Thyroid gland is among the most important endocrine glands in the body, responsible for producing hormones. Just like neurotransmitters, these hormones regulate the entire body’s metabolisms. If you are keen to understand the basics and thyroid hormones test, this article is for you! The thyroid gland is near the base of the neck, where it looks like a butterfly. These hormones generate many functions in the body, like whole-body metabolism comprising of different breathing patterns, body weight, body temperature, muscular system, heart rate, etc. If one fails to control the thyroid disease, the severity can lead to thyroid carcinoma. In the past, it was pretty challenging to detect such diseases or related infections at an early stage. Nowadays, miRNA Biomarkers are proactively used to recognize this carcinoma.
Definition of Hormones
A product of living cells that circulates in body fluids (such as blood and plasma) and produces a specific, often stimulatory effect on the activity of cells, usually isolated from its point of origin, is called a hormone. Besides, you can also call it a synthetic substance that acts as a hormone.
In other words, these are the chemical substances produced in the body that controls and regulates the activity of specific tissues and organs. Many hormones are secreted by special glands, such as thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland.
Association of T3 & T4 with Thyroid Gland
The tyrosine-based thyroid hormones are produced from thyroid glands that regulate a living body’s metabolisms. There are two primary forms of these hormones, such as T3 and T4. Both of them entirely include iodine, while its deficiency can lead to a disease named goiter. Doctors usually suggest going through a regular thyroid hormone test that analyzes several body alterations and overall blood health. The fundamental of all types of thyroid tests is the T4 blood test.
The half-life of the T4 test is more prolonged than the T3 blood evaluation. We can perform several tests to evaluate a disease. One can go through multiple thyroid functioning tests rather than only one to enhance the diagnostic accuracy. We should understand that a general thyroid hormone test helps measure the hormones’ blood levels to detect its related diseases.
Misconceptions About Hormones
People often confuse hormones with proteins. There is a misconception that all hormones are proteins, but that’s not so! Not all but a few of them, including small peptide hormones, are proteins. Protein hormones are peptide hormones.
What is the Purpose of the Thyroid Gland Test?
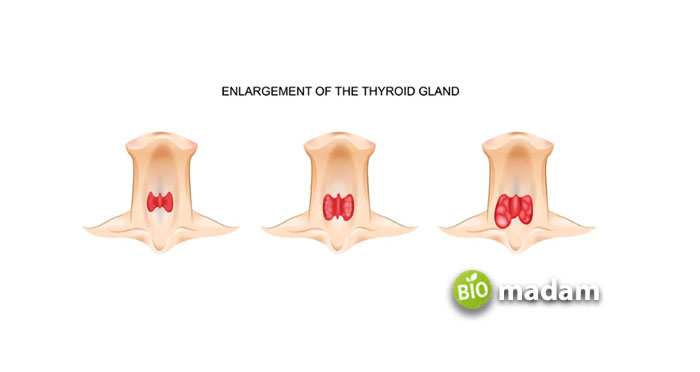
Different healthcare professionals adopt this testing methodology to see how your thyroid is working, its effect on hypo or hyperthyroidism. Following are the main objectives of the Thyroid Gland Test:
- Evaluate diseases
- Status of the gland (functional)
- Features of thyroid glands (anatomical)
- Causes behind dysfunctions of the thyroid
List of Major Thyroid Hormones Tests
Below is the list of all essential thyroid hormone tests, so a patient can consult his doctor and go through any of the following as prescribed.
- Serum PBI and BEI levels Test
- Serum T4 level Test
- Effective thyroxine ratio (ETR) Test
- Serum T3 level Test
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone: Serum TSH levels Test
- Plasma tyrosine value Test
Serum PBI and BEI levels Test
This chemical test detects thyroid processing by examining the amount of protein-bound iodine moving in the bloodstream.
Serum PBI and BEI Level Test Benefits
- One can perform this method when the iodine technique is unavailable.
- Furthermore, it is an indirect measure of thyroid hormones in the body.
Serum PBI and BEI Level Test Disadvantage
- The whole procedure is very time-consuming.
