Recently updated on March 2nd, 2024 at 08:07 am
Numerous scientific applications like PCR and rDNA are helping us for the betterment. One of these scientific technique called PCR helps amplify the genomic DNA. Many laboratories utilize different types of PCRs due to their specificity and sensitivity. Several scientists have used it for qualitative and quantitative tests. The general PCR steps involve denaturation, annealing, and extension. Other prominent substances include primers, Taq polymerases, and nucleotides.
List of Different Types of PCR
Scientists make use of different PCR techniques, so we have enlisted almost all of them below:
- Nested, semi-nested PCR
- Multiplex PCR
- RT-PCR
- Touchdown PCR
- Inverse PCR
- Allele-specific PCR
- Asymmetric PCR
- Arbitrary PCR
- Core sample PCR
- Degenerate PCR
- Assembly PCR
- Dial-out PCR
- Digital PCR
- Traditional PCR
- Hot start PCR
- In-silico PCR
- Inter-sequence PCR
- Ligation-mediated PCR
- Methylation-specific PCR
- Mini primer PCR
- Nanoparticle PCR
- Overlap-extension PCR
- Quantitative PCR
Commonly Used PCR Techniques

Out of all the above PCR techniques, the following are the most used:
- Simple PCR
- Nested PCR
- q-PRC (quantitative PCR) or Real-Time PCR
- RT -PCR (Reverse transcriptase PCR)
- Multiplex PCR
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
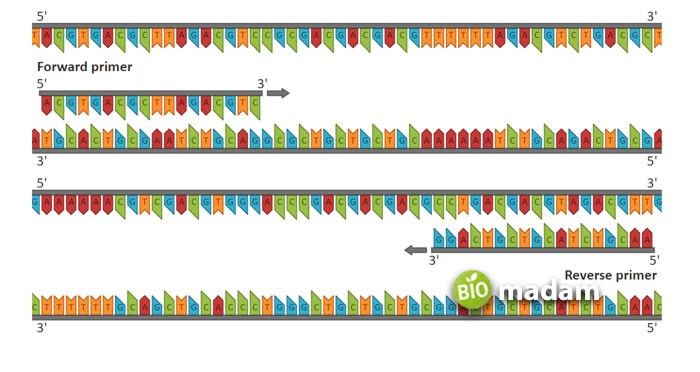
A simple polymerase chain reaction involves an essential component, which is:
dNTPs
- DNA template
- Primers (reverse and forward)
- Taq Polymerase
PCR Procedure
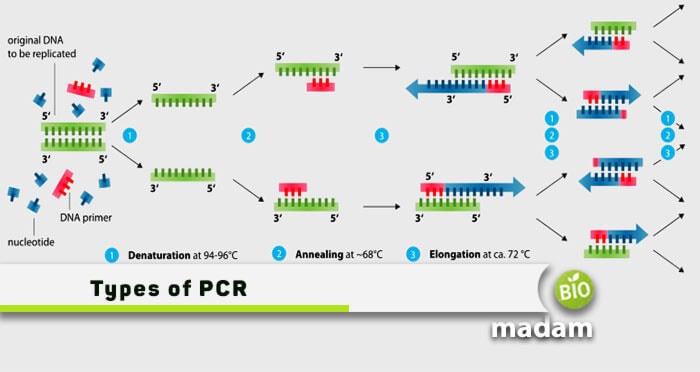
Genomic DNA is extracted by using CTAB buffer, and Eppendorf is used to collect a sample. In Eppendorf, extracted DNA and all above ingredients were added and put into PCR. This technique generally involves three basic steps.
In the first step, the genomic DNA (double-stranded) denatures and separates. Then, the primers bind to the complementary sequence in the following step. The last step forms its numerous copies.
