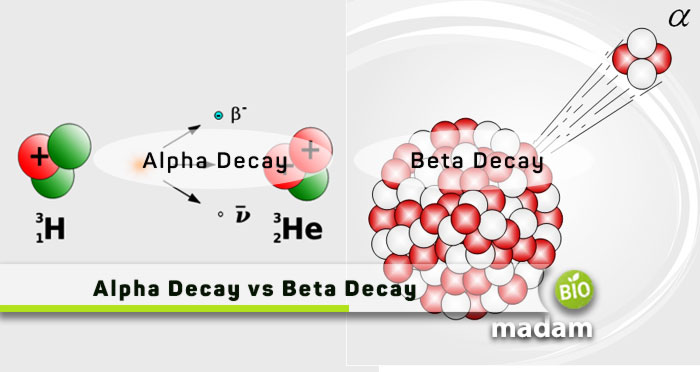
Alpha and beta decay are two of the three types of radioactive decay. Radioactive decay is a critical phenomenon we study in physics to understand radioactivity. It leads to physical and chemical change in elements. The main difference between alpha and beta decay is the particle the substance emits during the decay activity. The emission of alpha particles results in alpha decay. Similarly, beta particle emission leads to beta decay. Here are the brief differences between alpha and beta decay for you.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Alpha Decay | Beta Decay |
| Emitted Particles | Alpha particles | Beta particles |
| Other Names | Helium atom | Electron or Positron |
| Reason | Presence of many protons | Presence of numerous electrons |
| Position of Daughter Element | Two on Left | One on right |
| Effect on Nucleus | Disintegration | Conversion into proton |
What is Radioactive Decay?
Radioactive decay or radioactivity refers to the emission of particles from an atom, molecule, or compound due to nuclear instability. The emission of these particles allows the radioactive element to lose energy and stabilize. Henry Becquerel discovered decay in 1896 when he examined the photographic plates placed next to uranium. They had traces of the element despite no direct contact. The elements that exhibit radioactive decay are called radioactive elements. Radioactive decay is of three types, alpha, beta, and gamma. Let’s tell you about alpha and beta decay in detail.
What is Alpha Decay?
Alpha decay is the emission of alpha particles from an unstable nucleus. An alpha particle contains two neutrons and two protons, the same as the molecular composition of a helium nucleus. Eventually, the radioactive element transforms into another element with a mass number four less and atomic number two less than the radioactive element.
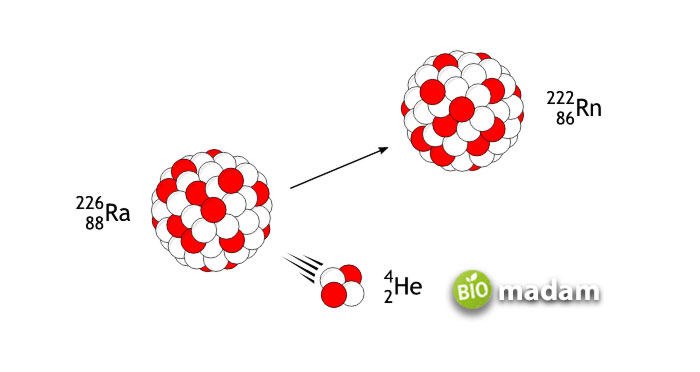
Mechanism of Alpha Decay
Alpha decay occurs when the parent atom emits nucleons and gives rise to a different element known as the daughter element. The radioactive decay results in the emission of a helium-4 atom along with high binding energy contained in the element. Electromagnetic forces and nuclear forces play the primary role in the process.
Properties of Alpha Decay
- Alpha decay produces a new element two places to the left of the parent element in the periodic table.
- Alpha particles are heavy in weight and stop within a few centimeters in the air.
- Alpha decay takes place in the heaviest nucleotides with a 5 MeV energy.
- The particles emit at a speed of 15,000 km per second.
- Alpha particles cannot pass through aluminum or paper.
Example of Alpha Decay
The transformation of “Uranium” into “Thorium” is the most common example of alpha decay transformation. This process is known as transmutation.