- Besides, it also measures the non-hormonal iodine and 3-iodotyrosine in the blood.
Serum PBI and BEI Level Normal Range
The normal range of serum PBI and BEI lies between 4.0- 8.0 µg%, but the best standard values vary from 4 to 5 µg%.
- In abnormal cases like hyperthyroidism, the value is greater than 8.0 µg%
- Similarly, in the case of hypothyroidism, the serum value falls below 3 µg%
Precaution and Limitation in Serum PBI and BEI Level Test
- Take all the precautionary measures to avoid contamination.
- Furthermore, keep all the syringes and glass iodine-free to prevent exogenous contamination.
- During the endogenous contamination, iodine-containing contrast media and iodine-containing drugs give a high level of false results.
- Besides, the trace elements affect the results as well. All such chemicals interfere with the iodine reduction reaction.
- Moreover, the increase or decrease in serum TBG levels affect the results of the test.
- The increased level will increase the value and vice versa.
High Probability of Serum TBG Increase in Following Cases
We enlisted the issues in patients at greater risk of increased serum TBG level in their blood. These include:
- Pregnancy
- Estrogen therapy
- On oral contraceptive pills
- Serum TBG decrease in hypoproteinemia states
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Androgen therapy
- An anabolic drug-like diazole
- Dicoumarol therapy
- Inherited TBG deficiency
Serum T4 level Test
Following are the most used methods of testing serum T4 level in blood:
- ELISA
- RIA radioimmunoassay
- Competitive protein binding assay (CPBA)
Serum T4 Level Normal Range
The standard serum T4 level in blood ranges between 5.0 – 12 µg%. This may vary with pregnant women. If a patient exceeds this limit, it results in overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism. On the contrary, if the patient lacks this normal range and falls below it, he suffers from hypothyroidism.
In the Case of Hyperthyroidism
The serum T4 level is above 12 µg% in case of hyperthyroidism.
In the Case of Hypothyroidism
The serum T4 level is less than 2.5 µg% in case of hyperthyroidism.
Effective Thyroxine Ratio (ETR) Test
In this era, this is the most effective method. It is a more reliable method that can be readily carried out on the sample of serum. It only required a radioisotope laboratory. Total serum thyroxine can be measured in a single procedure and the thyroid hormone protein’s binding capacity.
Serum T3 level Test
We mostly use RIA radioimmunoassay to measure the T3 levels in the blood. On the other side, CPBA is never considered a good and accurate method to measure T3 levels due to less affinity of T3 for TBG.
Serum T3 Level Normal Range
The T3 value appears slightly high in females than males. Its average range is from 100- 200 µg%, but:
In the Case of Hyperthyroidism
The T3 level rises above 350 µg% in hyperthyroidism.
In the Case of Hypothyroidism
On the other hand, the T3 blood level falls below 100 µg% in the case of hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone: Serum TSH levels Test
Measurement of serum TSH level is a susceptible index of thyroid hormone where technicians mostly use radioimmunoassay.
Serum TSH Levels Normal Range
The usual Serum TSH level is 0 – 3 µu/ml, where average being 1.6 µ/ml
Plasma Tyrosine Value Test
Rivlin et al, in 1965, studied plasma tyrosine levels in normal subjects. Tyrosine is an essential aromatic amino acid that synthesizes thyroid hormones.
Plasma Tyrosine Normal Value
Normally, the plasma tyrosine value ranges from 30 to 120 micromole per liter.
In the Case of Hyperthyroidism
Its value increases by more than 70%.
