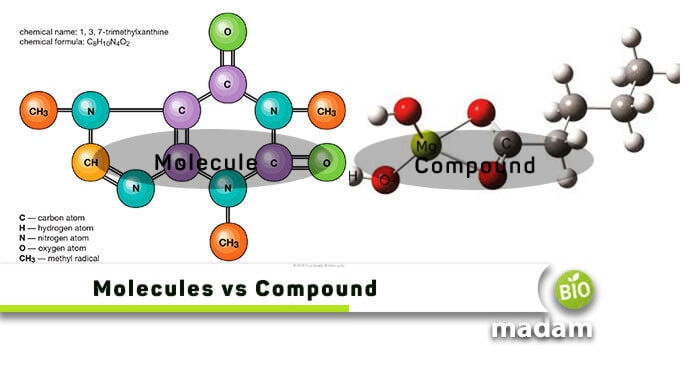
Molecules and compounds are two very basic terminologies that teachers add in the science books of as low as Grade 6 and 7. When two or more same atoms combine through a chemical bond, they form a molecule. On the other hand, a compound is formed by combining two or more atoms that can be of different elements. Hence, we can say that all compounds can be called molecules, but not all are compounds. Molecules and compounds can only be seen under an electron microscope unlike compound microscope.
Besides, there are many more differences between the two that we have planned to discuss in this article today. So, let’s begin with a quick comparison table before heading toward their detailed differences.
Comparison Table
| Parameters | Molecules | Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| Interrelation | Not all molecules are compounds | All compounds are molecules |
| Bonding Types | Ionic & Covalent | Ionic, Covalent & Metallic |
| Nature of Substance | Homo or hetero nuclear | Heteronuclear only |
| Visibility | Through microscope | With naked eye |
| Stability | Unstable | Stable |
| Example | Water, Cl2, & ozone | Fructose, gasoline, & ammonia |
Explanation of a Molecule
A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together by a chemical bond that are the smallest fundamental units and consist of all the properties. The chemical reaction of atoms forms molecules. These atoms are held together by shared electron pairs or covalent bonds. A molecule is weighed in gram molecular mass, also called a mole.
Mole: It is the sum of the atomic weights of all its component atoms
Furthermore, the SI unit of molecular mass is kilogram per mole & the formula tends to be:
M = m/n
m = mass of a substance (in grams)
n = number of moles of a substance
Different molecules have distinct weights that can be determined through mass spectrometry. In addition, molecules are always neutral as they have no positive or negative charge. They are represented by a chemical formula that shows the types of atoms in the molecule. It uses subscripts to show how many of each atom is present. Furthermore, they have low boiling points, melting points, and low solubility. You can observe molecules under electron microscopes but not under student microscopes
Types of Molecules
There are numerous types of molecules, based on no. of atoms involved, the similarity or dissimilarity, and their sizes.
Based on the Number of Atoms
Monoatomic Molecules – consisting of only one atom, for example, Argon, Helium, etc.
Diatomic Molecules – consisting of two atoms per molecule, for example, HCl, Cl2, etc.
Triatomic Molecules – contains three atoms in a molecule, for example, CO3, O3, etc.
Polyatomic Molecules – as the name indicates, this type can have more than three atoms, up to the molecule requirement, for example, glucose, sucrose, etc.
Based on Similarity or Dissimilarity of Atoms
Homoatomic Molecules – consists of atoms of the same elements, chemically combined, for example, hydrogen (H2), Sulfur (S8).
Heteroatomic Molecules – consists of atoms of different elements, chemically bonded together, for example, water (H2O), glucose (C6H12O6), etc.
Based on Size of Atoms
Macromolecules – having large molecular weight, such as proteins, carbs, lipids, etc.
Macromolecules – having comparatively low molecular weight, such as amino acids, fatty acids, etc.
Explanation of a Compound
It is a combination of different atoms or elements chemically bonded together. It is also important to note that all compounds are always molecules, but not every molecule can be a compound. We generally classify compounds into three types based on their bonding: covalent compounds, ionic compounds, and metallic compounds. Moreover, the elements in any compound are always present in fixed ratios; thus, compounds are homogenous, having a particular formula.
Besides, there is no way to separate a compound by physical means; hence, a compound requires special chemical methods of separation, for example, evaporation, crystallization, etc.
Types of Compounds
Compounds can also be of various types, based on their atoms, complexity, nature of components, and bonding.
Based on the Number of Atoms
Diatomic Compounds – a compound with two chemically bonded atoms are diatomic, such as H2, CO, etc.
Triatomic Compounds – a compound with three chemically bonded atoms, such as CO2, H2O, etc.
Polyatomic Compounds – compounds with four or more atoms chemically coupled refer to polyatomic nature, such as CaCO3, NH4NO3, etc.
Based on Complexity
Simple & Complex Compounds – we can differentiate the two terms based on their complexity; for instance, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are simple compounds, whereas fructose is a complex one.
Based on the Type of Components
Organic Compounds – any compound with a carbon atom involved is an organic compound, such as hydrocarbons, amines, alcohol, etc.
Inorganic Compounds – compounds excluding the carbon-hydrogen bonding are the inorganic compounds, for example, oxides, halides, etc.
Based on Bonding
Covalent Compounds – consist of compounds bonded through a shared pair of electrons, for example, HCl, H2O, etc.
Ionic Compounds – consists of compounds bonded through the complete transfer of electrons, for instance, NaCl, LiF, etc.
Brief Differences between Molecules and Compounds
Definition
Molecules
These are the results of a chemical combination of two or more atoms.
Compound
On the other hand, a compound is formed when different elements join together to present specific properties.
Characteristics
Molecules
A molecule can be heteroatomic or Homoatomic, based on its type.
Compound
Whereas, in contrast, a compound is always a combination of different elements.
Visibility
Molecules
These are usually not observed with a naked eye.
Compounds
On the other hand, compounds are visible to human beings, and we can hold their particles in our hands, for example, sugar crystals.
Stability
Molecules
These are not very stable, and the bonds are easily breakable.
Compounds
On the contrary, compounds have covalent or ionic bonding in them that makes them highly stable.
Difference in Bonding
Molecules
These can be bonded through ionic or covalent bonds only.
Compounds
The nature of a compound is formed from its ionic, covalent, or metallic bonding.
Conclusion
Despite being different, molecules and compounds are most of the time confused by students. So, it was necessary to provide a detailed article on their differences. Both molecules and compounds exist in our surroundings through special bonding but are differentiated based on separation techniques.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.