Humans are complex organisms composed of eukaryotic cells and have a similar anatomy and physiology in male and female counterparts. While organs like the heart, liver, left, and right lungs are the same in men and women, the reproductive and urinary systems vary. The urinary and reproductive systems in males are interlinked, known as the urogenital system. Besides its function in eliminating urine from the body, the urethra in men is also involved in transporting semen.
Let’s tell you more about the function of the urethra in males.
What is the Urethra?
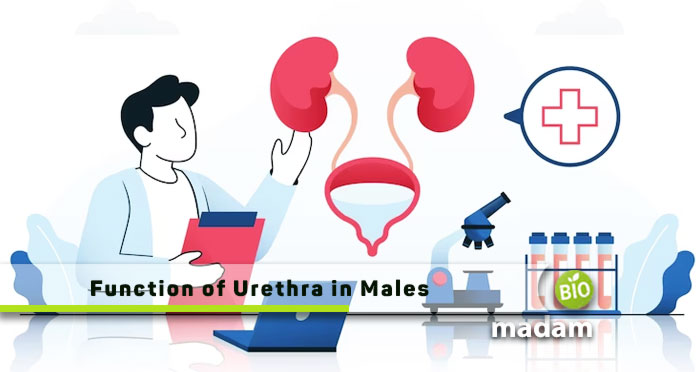
The urethra is a hollow tube in men and women present between the urinary meatus and the urinary bladder. This hollow tube brings the urine from the bladder to the distal end, where it eliminates the urine from the body. The urethra in males is longer than in females for the movement of semen and urine.
Urethra Anatomy in Males
The urethra in males runs from the proximal urethral orifice to the distal urethral orifice present at the tip of the glans penis. It is made up of smooth muscles, epithelial tissues, and connective tissues. It is divided into the prostatic urethra, seminal vesicle glands, and ejaculatory ducts. The prostatic urethra is the first section of the urethra and continues from the bladder neck to the prostate gland. The next section comprises the ejaculatory ducts that contain semen and fluids produced by the seminal vesicle gland and prostatic ducts.
The organ is divided into four parts in males: membranous, pre-prostatic, spongy, and prostatic. It is 18-22 cm long and appears double curvature when the organ is flaccid.
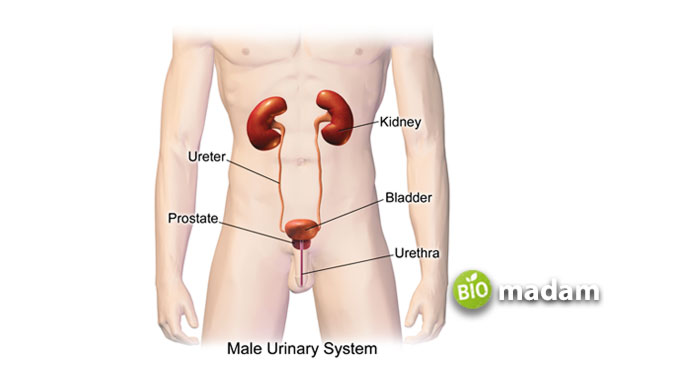
The urethras have two sphincter muscles that facilitate the process of urination. The first sphincter is the internal urethral sphincter or IUS, which comprises smooth muscles internally and striated muscle fibers on the outside. The sympathetic nervous system controls the internal urethral sphincter through the α-adrenergic excitatory receptors in the urethra and bladder neck. At the time of urination, the parasympathetic nervous system relaxes the sphincter by releasing acetylcholine. Moreover, some neurotransmitters excite the detrusor muscle, leading to the contraction of bladder muscles.
The other sphincter in the urethra is the external urethral sphincter located at the membranous urethra. It comprises striated muscles as the activity of this sphincter is controlled by the pelvic splanchnic nerves, primarily the pudendal nerve. It is responsible for keeping the external urethral sphincter tight around the urethra.
Urine can be reserved within the urinary bladder for a long time due to a higher combined pressure of the urethral sphincters than the bladder itself. When a person wants to urinate, the levator ani muscle is relaxed by the action of the pudendal nerve. Thus the internal sphincter relaxes, and you can urinate. Alternatively, urination in children of ages up to 5 years is involuntary.
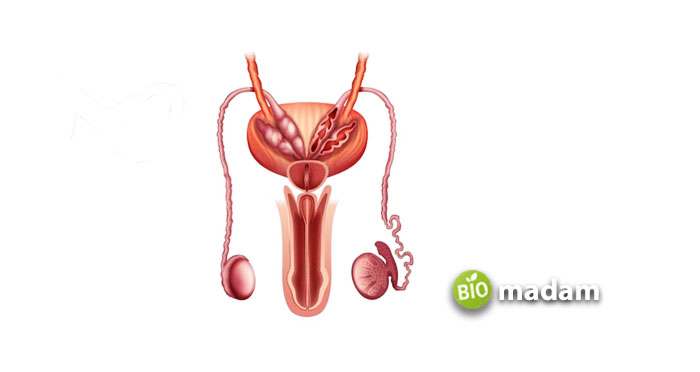
Function of Urethra in Males
The basic role of the urethra in males is the same as in females, but it also contributes as a reproductive organ in males. Here are the four main functions of the urethra in males:
- Urethra allows the movement of urine from the bladder to the exterior and out of the body.
- It carries the sperms and enables their expulsion during ejaculation.
- Another not-so-commonly-known function of this hollow muscle tube is the prevention of backflow of these fluids.
- The urethra also protects the urinary tract from infection and diseases.
The Bottom Line
The urethra is a part of both male and female bodies, yet it differs slightly in its functioning. The urethra is longer in males than females and is responsible for the movement of urine from the bladder and expels it out. It also plays a role in transporting sperm to the glans penis. Moreover, the urethra ensures that the fluids do not flow back and prevents bacterial infections.
FAQs
How many functions does the male urethra have?
The male urethra is a versatile organ and performs various functions. Besides the movement of urine from the urinary bladder, it transports sperm. It also ensures that the fluids do not travel back and prevents the entry of bacteria into the body.
What is the structure and function of the male urethra?
The male urethra is a thin muscular tube made of different epithelial tissues, connective tissues, and smooth muscles. It extends from the proximal urethral orifice to the distal urethral orifice present at the tip of the glans penis. The urethra comprises the prostatic urethra, seminal vesicle glands, and ejaculatory ducts. It carries urine from the bladder and semen from the ejaculatory ducts to the exterior of the body.
How long is the urethra in males?
The male urethra is longer than the urethra in females and measures between 18 and 22 cm. The mean length of the urethra in males is 22.3 cm.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.