells and regulate cell growth and division.
The Bottom Line
The plasma membrane, vacuole, and mitochondria are three crucial cell organelles. The plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, provides structural support, and protects the cell. Vacuole stores important molecules and ions, regulates the water balance, degrades various protein structures, and maintains the cell’s shape. Mitochondria produce ATP, regulate metabolism, and play a role in cell signaling and cell death. Understanding the functions of these organelles is essential for understanding cell biology.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.