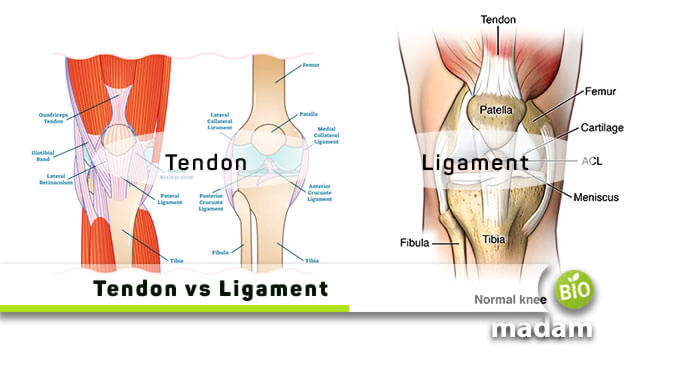
Tendon and ligament are the fibrous connective tissues composed of collagen fiber. These fibers give them a high tensile strength; thus, both tendons and ligaments play a significant role in musculoskeletal biomechanics. Moreover, these fibrous bands of connective tissues are active in stabilizing the skeleton & making our move.
Despite many differences between the two, tendons and ligaments help sustain injuries through the fascicles present. Tendons are pretty strong with no flexibility. Whereas, on the other hand, ligaments are soft and flexible, connecting bone to bone. Let’s dig into the article below to grasp more differences between the two. We will start by presenting a brief comparison table.
Comparison Table
| Basis of Comparison | Tendons | Ligaments |
|---|---|---|
| Connecting Capability | Skeletal muscles to bones | Bones to bones |
| Nature | Strong and non-flexible | Soft and flexible |
| Modified From | White Fibrous Tissue | White/Yellow Elastic Tissue |
| Classification | None | Into further three types |
| Fibroblast Nature | Lies in continuous rows | In scattered form |
| Fibers Nature | Compact & parallel bundle | Compact |
| Proteoglycan Amount | Low | Comparatively High |
Explain Tendons
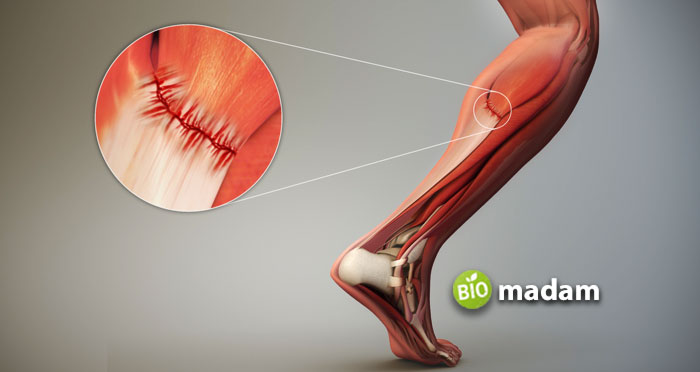
These abundant connective tissues in a body help connect muscles to the bones. Therefore, a tendon is a part of the muscle unit as it can never function without muscle acting as a mediator. Moreover, these fibrous tissues have an important but limited ability to stretch.
Composition of Fibrous Connective Tissues
Tendons entirely consist of the fibrous tissues that have collagen fibers inside. So, the primary tendon units are the collagen fibers formed from a bunch of collagen fibrils. These fibrils are previously prepared from a bundle of fibers, also termed as subfasicle. Then comes the secondary fiber bundle from these subfasicles that are pronounced as fascicles. Furthermore, all these fascicles together generate the tertiary fiber bundles to form an entire tendon unit. Thus, these primary, secondary, and tertiary fibers come covered with connective tissue sheath, called endotenon.
Tendon Sheath
A synovial sheath surrounding the tendon allows them to glide freely and also produce synovial fluid contributing to their nutrition. Besides, tendons can change their direction one or more times in several body regions (foot and ankle) by wrapping around the bony pulleys.
