Recently updated on October 5th, 2023 at 05:53 am
While the heart, stomach, arms, or legs seem like the most important parts of the body, there’s so much more! The human body comprises multiple organs, different tissues, like epithelial and connective, and cells that work together to produce a particular function. From the heart that pumps blood throughout the body to the small red blood cells that carry oxygen – every component plays a vital role.
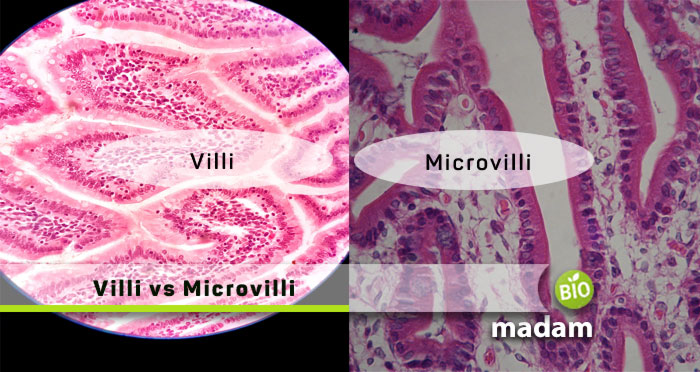
One such part of the human anatomy is the villi and microvilli, having different physiologies. Unlike the large intestine, they are present in the small intestine and contribute to the absorption of food. If the food is not absorbed, your body will not receive the micro and macronutrients. Though they are present in the intestine, there are some distinct differences between villi and microvilli. Let’s talk about their structure and function in detail.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Villi | Microvilli |
| Size | 0.5mm-1.6mm | 0.5µm & 1.0µm |
| Location | Intestinal lumen | Epithelial cell surface |
| Function | Absorption | Absorption, adhesion, and secretion |
| Cellular Level | No | Yes |
| Interlinking Proteins | No | Villin, fimbrin, epsin |
| Formation of Brush Border | Formed on villi | Formed by microvilli |
What are Villi?
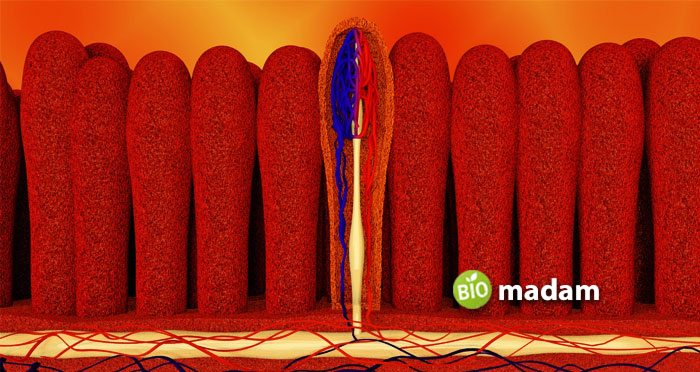
Villi are small finger-like projections present on the walls of the small intestine. They are found in the lumen of the intestine. Villi are typically 0.5mm to 1.6mm in length. They project from the mucosal folding on the intestinal walls. Villi help in the absorption of nutrients from the small intestine into the blood by offering a larger surface area. Their main function involves the absorption of nutrients, minerals, and electrolytes.
They have glands on the surface that secrete digestive enzymes. Each villus has multiple microvilli emerging from the epithelial cells forming a border. Lymph and blood vessels enable the transmission of nutrients, electrolytes, and minerals. Villi are not highly permeable to passive diffusion.
What are Microvilli?
Microvilli are microscopic projections on the cells and organs that increase the surface area. They also form a brush layer on the villi in the intestine. Microvilli are cellular structures. They form the boundary with the plasma membrane and contain cytoplasm. They look similar to villi in structure, but they are smaller than the latter. Microvilli are usually 0.5µm to 1.0µm long and 0.1µm thick. They are also thicker than cilia.
They help reduce the volume of the cell when needed. Microvilli are held together by proteins like villin, epsin, fimbrin, etc. The glycocalyx layer covers the microvilli and enables the material to bind to the microvilli for absorption. Microvilli also allow secretion and adhesion. They are present in organs like the mouth, nose, and ears. The function of microvilli in eggs is to allow the anchoring of sperm to the egg cell.
Similarities Between Villi and Microvilli
- Villi and microvilli are finger-like projections.
- They increase the surface area for absorption and transport.
- Both are present in the intestine.
Difference Between Villi and Microvilli
Definition
Villi
Villi are hair-like projections found inside the small intestine lumen.
Microvilli
Microvilli are smaller than villi and present on various organs.
Size
Villi
Villi are 0.5mm to 1.6mm in length, and you can see them.
Microvilli
Whereas microvilli are microscopic structures ranging between 0.5µm and 1.0µm in length and 0.1µm thick.
Location
Villi
Villi are present in the lumen of the small intestine.
Microvilli
Contrarily, microvilli are found in the small intestine and on the membrane of other epithelial cells.
Function
Villi
Villi are majorly involved in increasing the surface area for absorption.
Microvilli
While microvilli facilitate diffusion, absorption, cellular adhesion, and secretion by providing a larger surface area.
Organization Level
Villi
Villi are not cellular structures and exhibit as long hair-like projections.
Microvilli
Yet, microvilli are cellular structures containing the cytoplasm.
Proteins
Villi
Interlinking proteins are not found in villi.
Microvilli
On the other hand, microvilli have interlinking proteins like villin, epsin, and fimbrin that help in binding.
Brush Border
Villi
Villi do not form brush borders on any organ or tissue.
Microvilli
However, microvilli form a layer or brush border on villi in the intestinal lumen.
The Bottom Line
Villi and microvilli play a major function in the absorption of nutrients. Villi are the most vital component that absorbs nutrients from the food in the small intestine. Besides absorption, microvilli also support secretion and adhesion to cells. Microvilli are microscopic cellular structures, whereas villi are larger in size. Microvilli arise from epithelial cells and present as a brush border on villi in the intestine.
FAQs
Where are villi and microvilli found?
Villi are found in the lumen of the small intestine of organisms. Furthermore, microvilli occur as microscopic projections on epithelial cells.
What are the similarities between villi and microvilli?
Villi and microvilli are both finger-like projections though they differ in size. They are both involved in the absorption of nutrients. However, microvilli also perform multiple other functions.
Discuss cilia vs. microvilli
Motility is one of the most prominent differences between microvilli and cilia. Cilia are motile, whereas microvilli are non-motile. Cilia help in cell locomotion while microvilli facilitate absorption.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.