Quick Answer: Biochemistry is a branch of science that studies the chemical composition and processes of living organisms.
The scope of biochemistry includes understanding biomolecules, metabolism, genetics, molecular biology, and the chemical basis of health, disease, and life itself.
What is Biochemistry?
Biochemistry is often described as a bridge between biology and chemistry. In simple terms, it combines the principles of both sciences to explain how life works at a chemical level.
More formally, biochemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study of chemical composition and chemical reactions occurring within living organisms. It focuses on how cells function, how biomolecules interact, and how energy is produced and utilized in living systems.
Many students assume that biochemistry is only useful for pharmaceutical industries or laboratory testing careers. In reality, the scope of biochemistry extends far beyond this, influencing medicine, genetics, biotechnology, agriculture, nutrition, and environmental science.
What Does Biochemistry Study?
- Biomolecules (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids)
- Enzymes and metabolism
- Cellular respiration and energy transfer
- Genetic information and molecular signaling
Scholarly Definitions of Biochemistry
Biochemistry is defined in academic terms as the study of the structure, function, and chemical composition of living beings. It explains how biological molecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids interact to sustain life.
This branch of science helps us understand:
- How cells are formed and maintained
- How organisms obtain energy from food
- The chemical basis of heredity
- The molecular changes involved in diseases and infections
By integrating chemistry with biology, biochemistry allows scientists to study life processes in greater detail than either discipline alone.
Historical Development of Biochemistry
The development of biochemistry has been gradual, shaped by discoveries in chemistry, biology, and medicine.
Early Foundations of Biochemistry
Many scientists believe that biochemistry formally began in 1833, when the French chemist Anselme Payen discovered the enzyme diastase. This discovery demonstrated that chemical substances within living organisms could catalyze biological reactions.
Later, in 1842, Justus von Liebig proposed a chemical theory of metabolism, explaining how chemical reactions drive physiological processes in living organisms.
Key Scientific Contributions
Several scientists played crucial roles in shaping modern biochemistry:
- Eduard Buchner demonstrated alcoholic fermentation without living cells, proving that enzymes could function independently. He received the Nobel Prize in 1907.
- Emil Fischer made significant contributions to protein and carbohydrate chemistry.
- George Beadle and Edward Tatum introduced the “one gene–one enzyme” hypothesis, linking genetics directly with biochemical reactions.
The discovery of genes, enzymes, and molecular structures marked the golden period of biochemistry, allowing scientists to explain life at the molecular level.
Major Branches of Biochemistry
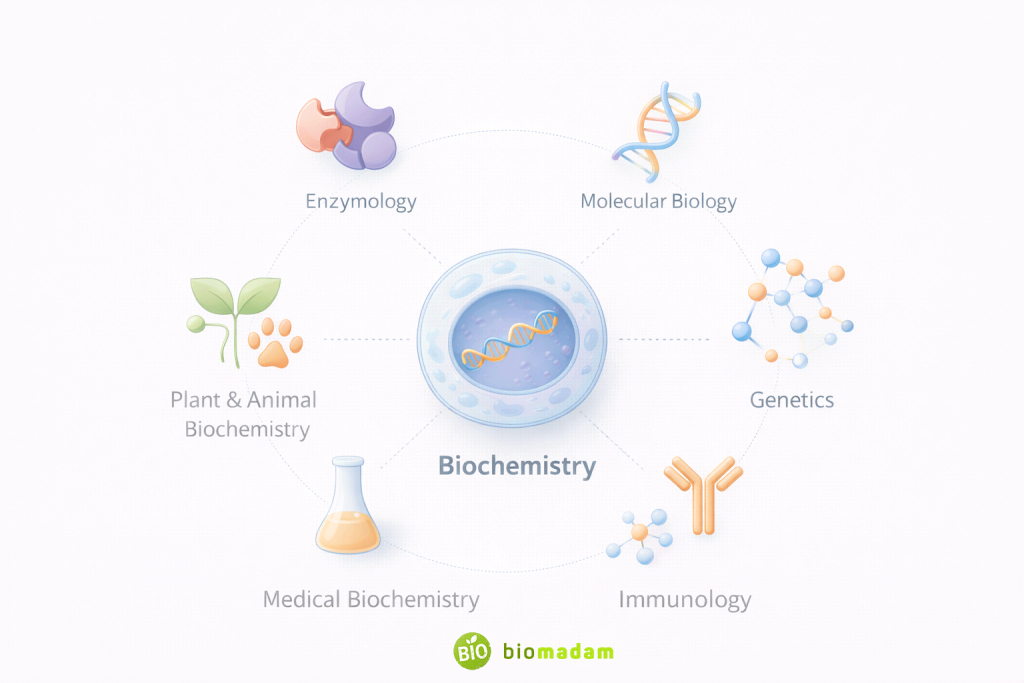
Biochemistry is a vast field with multiple specialized branches. After learning the basics, students often choose a sub-discipline based on their interests.
