Most people are born with normal eyesight. However, they experience changes in vision due to genetics and environmental factors. Nearsightedness and far-sightedness are two common conditions associated with eyesight. They are not eye diseases or infections, instead, are “refractive errors.” They occur due to improper focus of the image on the retina.
Nearsightedness means that you can only see near objects clearly. Whereas, farsighted people have trouble looking at nearby objects in detail. These conditions are curable, and you can manage them using spectacles. Let’s tell you all differences between near-sightedness and far-sightedness.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Nearsightedness | Farsightedness |
| Another Name | Myopia | Hyperopia |
| Clear Vision | Nearby objects | Distant objects |
| Prevalence | More prevalent | Less prevalent |
| Eyeball Shape | Longer | Shorter |
| Image Formation | Before the retina | After the retina |
| Progression | During adolescence | Teenage |
| Lens Power | Negative | Positive |
| Diagnosis | Acuity test | Refraction exam |
What are Refractive Errors?
Eyesight and vision are attributed to your eye’s ability to focus on the light rays and create an image. When the light rays fall on the pupil, they converge to form an image on the retina. The retina is a thin layer of tissue behind the eye. It plays a vital role in image interpretation and viewing. If your eye does not focus the light onto the retina, it can result in a refractive error. People with refractive errors wear glasses and contact lenses to see better. Corrective surgeries also help improve eyesight.
What is Near Sightedness?
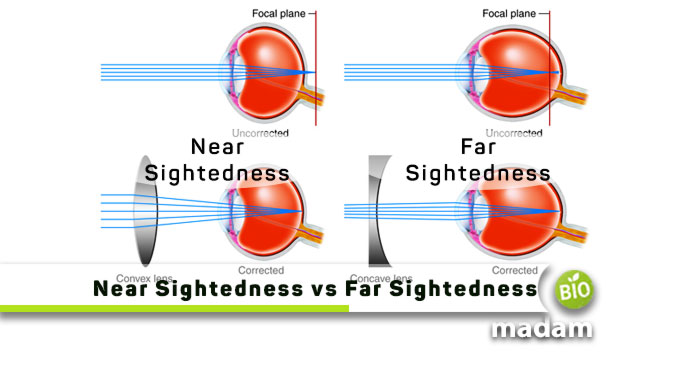
Nearsightedness is one of the refractive errors in the eyes. It refers to seeing nearby objects clearly but the inability to focus on distant objects. It is also known as Myopia. Nearsightedness results when the eyeball is too long. It does not focus the light onto the retina. Instead, the light converges at a point before the retina. Due to this, distant objects cannot be observed properly and appear blurry. Nearsightedness may also occur if the curvature of the lens is more steep than normal. The prevalence of near-sightedness is more than farsightedness. It usually develops during childhood and worsens over adolescence.
The management and treatment depend on the severity of the condition. Some people may need to wear glasses all the time. On the contrary, some may only need them to look at a projector screen, and others require them when driving. Lenses for nearsightedness have a negative number. A higher number means worsening condition that requires a high-power lens.
Diagnosis of Near Sightedness
If you have seen a person reading a chart with differently-sized alphabets on a wall, that’s an acuity test. The acuity test is one of the basic assessment tests for nearsightedness. Further tests are later performed if you find difficulty reading those words.

What is Far Sightedness?
Farsightedness is the opposite of near-sightedness. People with far-sightedness can only see distant objects and struggle with focusing on nearby objects. It is also known as Hyperopia. As opposed to nearsightedness, the eyeball of a far-sighted person is shorter than usual. The light converges behind the retina instead of on it. Far Sightedness may also develop if the lens is flatter than normal. Some children might be born with farsightedness.
People with far-sightedness usually wear glasses for reading and workings on computers. Besides glasses, they can use contact lenses and have corrective surgeries. Lenses for farsightedness have a positive number.
Diagnosis of Far Sightedness
Farsightedness cannot be examined in the same way as nearsightedness. It is especially difficult to evaluate cases of low to mild far-sightedness. Thus, most far-sightedness cases require a refraction examination and eye health assessment to diagnose far-sightedness.