List of Thyroid Hormones Tests Normal Ranges
| Test | Abbreviation | Typical Ranges |
|---|---|---|
| Serum Thyroxine | T4 | 4.5-12 ug/dl |
| Serum Triiodothyronine | T3 | 80-180 ng/dl |
| Serum Thyrotropin | TSH | 0.5-6 uU/ml |
| Serum Thyroglobuline | Tg | 0-30 ng/m |
| Thyroid Hormone binding ratio | THBR | 0.9-1.1 |
| Free Thyroxine Index | FT4I | 4-12 |
| Free Thyroxine | FT4 | 0.7-1.8 ng/dl |
| Free Thyroxine Fraction | FT4F | 0.03-0.005% |
| Free Triiodothyronine I | FT3 | 230-619 pg/d |
| Free T3 index | FT31 | 80-180 |
| Radioactive iodine uptake | RAIU | 9-30%Physicians must recommend these and other blood tests. These are mandatory to diagnose thyroid disease, and one can take these tests to check the status but consult a physician to start a proper medication. It may cost a few dollars but can save hundreds of dollars you will need to pay after facing critical conditions. |
Thyroid Tests Based on the Primary Function
Now let’s discuss the best thyroid tests depending on their primary function. Ponder upon the list given below:
- Radioactive Uptake Studies
- Serum PBI 131 (Serum Protein-Bound to Iodine)
- T3 Suppression Test
- TSH Stimulation Test
- Tryptophan Releasing Hormone (TRH) Stimulation Test
Radioactive Uptake Studies
For the thyroid gland, iodine plays a crucial role in its metabolism. A trace element known as I-131 is used to study thyroid function that is more convenient to use due to its shelf life. Other trace elements like I-132 and I-123 are most commonly used in pregnant women and pediatric practice.
Normal Range
- The normal value from radioactive uptake studies is 20 to 40 %
- In Indian subjects, its value is from 15 to 30 %
- Not just this, but the value can vary due to iodine intake, from person to person or population to population.
Serum PBI 131 (Serum Protein-Bound to iodine)
I-131 accumulates in the thyroid gland and appears as a labeled hormone bound to a protein; it is a slow process. If the hyperthyroidism level of protein-bound radioactivity increases in plasma by scintillation method, it can be measured accurately. The result is conveniently expressed as conversion ratio, which indicates the proportions of the total plasma radioactivity at 24 hrs.
Normal Value
The normal value for serum PBI 131 is 35%
T3 Suppression Test
After 24 hours, radioactive iodine uptake is observed, so the basal values and serum T4 values are obtained.
- 20 ugs of T3, four times a day, are daily given for 10 days.
- 25 ug three times a day for 7 days could be given alternatively.
RIU is repeated after T# administration, and serum T4 values are also determined.
Interpretation
A suppression is indicated by the 24 hours RIU, falling to < 50 % of the initial uptake as (exogenous t3 suppression) TSH and total T4 to approx. 2ug/100 ml or less. This suppression indicates autonomous thyroid function.
TSH Stimulation Test
After 24 hours, RIU studies 3 injections of TSH, and each % USP unit are given at 24 hours intervals.
24 hours thyroidal RIU is measured after 42 hours and after the final TSH dose.
Interpretation
In the case of primary hyperthyroidism, there is the failure of stimulation of the thyroid gland. On the contrary, in secondary hyperthyroidism, the stimulation of the gland shows an increase in RIU.
Tryptophan Releasing Hormone (TRH) Stimulation Test
With the availability of synthetic TRH, which is a tripeptide suitable for human use, it is now possible to assess the functional integrity of thyrotrophic cells or the factors that influence the secretory response.
Procedure
200 to 400 ug of TRH has administrated IV and blood samples at 0, 20, 40, and 60 minutes analyzed for TSH content.
Interpretation
A peak response in normal is about 4 times elevation of TSH at 20 minutes sample compared to basal TSH level.
In Primary Hypothyroidism or Low Levels Hormones
The response will be exaggerated and prolonged.
In Secondary Hypothyroidism
Furthermore, the secondary hypothyroidism response will be blunted.
In Tertiary Hypothyroidism
Hypothalamic in origin, increase in TSH is delayed during tertiary hypothyroidism.
Test Based on Metabolic Effects of Thyroid Hormones
Just like the tests based on thyroid hormone’s primary functions, there are other tests based on its metabolic effects, such as:
- BMR ( Basal Metabolic Rate)
- Serum Cholesterol Level
- Serum Creatine Level
- Serum Uric Acid Level
- Serum CK Level
BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate)
This test is helpful full of diagnosing in case of a severe diseases or conditions relating to the thyroid.