Tendonitis
Tendon inflammation occurs when torn due to stretching beyond the capacity, such as during the sport. Tendons vary in shape and length. If the muscle has a long tendon at one end, it usually has a shorter one at the other end. Besides, tendons are not uniform in composition along their length. There is regional variation in water and collagen. When the tendon wraps up bony pulleys, it may contain type II collagen.
Explain Ligaments
Ligaments are the fibrous connective tissues, function as a bridge to connect a bone with other bone, and are also called articular ligaments, true ligaments, and articular larua. They are found at the joints to stabilize them, allowing all kinds of motions, from simple to complex. There are approximately 900 ligaments in the human body. The injury in ligaments is called sprain (stretching or tearing of ligaments).
As all ligaments are connective tissues, these fibrous cells are composed of extremely condensed collagen fibers (spindle in shape), called fibrocytes. If we generally see, there are two ligament types, such as white fibrous ligaments and yellow fibrous ligaments. The former has more collagen fibers than the latter one, so it’s more tough and inelastic. On the other hand, the yellow ligament is pretty soft and elastic. The main ligament classification is in three types:
- Peritoneal Ligaments
- Fetal Remnant Ligaments
Peritoneal Ligaments
Peritoneal ligaments are a double layer of the peritoneum from the lining of the abdominal cavity. These can be in the stomach and spleen that has several important functions.
Peritoneal Ligaments of the Stomach
- Lesser omentum
- Hepatogastric ligament
- Hepatoduodenal ligament
- Gastro splenic ligament
- Greater omentum
Peritoneal Ligaments of the Spleen
- Splenorenal ligament
- Phrenic colic ligament
Fetal Remnant Ligaments
These are the remnants of the fetal tubular structure, hence present since the time of birth.
Differences between Tendons and Ligaments
We have mentioned below the differences between tendons and ligaments separately below for your improved understanding. So, do check them out!
Description
Tendons
These are the inelastic yet flexible fibrous connective tissues that work to connect skeletal muscles and bones.
Ligaments
These are the short fibrous connective tissues connecting a bone to another bone. A ligament can also hold two joints together.
Presence
Tendons
These are present at the tips of all skeletal muscles and are modified from white fibrous tissues.
Ligaments
In contrast, ligaments are present in all joints, modified from white or yellow elastic tissues.
Nature of Tissues
Tendons
Such fibrous tissues are tough and highly inelastic.
Ligaments
As these connect bone to bone, thus are very smooth and flexible.
Fibroblasts & Fibers
Tendons
Tendons arrange fibroblasts in continuous rows, while the fibers are densely arranged in parallel bundles.
Ligaments
On the contrary, ligaments have scattered fibroblasts with similar dense structures, but no parallel activity is seen.
Types of Injuries
Both the connective tissues can cause several injuries but of different types.
Tendons
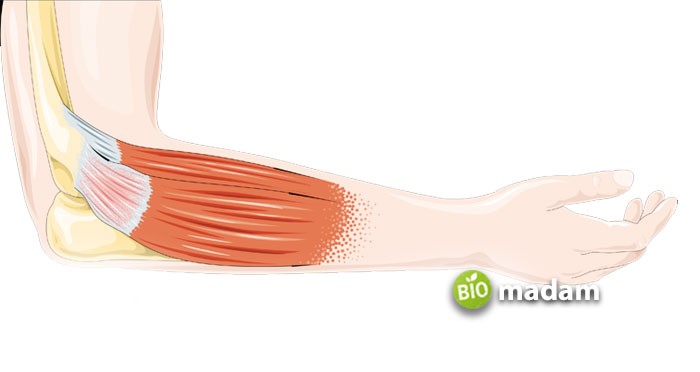
If there is excessive external pressure on tendons, it may cause tenosynovitis, tendinitis, and avulsion.
Ligaments
On the other hand, extreme outside pressure on ligaments can tear them apart and causes sprains.
The Outlook
We see both contrasting terminologies as very important for a human’s skeletal system. Despite many unique differences, tendons and ligaments will remain the musculoskeletal system’s components of dense collagen fiber layers.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.