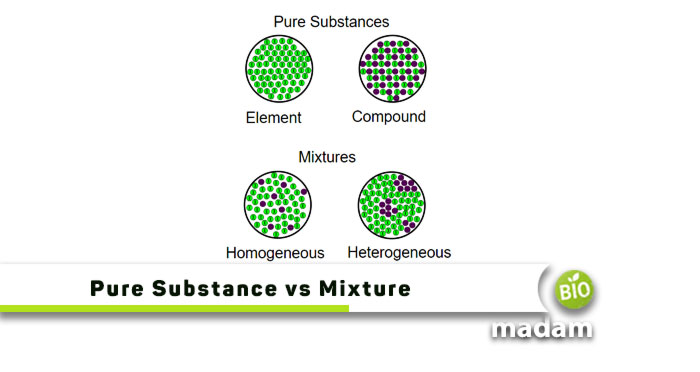
Anything in any state of matter is a substance, whether solid, liquid, or gas. Everything around us is either a pure substance or a mixture of one or more substances. Pure substances are defined as materials in their pure form that cannot be disintegrated into one or more forms by physical means; you cannot obtain multiple states of matter from them. On the other hand, mixtures have one or more states of matter combined. Examples of mixtures include saltwater (salt + water), air (various gases), and salad (solid + solid + liquid).
Their characteristics depict numerous differences between pure substances and mixtures, including composition. Let’s dive into pure substances and mixtures to understand the distinct features properly.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Pure Substance | Mixture |
| Types | Elements, compounds | Homogeneous, heterogeneous |
| Purity | Pure | Impure |
| Properties | Uniform | Vary |
| Separation into Components | Chemical treatments | Physical processes |
| Examples | Hydrogen, Lead, Water | Saltwater, and cough suspension |
What are Pure Substances?
Pure substances are made of atoms or compounds and cannot be separated into other components by physical means like boiling or melting. Elements and compounds are pure substances. They are made of one or more kinds of atoms that join together to form a chemical structure that does not break down into further components until atomic-level treatments are used. Here are the differences between elements and compounds.
Types of Pure Substances
Elements
Elements are composed of one kind of atom only. You can find many elements in the periodic table that are the fundamental component of compounds and molecules. Examples of elements are Hydrogen (H), Chlorine (Cl), Mercury (Hg), Lead (Pb), etc.
Compounds
On the other hand, compounds are composed of different kinds of elements or atoms that form a new substance; examples include water (H2O) produced by the combination of hydrogen and oxygen and table salt Sodium Chloride (NaCl) that results from the fusion of Sodium and Chloride. However, compounds and mixtures are not the same.
What are Mixtures?
Mixtures refer to adding one pure substance to another to produce a product that can be disintegrated into its components through physical means like melting or boiling. Mixtures may be formed between solid/ solid, solid/ liquid, liquid/ liquid, liquid/ gas, gas/ solid, etc. However, the most common mixtures are solid/ liquid mixtures in which solids are solutes and liquids are solvents. Mixtures are divided into two categories based on their physical and chemical composition; homogenous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Homogenous Mixtures
Homogenous mixtures are composed of one or more elements or substances that combine to form a uniform mixture. The components of homogenous mixtures combine entirely and do not look like one or more different substances are present in them. Some common examples include the dissolution of salt in water. The salt dissolves in water completely, but you can remove it by evaporation. Homogenous mixtures are also typically known as solutions.
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Heterogeneous mixtures are those which do not combine properly and the solute is not evenly distributed throughout the solvent. Common heterogeneous mixtures are suspensions and emulsions. Suspensions are made by mixing a solute in a solvent that it does not properly dissolve in. Conversely, emulsions are two immiscible liquids combined together. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include cough suspensions that need thorough mixing before taking them to ensure each dose gets the right amount of drug in the cough suspension. So, solutions and suspensions are different from each other.

Similarities Between Pure Substance and Mixture
- Pure substances and mixtures have a definite weight and volume depending on their composition.
- They both can be used to prepare other mixtures and impure substances.
- They have particular melting and boiling points depending on their chemical structure or the type of atoms present.
Differences Between Pure Substances and Mixtures
Definition
Pure Substances
Pure substances are made of atoms of one type or different types combined together.
Mixtures
While mixtures have multiple pure substances in the same varying state mixed together.
Types
Pure Substances
Pure substances are of two types; Elements and compounds. Elements are made of the same kind of atoms, whereas compounds are formed by the combination of different kinds of atoms.
Mixtures
Mixtures are categorized into homogenous and heterogeneous mixtures. Homogenous mixtures are completely solubilized, yet heterogeneous mixtures have an insoluble or immiscible solute.
Purity
Pure Substances
As the name says, pure substances are in a pure form without the addition of any external factor.
Mixtures
Alternatively, mixtures are considered impure as one or more pure substances fuse to form another substance that is not pure in nature.
Properties
Pure Substances
The chemical and physical properties of a pure substance stay the same throughout.
Mixtures
Whereas the physical and chemical properties of a mixture vary because of different substances present in mixtures.
Separation Into Components
Pure Substances
It is not possible to break down pure substances into atoms and molecules by using physical processes.
Mixtures
On the other hand, you can obtain the different components of a mixture by physical processes like boiling.
Examples
Pure Substances
Examples of pure substances include elements or compounds like water, hydrogen, chlorine, etc.
Mixtures
Examples of mixtures are saltwater, oil in water, cough suspensions, etc.
FAQs
What other classifications of pure substances exist?
Pure substances can also be categorized as solids, liquids, and gases as atoms form one of these three types of matter together.
Are mixtures easily separable?
Though you can easily separate mixtures through physical processes, it is not readily possible with all. Azeotropes are those mixtures that you cannot separate easily. One such example is the air which cannot be easily separated into its components.
What is the difference between molecules and compounds?
All compounds are molecules but all molecules are not compounds. Compounds are microscopic entities that make up everything around us comprising more than one element. Alternatively, mixtures can be seen by the naked eye and are composed of two or more substances.
What are colloids?
Colloids are the types of mixtures, besides solutions and suspensions. Colloids can be homogenous or heterogeneous depending on the size of the colloidal particles in the mixture.
What are impure substances?
Impure substances are mixtures formed by the fusion of two or more pure substances. They have a variable composition and can often be separated into components. The boiling and melting points of impure substances vary from the physical characteristics of their pure components.
The Bottom Line
Pure substances and mixtures are critical in chemistry as they enable you to study pure and impure materials. The physical properties of pure substances are uniform, but mixtures have varying properties due to the presence of different substances. Pure substances are made of one or more atoms, whereas mixtures contain multiple elements and compounds to form a new product.

Meet me; I am Paulina Zaniewska, who’s more hooked on providing the best health blog. I’ve always been so determined to compete as a nutritionist, and here I am, done with a Master’s in food technology. My brilliant performance throughout encouraged me to help people.