Some major branches of biochemistry include:
- Enzymology – Study of enzymes and their catalytic roles
- Molecular Biology – Structure and function of DNA, RNA, and gene expression
- Genetics – Chemical basis of inheritance and variation
- Immunology – Biochemical mechanisms of immune responses
- Metabolism – Anabolic and catabolic reactions in living systems
- Medical Biochemistry – Biochemical basis of diseases and diagnostics
- Plant and Animal Biochemistry – Chemical processes in plants and animals
Each branch contributes uniquely to scientific research and practical applications.
| Branch | Focus Area |
| Enzymology | Enzyme structure & catalysis |
| Molecular Biology | DNA, RNA, gene expression |
| Genetics | Inheritance & variation |
| Metabolism | Chemical reactions in cells |
| Medical Biochemistry | Disease mechanisms |
Scope of Biochemistry in Modern Science
The scope of biochemistry has expanded rapidly with advances in technology and research. Today, biochemistry plays a central role in:
- Understanding disease mechanisms at the molecular level
- Drug discovery and pharmaceutical development
- Genetic engineering and biotechnology
- Nutritional science and metabolism research
- Environmental and agricultural studies
Because life processes are fundamentally chemical, biochemistry forms the foundation of many modern scientific breakthroughs.
Advances in genomics, proteomics, and bioinformatics have further expanded the scope of biochemistry, enabling large-scale analysis of biological systems.
Relationship Between Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
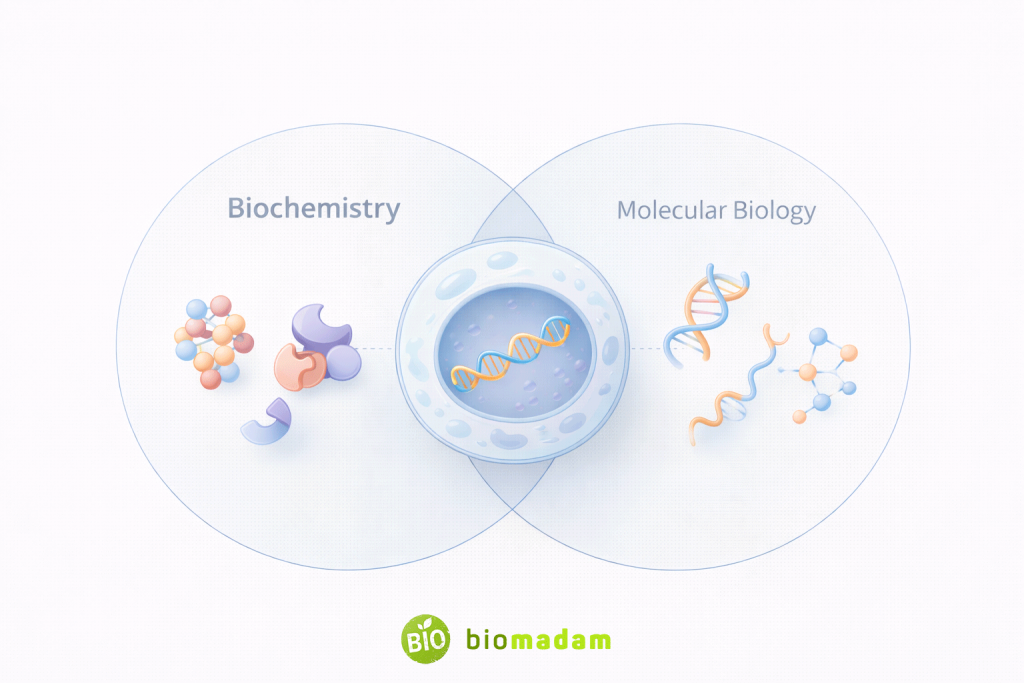
Biochemistry and molecular biology are closely interconnected fields. While biochemistry focuses on the chemical reactions and molecules of life, molecular biology studies biological processes at the molecular level, particularly involving DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Molecular biology can be considered a specialized sub-discipline that overlaps with biochemistry and genetics. Techniques such as PCR, gel electrophoresis, and molecular cloning are commonly used in both fields, highlighting their strong interdependence.
Career Scope in Biochemistry (Overview)
Biochemistry offers a wide range of academic and professional opportunities. Graduates may pursue careers in:
- Scientific research
- Teaching and academia
- Medical and diagnostic laboratories
- Biotechnology and industrial research
A detailed discussion of real-world applications and career paths is covered in our dedicated article on the applications of biochemistry.
Conclusion
Biochemistry is a fundamental scientific discipline that explains the chemistry of life. Its scope includes studying biomolecules, metabolic pathways, genetics, and molecular mechanisms that sustain living organisms. As science and technology continue to advance, the importance and scope of biochemistry will only grow, making it a vital field for students and researchers alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the scope of biochemistry?
The scope of biochemistry includes studying chemical processes in living organisms, such as metabolism, genetics, molecular biology, and disease mechanisms.
Is biochemistry part of biology or chemistry?
Biochemistry is a hybrid science that combines principles of both biology and chemistry.
What are the main branches of biochemistry?
Major branches include enzymology, molecular biology, genetics, immunology, metabolism, and medical biochemistry.
Why is biochemistry important?
Biochemistry is essential for understanding life processes, developing medicines, advancing biotechnology, and improving human health.

The Science Editorial Team creates clear, accurate, and student-friendly explanations of scientific concepts across biology, chemistry, physics, taxonomy, anatomy, and related life sciences. Content is written for educational and informational purposes using standard academic references and reliable sources. Read more about the → Science Editorial Team