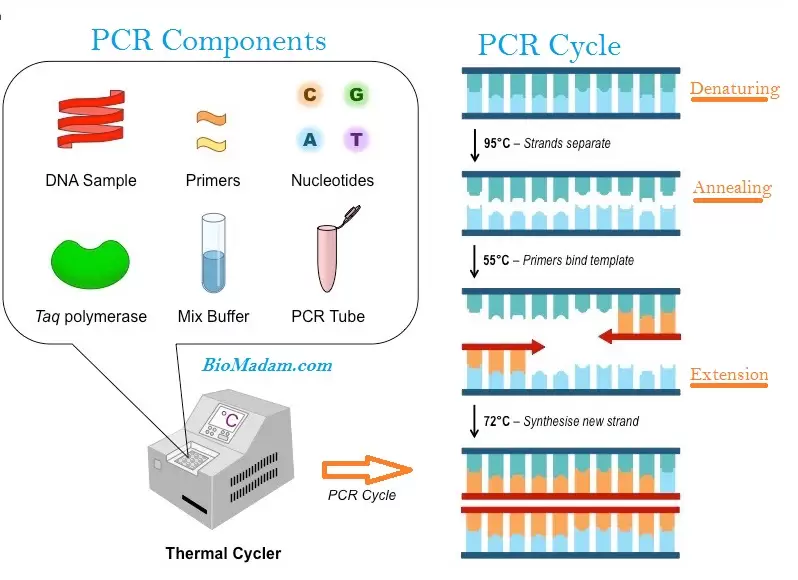
Every PCR cycle maintains a constant temperature. It is 94-98 degrees in the first step, which declines to 37-60 degrees in the next. The final stage maintains a temperature up to 78 degrees.
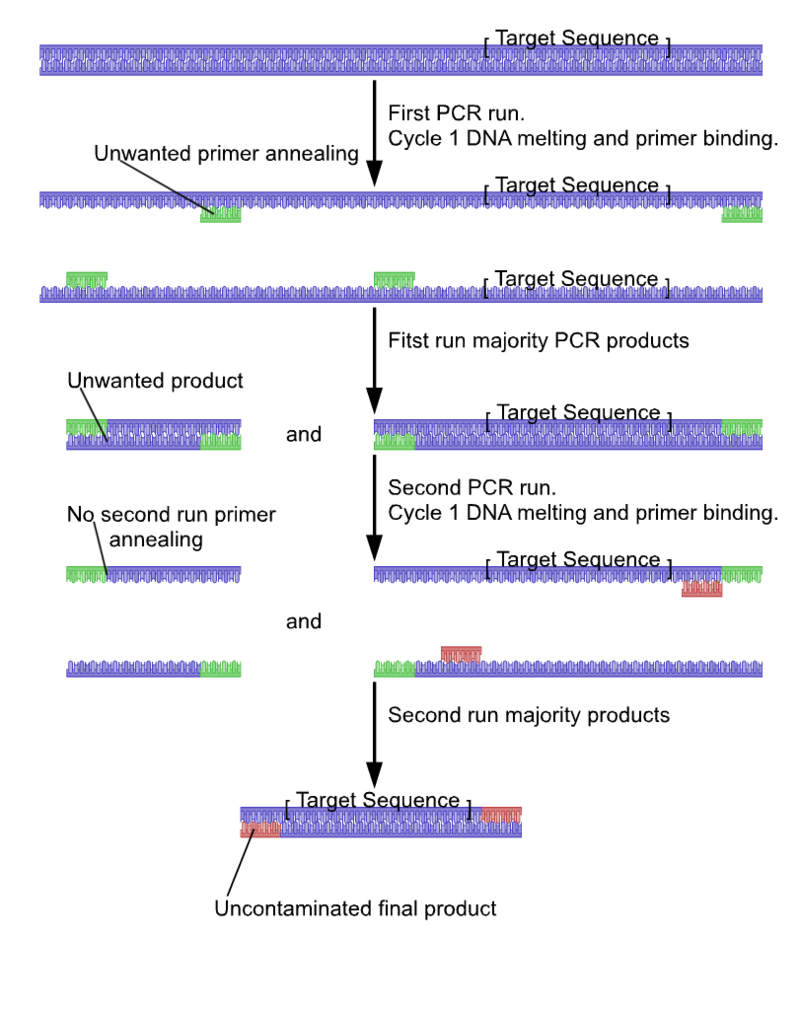
Nested PCR
Nested PCR is the improvement of the polymerase chain reaction that enhances its specificity. It reduces the nonspecific binding of products. The nested PCR technique uses two sets of primers. The first one takes part in the 1st PCR reaction. Then, the second is utilized in the product of the first reaction for amplifying purposes.
