The endocrine and nervous systems carry out bodily processes by transmitting signals. The nervous system, including the somatic and autonomic, is the most critical part of the human body. The brain is a part of the nervous system and regulates coordination, memory, thirst, sleep cycle, etc. It is furthermore categorized into six regions that contribute to different functions. Amygdala is one such component of the human brain that plays a role in emotions. Besides the function of the amygdala in emotions, there is more to know about it.
What is Amygdala?
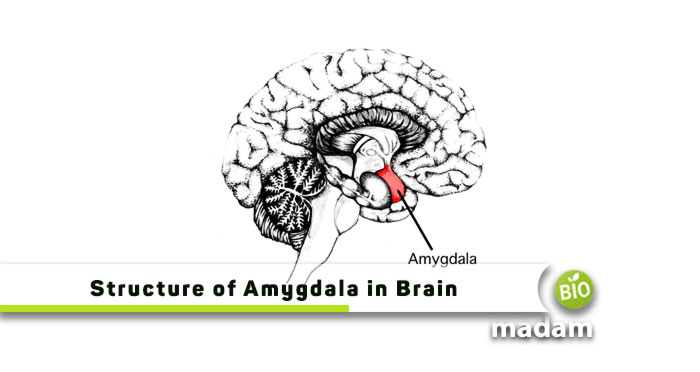
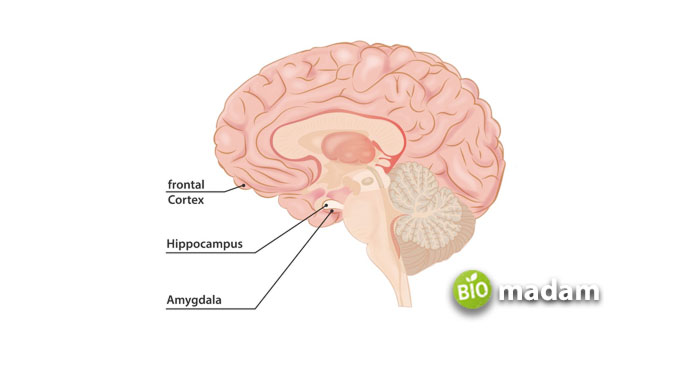
The amygdala is a complex structure of nuclei in the brain’s temporal lobe, adjacent to the hippocampus. The word “Amygdala” is of Latin origin that translates to “almond.” The word represents the organ’s shape within the brain. While they are typically considered singular, the brain contains two amygdalae. They are present in each cerebral hemisphere.
Each amygdala has three parts:
- The basolateral group is present slightly on the lower side. It connects with the cerebral cortex, primarily the frontal and prefrontal lobes.
- The medial subnuclei connect with the cortex and olfactory bulbs, contributing to a sense of smell and olfactory function.
- The anterior and central nuclei in the amygdala are connected to the hypothalamus, brainstem, and sensory structures.
The connections of the amygdala to other structures within the brain allow it to process cognitive information using systems that regulate lower functions like touch, sensitivity, and breathing patterns. Thus, the amygdala controls physiological responses according to cognitive information, such as in the sympathetic nervous system. These connections also mediate the fight or flight response.
Functions of Amygdala in the Brain
The main function of the amygdala in the brain is its role in emotions and memory. The amygdala is believed to have a primary role in your memories of fear or pleasure.
Emotional Behavior & Learning
Emotional behavior and learning are one of the primary functions of the amygdala in the brain. It results in robust learning through neuromodulatory input. It results from converging sensory information regarding the unconditioned and conditioned stimulus. The amygdala’s response to the conditioned stimuli changes as the individual learns. The activation of the neurons in the basolateral amygdala stimulates learning. The information from the basolateral complex to the central part creates various behavioral and physiological responses related to emotional states. The behaviors modulated by the amygdala as a result of emotional learning may include increased blood pressure and skin conductance. At the same time, some organisms may exhibit freezing as a defensive behavior through the stimulus provided by the amygdala to motor neurons.
The emotional learning function of the amygdala also contributes to cognitive processes like memory formation, decision-making, and attention. Thus, they play a primary role in social behaviors. The participation of the amygdala in social behavior is attributed to the connection of the amygdala with the sensory and prefrontal cortices. The amygdala’s neural activity also reflects visual stimuli’s emotional significance. The emotional learning and memory function allows you to reflect upon past positive and negative emotions to make better decisions.
Aggression
Besides forming memories related to fear and pleasure, the amygdala also contributes to aggression in animals and humans. Groves and Schlesinger discussed its role in the limbic system in inducing aggression in 1982. It was seen that the surgical removal of the amygdala in violent animals reduced aggression. Thus, the amygdala is a major contributor to aggression in animals.
Sexual Orientation
Amygdala displays changes in people with different sexual orientations. For example, studies show patterns in the amygdala of homosexual males similar to those in heterosexual females. They have more widespread connections in the left amygdala compared to other individuals. Similarly, the patterns in homosexual females mimic those in heterosexual men due to more widespread connections in the right amygdala.
Addiction
The amygdala also shows relevance to addiction in addicted people. The basolateral amygdala is involved in relapsing in addicts. It initiates the influence of stress on an addict’s memory related to drugs or other kinds of addiction, such as internet addiction. People with internet addiction have altered functional connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Thus, it was concluded that this addiction might also be associated with emotion processing and emotional disturbance. Stress-coping strategies combined with adequate management with an addiction expert can help improve.
The Bottom Line
The nervous system is a critical part of human processing as guides us every day in our daily activities, like walking, running, sleeping, changing moods, etc. Amygdala is a prominent part of the brain that has a fundamental role in memory and emotions. It is further connected to other brain parts, allowing it to contribute to various functions. Amygdala’s role in producing emotions has been well-known among researchers. However, studies have shown its involvement in emotional learning, memory, aggression, and addiction. Furthermore, a difference in the amygdala pattern of homosexual and heterosexual individuals has also been observed.
FAQs
What is the main role of the amygdala in your emotional intelligence?
The amygdala has a primary role in processing emotions and memories, especially those associated with fear. It contributes to emotional learning and behavior, thus impacting emotional intelligence.
What happens when the amygdala is overactive?
Amygdala is thought to stimulate anxiety in humans, and an overstimulated amygdala may outweigh the logical parts. Eventually, the brain causes you to panic in case your amygdala is overstimulated.
What hormone stimulates the amygdala?
The central nucleus of the amygdala and lateral BNST have corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). These hormones control autonomic functions and emotional behaviors.
Is the amygdala responsible for sleep?
Besides the primary function of regulating memory and emotions, it also plays an additional role in sleep. However, the hypothalamus is the basic sleep regulation center in the brain.
What regulates the amygdala?
The amygdala is involved in cognitive regulation and is regulated by the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC). This part of the brain is involved in fear expression.
What is the 6-second rule amygdala?
Sometimes, the amygdala takes control of an individual’s ability to respond to a situation rationally. The 6-second rule to overcome amygdala hijacking is to wait for six seconds to let the situation diffuse.
Does the amygdala control anger?
The amygdala controls feelings associated with aggression and hostile behavior. The amygdala plays a prominent role in emotions and emotional intelligence, especially anger, fear, and anxiety.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.