Similarities Between Near Sightedness and Far Sightedness
- Nearsightedness and far-sightedness are refractive errors.
- They are caused by a difference in the shape of the eyeball.
- Common signs and symptoms of both include eye strain, headache, or squinting.
- People with near-sightedness and far-sightedness need glasses, contact lenses, or corrective surgeries to see properly.
Differences Between Near Sightedness and Far Sightedness
Definition
Near Sightedness
Nearsightedness is a refractive disorder in which people can only see nearby objects clearly.
Far Sightedness
Farsightedness allows people to see only distant objects clearly.
Other Name
Near Sightedness
The other name for nearsightedness is Myopia.
Far Sightedness
Whereas the other name for far-sightedness is Hyperopia.
Clear Vision
Near Sightedness
You can see nearby objects clearly in nearsightedness.
Far Sightedness
On the other hand, you can see faraway objects clearly with farsightedness.
Blurred Vision
Near Sightedness
Nearsightedness does not allow you to see distant objects clearly.
Far Sightedness
Contrarily, near objects seem blurred in far-sightedness.
Prevalence
Near Sightedness
Nearsightedness is more prevalent than far-sightedness.
Far Sightedness
Yet, far-sightedness is less prevalent compared to near-sightedness.
Eyeball Shape
Near Sightedness
The eyeball of people suffering from nearsightedness may be too long.
Far Sightedness
Alternatively, people with far-sightedness have shorter eyeballs than others.
Image Formation
Near Sightedness
When the light converges, it forms an image before the retina in nearsightedness.
Far Sightedness
Whereas the image is formed after the retina, giving an unclear view of nearby objects.
Progression
Near Sightedness
Nearsightedness develops during childhood and worsens over adolescence.
Far Sightedness
Some children may be born with far-sightedness.
Lens Power
Near Sightedness
Lenses of near-sighted glasses or lenses have a negative number. A higher number means more power is needed to correct the issue.
Far Sightedness
While far-sighted lenses have a positive number. The power of lend increases with the increase in number.
Diagnosis
Near Sightedness
Nearsightedness can be diagnosed by an acuity test. You are asked to read a distant chart with the alphabet on it.
Far Sightedness
While doctors typically diagnose far-sightedness through a refraction examination and eye health assessment.
The Bottom Line
Nearsightedness and far-sightedness are refractive disorders that make your vision blurry. Near-sighted people can see nearby objects clearly. On the other hand, far-sightedness lets you see distant objects. It is usually due to the size of the eyeball and light convergence. Both these conditions can be managed with glasses and lenses or through corrective surgery.
FAQS
Nearsighted vs Far-sighted which is more common?
Nearsightedness is more common than farsightedness. People usually develop near-sightedness in early childhood or teenage.
What is astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a genetic disorder in which your vision is blurry at all distances. It commonly results from imperfection in the curvature of your eye’s lens or cornea. Sometimes, you may also get astigmatism following an injury.
Can you be near-sighted and far-sighted at the same time?
Yes, you could be near-sighted and far-sighted at the same time. This condition is called anisometropia. It happens as a result of different refractive powers in both eyes.
What causes nearsightedness?
Nearsightedness occurs when the light rays refract incorrectly due to your eye shape. It focuses on the image in front of the retina before it.
Read more:
- https://www.biomadam.com/benefits-of-eating-celery-at-night
- https://www.biomadam.com/nutrition-facts-of-dragon-fruit

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.

I have nearsightedness and I was really worried about how my glasses would look on me. I tried out the Difference Between Near and Far Sightedness and it was a life saver! The glasses made me feel more confident and I felt like I could see better without my glasses.
Thank you for the information, Anna! Your eye doctor will propose eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery as the most effective therapy to fix the vision problem, whether the patient has myopia or hyperopia. On the other hand, some natural therapy alternatives can help you delay the advancement of eye-vision difficulties. This includes spending more time outside, wearing sunglasses to protect your eyes from the sun, eating healthily, reducing eye strain, stopping smoking, and so on.