Recently updated on January 27th, 2023 at 09:00 am
Thyroid problems are a lot more prevalent than we think. Around 20 million people in the United States have some kind of thyroid issue, and 60% of them are unaware of their condition. Thyroid issues are becoming common yet more easily diagnosed, providing a better chance of treatment and management.
Women have five to eight times more chances of thyroid issues than men. Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are both thyroid diseases and can be managed after diagnosis. Both these conditions may present in different forms. Here’s everything you need to know about thyroid and the difference between hyperthyroid and hypothyroid.
Comparison Table
| Factor | Hyperthyroidism | Hypothyroidism |
| Definition | Increased thyroid hormones | Decreased thyroid hormones |
| Symptoms | Weight loss, diarrhea, bulging eyes, etc. | Weight gain, constipation, depression, etc. |
| Causes | Excessive iodine, and hypothyroid medicine | Insufficient iodine, and hyperthyroid medicine |
| Autoimmune causes | Graves’ disease | Hashimoto’s thyroiditis |
| Weight changes | Weight loss | Weight gain |
| Temperature tolerance | Heat intolerance | Cold intolerance |
| Treatment | Radiotherapy/surgery | Medications |
What is Thyroid?
The thyroid is one of the most important glands of the body involved in regulating normal body functions. It is a butterfly-shaped, small gland present at the base of the neck below Adam’s apple. The thyroid produces hormones like T3 (Triiodothyronine) and T4 (Thyroxine) that affect metabolism and eventually many other functions.
Thyroid Problems
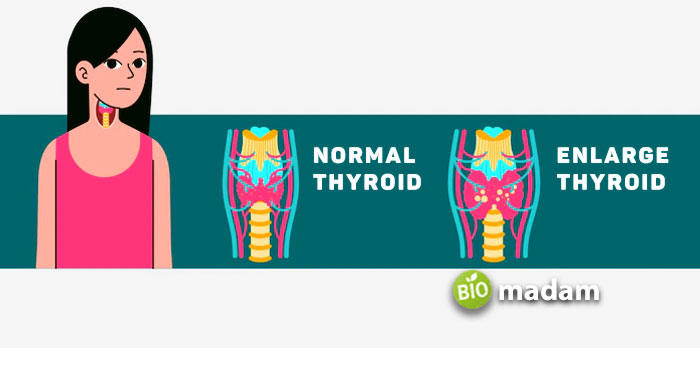
An excess or decrease in the number of thyroid hormones can cause serious problems like Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism.
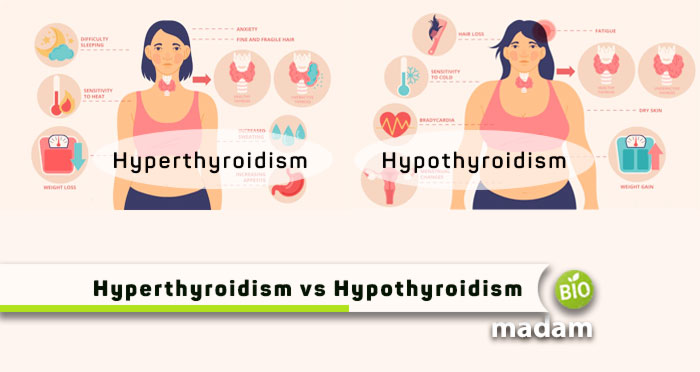
- Hyperthyroidism is when your body produces excessive thyroid hormones, resulting in sudden weight loss paired with other symptoms.
- On the other hand, hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces fewer hormones than required by the body, which slows down metabolism and results in weight gain.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a condition when your body produces an excess amount of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism usually occurs in the form of
Thyroiditis (Inflammation of the Thyroid)
It is a short-term condition that typically expresses itself during pregnancy. Thyroiditis enables more thyroxin to enter the bloodstream, causing elevated thyroid hormones in your body.
Graves’ Disease (Autoimmune Disorder)
Graves disease is an autoimmune disease which means that the body’s defense system attacks parts of the body, causing irregularities. Graves’ disease increases the levels of thyroid hormones in the body resulting in metabolic problems.
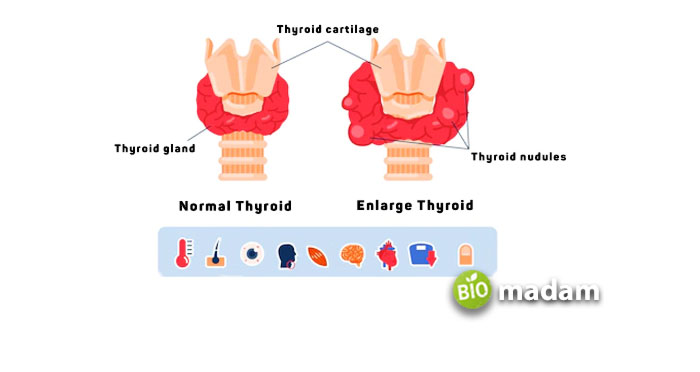
Thyroid nodule (Causing a High Amount of T4)
Thyroid nodules occur in both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Though they are benign, they elevate Thyroxine (T4) levels in the body. Thyroid nodules increase the size of your thyroid.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can be caused due to numerous reasons, including excessive intake of iodine. As your body produces enough thyroid and conditions like Graves’ disease add to the overall amount of iodine in blood, taking excess oral iodine has the same effect. The iodine you intake through diet determines the amount of thyroid hormone produced. Iodized salt and seaweed contain a significant amount of iodine and should be used considerably.