The formation of Thorium from Uranium with the ejection of alpha particles can be represented as:
238U92 → 234Th90 + 4He2
What is Beta Decay?
Beta decay is the emission of beta particles from unstable nuclei to stabilize them. The atoms may emit a beta plus or beta minus particle. Beta-plus particles are known as positrons, while beta-minus particles are electrons.
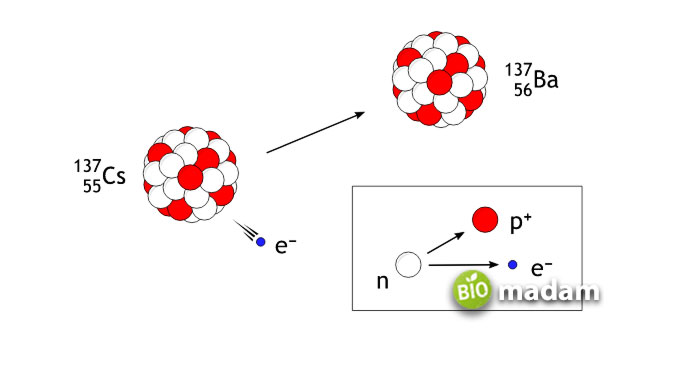
Mechanism of Beta Decay
Beta decay takes place in a nucleus with numerous neutrons to turn into a proton, electron, and anti-neutrino. The emission of electrons gives it the name beta decay. As a result of beta decay, the number of neutrons reduces by one, and the number of protons increases. It leads to change in physical and chemical properties in the parent element.
Properties of Beta Decay
- Beta decay results in the emission of high-energy electrons or positrons.
- Beta particles are faster than alpha particles.
- The proton in the nucleus of the atom transforms into a neutron.
- Beta particles can penetrate aluminum to several millimeters.
- The ejection of the electron produces an element one place right to the original substance in the periodic table.
Example of Beta Decay
The emission reduces the number of electrons, eventually leading to an increase in the number of protons. Beta decay can be well understood by:
234Th90 → 234Pa91 + 0e-1
Similarities Between Alpha and Beta Decay
- Alpha and beta decay are types of radioactive decay.
- Decay takes place in unstable nuclei.
- They result in the transformation of the original atom.
Differences Between Alpha and Beta Decay
Definition
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay is the emission of alpha particles from an unstable nucleus.
Beta Decay
Beta decay refers to the emission of beta particles from atoms and molecules.
Emitted Particles
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay results in the emission of alpha particles which resemble the helium atom.
Beta Decay
On the contrary, beta decay releases high-energy beta particles from the substance in the form of electrons or positrons.
Reason
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay results from too many protons in an unstable nucleus.
Beta Decay
Alternatively, beta decay occurs as a result of a high number of electrons in an unstable atom.
Result
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay gives rise to an atom with an atomic number of two less and four less atomic mass.
Beta Decay
Conversely, beta decay produces a new nucleus with one more atomic mass than the initial atom.
Position of Daughter Element
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay produces a new element two places to the left on the periodic table.
Beta Decay
While beta decay creates an element one place on the right of the parent element on the periodic table.
Effect on Nucleus
Alpha Decay
During alpha decay, the nucleus disintegrates after the loss of alpha particles.
Beta Decay
On the contrary, beta decay converts the nucleus into a proton on releasing electrons.
The Bottom Line
Alpha and beta decay result from alpha and beta particles emission from unstable nuclei. Besides this major difference between alpha and beta decay, chemical and physical changes take place in the structure as a result of decay. The loss of alpha particles in alpha particles disintegrates the nuclei and produces a new element with two less atomic numbers and four less atomic masses. On the other hand, beta decay produces a new element one place right on the periodic table.

Hi, my name is Eva. I am currently practicing as a clinical social worker, that being my childhood desire. As a licensed therapist holding MPhil in Clinical Psychology, I am now on biomadam to provide the natives with the best family advice! Do you have any questions? See you in the comment section.