The Procedure of Nested PCR
The target DNA, in the first step of nested PCR, amplifies through a set of primers. The product of the first step strengthens by the second set of primers that are complementary to the first step product. The reason to employ two sets of PCR primers is that it can lessen product contamination and also improves specificity.
Quantitative PCR
Quantitative PCR is also called real-time PCR, which is a highly sensitive and reproducible technique. We can use this technique quantitatively and semi-quantitatively.
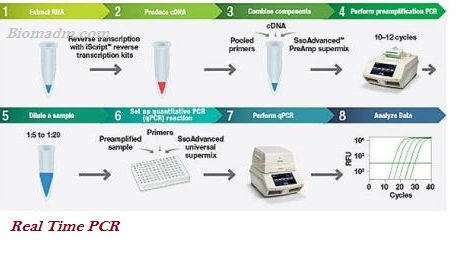
Real-Time PCR Principle
It’s the basic principle involved in Thermal Cycler. The thermal cycler is an instrument linking to the PCR to facilitate a thermal cycler reaction. It is a standard detecting method, used in Cyber Green fluorescent dye, inserted with DNA. Moreover, another technique called the Taqman probe (fluorescent-labeled) is used. It is a laboratory process consisting of amplification by quantitation; reaction products for each cycle.
Advantages of Real-Time PCR
The improvement in biology helped us get multiple advantages through Real-Time PCR, such as:
- Rapid detection of viral and bacterial infections like HIV, HCV, HBV by using miRNA
- Highly specific to use
- Highly sensitive
- Reproducible
- Reduce Contamination
- Give quantitation result
- Software-driven operation
Multiplex PCR
Several genomic DNA sequences are amplified in a single step of PCR. It utilizes multiple primers and DNA polymerases as thermocyclers. A multiplex PCR uses a heat-mediated DNA polymerase, which is further used to detect different pathogens in a single reaction. The designing of primers is a bit different for multiplex PCR.
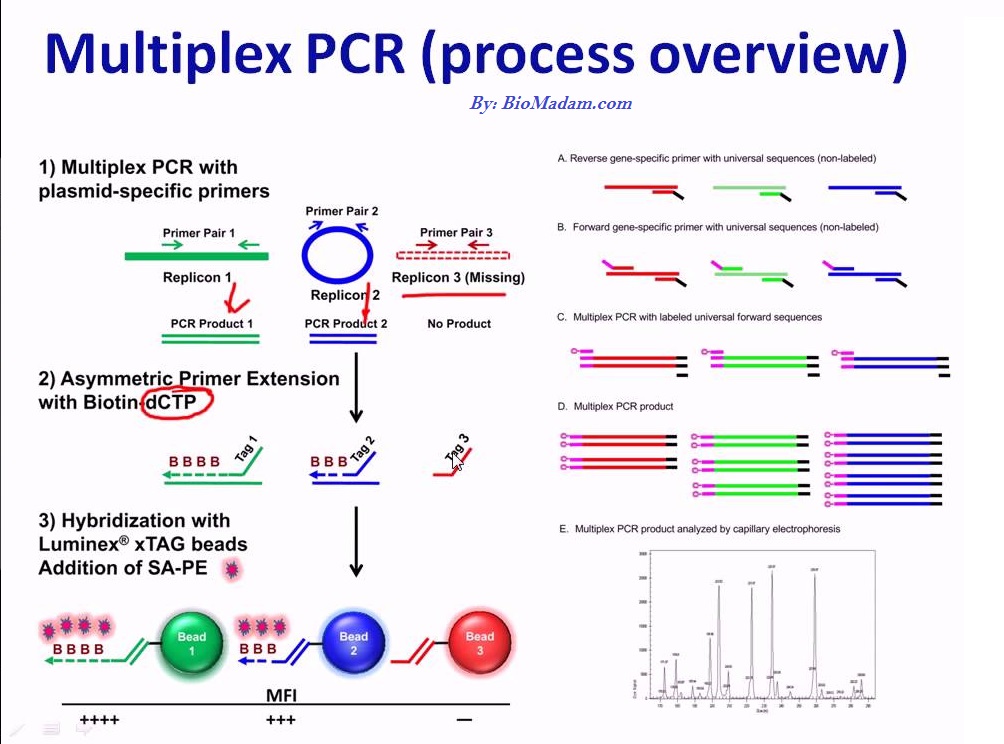
Types of Multiplex PCR
Single Template PCR
We use single template PCR to amplify a specific sequence of DNA templates with multiple forward and reverse primers.