Interpretation
A BMR between 5 % to 20% is considered normal in a body.
Hyperthyroidism
When the normal range surpasses 20% and goes to +50% – 70%, hyperthyroidism occurs.
Hypothyroidism
When the normal range goes below 5%, lying between -30% – 60%, hypothyroidism occurs.
Serum Cholesterol Level
Besides the above test, this serum cholesterol level is helpful in hypothyroidism, where its level becomes high.
Interpretation
90% serum cholesterol level greater than 250 mg%
Serum Creatine Level
If you compare serum creatine level to BMR, its value remains between 0.6% to 1.6%.
Interpretation
Normal serum creatine and normal BMR excluded thyroid dysfunction and held that raised serum creatine is highly significant even though BMR is normal when thyroid disorders are present.
Serum Uric Acid
Its value increases in myxoedematous males and postmenopausal women.
Standard Range
The serum uric acid usually ranges from 6.5 to 11.0 mg %
Serum CK Level
One can check the thyroid-related diseases through this test as the serum CK levels are often raised in hypothyroidism and thyrotoxic myopathy.
Working of Thyroid Gland
The functioning of the thyroid gland is essential for the body as it lies in the endocrine system. It includes using iodine from food and utilizing it to generate body metabolisms. Now, most people ask about the endocrine system and its works. It’s a critical question indeed!
The endocrine system has different functions as it comprises glands that produce, store, and release hormones in the bloodstream. These then reach the body cell and maintain whole-body metabolism. Thyroid glands, in this particular system, further produces the following hormones:
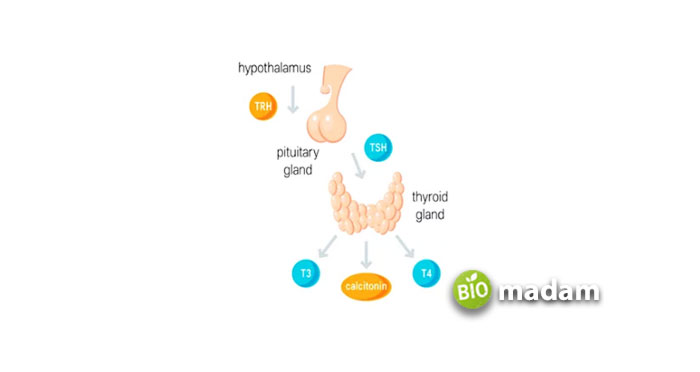
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Thyroxine (T4)
Production of T3 and T4
The thyroid gland consists of thyroid follicular cells responsible for producing triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). This process is regulated by the thyroid-stimulating hormone that is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland.
Thyroid Disease States
We have talked about almost all tests that can detect diseases relating to thyroid hormones, but how do they occur? The answer is quite simple! We are humans with everyday body changes that can result in low or high production of such hormones. It ultimately affects human health. There are two main types of thyroid diseases called hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism means deficiency of hormones. In other words, this disease occurs due to a decrease in body iodine. Hence, the problem appears in people with iodine insufficiency and other inflammatory issues of the thyroid. The most common signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism arise during childhood, such as lethargy, sensitivity towards cold, reproductive failures, etc.
Similarly, there’s another condition called hyperthyroidism, which is also an immune disorder. The autoantibodies in this condition bind and activate the TSH receptors and stimulate thyroid hormone synthesis. The situation, hypothyroidism, can later be treated with anti-thyroid drugs. Common symptoms include insomnia, high heart rate, muscle weakness, etc.
Final Words
Concluding the above, thyroid gland testing is important to check how your body hormones are working. Regular testing will help in evaluating the diseases and knowing the actual cause behind thyroid dysfunction. This is why it’s essential to know the normal thyroid hormone range. With advancements in medical technology, including the use of miRNA biomarkers, diagnosing thyroid carcinoma and related conditions has become more proactive. So, by staying on top of your thyroid health and working closely with your doctor, you can stay healthy and avoid serious issues down the road.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.