Thyroid Medicine
You might not know this, but taking hyperthyroid medication without monitoring the thyroid hormone levels can also lead to hyperthyroidism. If you alternate the dose of your hypothyroidism medicine without consulting the doctor, you may take a lot of thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Hereditary
Diseases like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are hereditary and may run in families. There is no cure for such diseases except for managing them properly to ensure the condition does not aggravate.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Each person having a hyperactive thyroid may have different symptoms from the other. Here are some of the symptoms commonly similar in people with hyperthyroidism.
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Swelling of the neck due to an enlarged thyroid
- Bowel changes (diarrhea)
- Shakiness
- Muscle weakness
- Warm and thin skin
- Excessive sweating
- Excessive hair loss
- Changes in sleep
- Menstrual changes
- Bulging eyes
What is Hypothyroidism?
As opposed to hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism is a condition in which your thyroid gland does not produce hormones properly, resulting in a decreased amount of thyroid hormones necessary for body functions. While hyperthyroidism is more common in women and teenagers, hypothyroidism is also found in children.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism could be caused by multiple factors, most prominently medication and surgery. Let’s tell you about the causes of hypothyroidism in detail.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease that causes the enlargement of your thyroid by affecting your thyroid’s ability to produce hormones. The root cause of Hashimoto’s disease has not been discovered, yet scientists believe genetic and environmental factors influence it.
Hyperthyroid Medication
Like excessive use of hypothyroid medicines can lead to hyperthyroidism, it also occurs the other way round. Suppose your doctor has prescribed you medication for hyperthyroidism, and you change the regimen without monitoring the thyroid levels. In that case, it may cause deficient levels of thyroid hormones in the body.
Radiation/Surgery
Hypothyroidism is also often a result of damaged thyroid or if you have received a radiological treatment for thyroid disease. The radioactive waves affect the production of hormones from the gland. Similarly, if some part of your thyroid has been removed during surgery, you will need to take thyroid medicines to compensate for the loss of naturally produced T3 and T4 in your body.
Iodine Deficiency
As mentioned, iodine is an essential element in the production of thyroid hormones. Taking an insufficient amount of iodine suppresses thyroid hormone production, and you become hypothyroid.
Pituitary Gland Disorder
Pituitary gland disorder is one of the rarest reasons for hypothyroidism, yet a benign tumor of the pituitary gland can influence thyroid production. The tumor or any other condition of the pituitary gland may restrict the production of Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
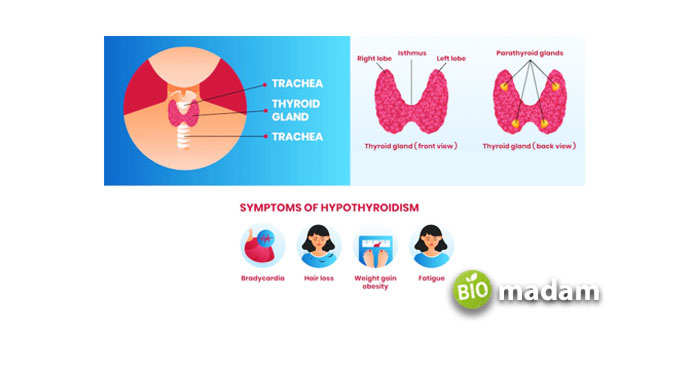
- Weight gain
- Muscle stiffness and tenderness
- Sensitivity to cold
- Puffy face with dry skin
- Thinning hair
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Impaired memory
- Depression
Difference Between Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
Definition
Hyperthyroid
A hyperactive thyroid producing more thyroid hormones than normal causes hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroid
Contractitorily, if your thyroid gland produces less thyroid hormone than usual, it causes hypothyroidism.
Symptoms
Hyperthyroidism
The signs or symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, diarrhea, and bulging eyes.
Hypothyroidism
On the other hand, the symptoms of hypothyroidism include weight gain, constipation, impaired memory, and depression.
Causes
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is commonly caused by excessive hypothyroid medicine, iodine, or genetic reasons.
Hypothyroidism
Alternatively, hypothyroidism usually occurs due to excessive intake of hyperthyroid medication, insufficient iodine, surgery, or radiation.
Autoimmune Diseases
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism may be caused because of Graves’ disease, which is an autoimmune disease.
Hypothyroidism
Yet hypothyroidism is sometimes caused by Hashimoto’s disease, in which the antibodies obstruct the thyroid gland’s ability to produce hormones.
Weight Changes
Hyperthyroidism
Elevated thyroid levels in the body increase metabolism leading to sudden weight loss.
Hypothyroidism
In contrast, reduced thyroid levels in the blood slow down metabolism leading to weight gain.
Temperature Tolerance
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is typically characterized by heat intolerance.
Hypothyroidism
In comparison, hypothyroidism is commonly known as shivering and cold intolerance.
Treatment
Hyperthyroidism
If the thyroid hormone levels are higher than normal, they are primarily treated through radiotherapy or surgery.
Hypothyroidism
Conversely, hypothyroidism is usually managed by thyroid medication such as Levothyroxine.

FAQs
What is Goiter?
Goiter refers to the enlargement of the thyroid gland that may be a result of an underlying condition. An insufficient amount of iodine is one of the significant causes of goiter.
How common is hyperthyroidism?
It is estimated that one out of every American aged 12 years or more is suffering from a hyperactive thyroid.
Is hypothyroidism worse than hyperthyroidism?
None of the conditions is worse than the other and has similar management. However, hypothyroidism is more common than hyperthyroidism.
The Bottom Line
Hypothyroid and hyperthyroid are conditions of the thyroid gland that result from an increase or decrease in the levels of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism is typically indicated by sudden weight loss, whereas hypothyroidism expresses through weight gain. While thyroid issues are becoming more common, they are manageable and treatable with suitable measures.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.