Multi-Template PCR
Multiple templates are used with several forward and reverse primers within a single reaction Eppendorf.
Primers of Multiplex PCR
Primers that are used in multiplex PCR designs in short length about 18-22 base pairs.
Advantages of Multiplex PCR
This procedure is advantageous as:
- Highly Efficient than other PCR.
- Amplicon Provide internal control.
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Reverse Transcriptase PCR is used for cDNA synthesis from RNA. It is also denoted as RT-PCR, which is different from real-time PCR (q PCR)
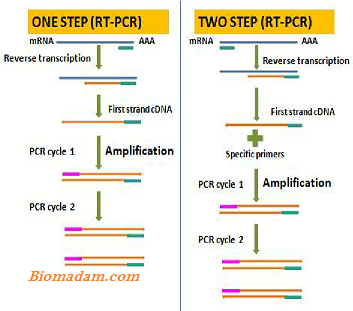
Reverse Transcriptase PCR Principle
The first step in this type of PCR is to form cDNA from RNA through an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. The next step amplifies this cDNA using PCR, where this single-stranded cDNA is converted into double-strand DNA. The main point of this entire procedure is the purification of mRNA, a type of RNA. If mRNA is unfortunately not purified, contamination will occur. Furthermore, a reverse transcriptase PCR includes either 1st step or 2nd step method.
In the 1st step method, conversion of cDNA and amplification occurs in a single reaction tube. Whereas in the 2nd step method, cDNA and amplification proceed in different tubes. Nowadays, this second step method is considered more convenient than the 1st one.
RT-PCR Procedure
The reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction follows the steps below:
- Initially extract RNA
- This extracted material is added into reaction mixture (included reverse transcriptase, primers, target material and nucleotides)
- Primers are further used for annealing the RNA strand if the target is present
- Reverse transcriptase converts mRNA into cDNA
- The primers extend this strand
- The temperature is kept constant, 90-degrees, to denature the specific DNA/RNA strand.
- The next step lowers the temperature to anneal the newly formed cDNA.
- A polymerase enzyme is employed to synthesize new DNA.
- These multiple cycles help us get numerous copies.
Application of RT-PCR
Just like other PCR techniques, this RT-PCR also has several benefits, including:
- It is used to detect genetic diseases
- It is most commonly used to detect RNA virus infection by converting it into cDNA.
- It is also used in gene profiling.
- In the future, molecular diagnosis may depend on RNA so that RT-PCR can be used in the coming years.
Applications of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
PCR is a laboratory technique used to amplify genomic DNA, and for most other purposes, PCR is used. We can use all PCR procedures for various purposes, such as diagnosing diseases, RNA virus infection, and cancer therapy. It is most commonly used in fingerprinting. Some critical applications are given below:
- In diagnosis therapy
- In nucleic acid detection assays
- In the medical field
- In agricultural sciences
- In mycology-parasitology
- In dentistry
- In virological diagnostics
- In insert analysis
- In systematic molecular evolution
- In cancer therapy
- In therapy-resistant assessment
- PCR-as biomarker
- In forensic medicine
- In virology
- In bacteriology
- In phytopathology
- In PCR-fingerprinting
- In the detection of microbiological gene
Wrapping Up
Summing up the entire procedure, this PCR, Nested PCR, Real-Time PCR, Reverse Transcriptase PCR, and Multiplex PCR are the best-advanced procedures. Scientists are using them in different fields like molecular biology, biochemistry, biotechnology, bioinformatics, and labs. The fundamental purpose is to acquire the best qualitative and quantitative results.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.