Our body comprises several systems like nervous, endocrine, exocrine, respiratory, circulatory, etc. The nervous system is among the most critical systems of the body. It picks up the signals from organs and generates a suitable action. The nervous system is classified into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The central nervous system further comprises the brain and the spinal cord. At the same time, the peripheral nervous system consists of all nerves and neuromuscular junctions involved in the exchange of signals. Somatic and autonomic nervous systems are further branches of the peripheral nervous system and we are here to discuss their differences in detail today! Though, it may sound complicated, but here’s everything you need to know when finding somatic vs. autonomic nervous systems.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | SNS | ANS |
| Definition | Controls voluntary functions | Controls involuntary functions |
| Types | No further types | Sympathetic & parasympathetic |
| Movement | Voluntary | Involuntary |
| Muscle Type | Skeletal muscles | Smooth and cardiac muscles |
| Neurotransmitters | Excitatory | Excitatory & inhibitory |
| Complexity | Less complex | More complex |
| Examples | Skeletal muscle movement | Stomach, heart, pupil |
What is the Peripheral Nervous System?
The word peripheral comes from a root word, “periphery,” which means from the outside. So, a peripheral nervous system is the one that lies outside the brain and spinal cord. If you wonder what the peripheral nervous system does, know that its primary function is to carry information from the central nervous system and transmit it to the specified part of the body. Whatever information is collected from the CNS is sent through the cranial and spinal nerves. These nerve cells, also called neurons, are composed of axons, dendrites, and soma (body) to circulate the neural signals around the body. A neuron can be sensory, motor, or mixed – based on its key function.
The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and autonomic nervous system, and knowing everything about somatic vs. autonomic is our main focus today!
What is the Somatic Nervous System?
The most common name for the somatic nervous system is the voluntary system, meaning that it involves the actions of muscle signals from the body. Once the skeletal muscle receives a certain stimulus from the sensory receptors, it performs the activity. The somatic nervous system consists of afferent and efferent nerves. The afferent nerves pick up the signals from sensory receptors, whereas the efferent nerves direct them to the muscles. It also contributes to the input of the senses. An interesting fact is that all this communication occurs through neurotransmitters – either excitatory or inhibitory.
Acetylcholine is a unique chemical that acts as a neurotransmitter as well as a hormone. Here, in the somatic nervous system, it functions as an excitatory neurotransmitter, releasing from the axon and acting on the acetylcholine receptors in the muscles for contraction. The neurotransmitter signals are set through the upper motor neuron to the skeletal muscle through the axons. Besides controlling voluntary movements, the somatic nervous system is observed to play its part in involuntary movements as well. These special movements are called the “reflex arcs.” The skeletal muscle in this situation works without coordinating with the main CNS. These arcs are further subcategorized into autonomic and somatic reflex arcs.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
In contrast to the somatic nervous system, the autonomic nervous system is most directly involved in the involuntary actions of your body. This part of the peripheral nervous system helps smooth muscle movement, for example, the digestive system of the stomach, controlling heartbeat, pupil dilation, urination, and homeostasis. Acetylcholine acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter that slows down or inhibits various movements.
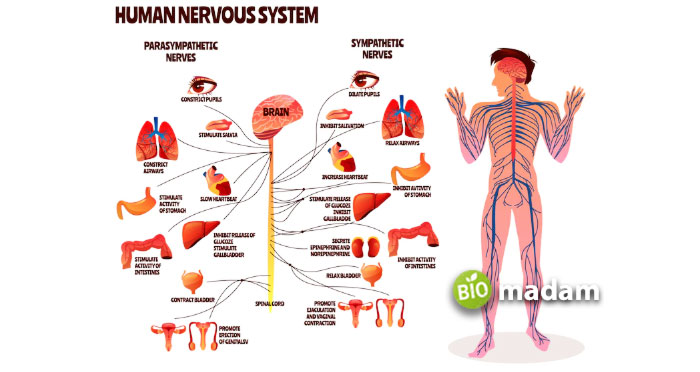
This involuntary part of the nervous system is further branched into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is also known as the “fight or flight” response of the body to stress conditions. Conversely, the parasympathetic nervous system brings the body back to normal. It is more active during the state of rest, like sleeping.
Similarities Between Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems
While there must be many primary differences between somatic and autonomic systems, both types are similar from the roots:
- The somatic and autonomic nervous systems are divisions of the peripheral nervous system.
- They comprise cranial and spinal nerves arising from the brain and spinal cord, respectively.
- Both systems use neurotransmitters, afferent and efferent nerves, to help in signal transmission.
- Both systems contribute to muscle movements in the body.
- They receive, transmit, and send signals in the form of nerve impulses through neurotransmitters.
- They are mainly found in vertebrates and not in invertebrates.
Somatic vs Autonomic Nervous System – Key Differences
Definition
Somatic Nervous System
It is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for all the voluntary muscle movements of the body.
Autonomic Nervous System
On the contrary, the autonomic nervous system regulates the involuntary movement of tissues and organs.
Movement
Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system manages voluntary muscle movements, which means these actions are under control. It also comprises the somatic reflex.
Autonomic Nervous System
As opposed to the somatic nervous system, the autonomic nervous system manages involuntary reflexes and movements, such as dilation of pupils.
Type of Muscles
Somatic Nervous System
Another primary somatic and autonomic nervous system difference is the muscles involved. This type of PNS acts on skeletal muscles to provide voluntary movement.
Autonomic Nervous System
On the other hand, the autonomic nervous system acts on cardiac and smooth muscles; thus, their functioning is not under control.
Neurotransmitters
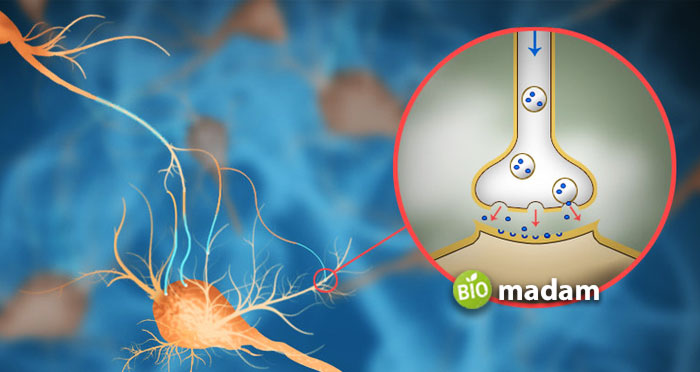
Somatic Nervous System
All the voluntary actions within a body are produced through the excitatory neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine. In other words, the somatic nervous system involves excitatory acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter.
Autonomic Nervous System
In contrast, autonomic nervous systems work as the exact opposite. However, the neurotransmitter released here can be excitatory or inhibitory.
Neurons in Efferent Pathways
Somatic Nervous System
This branch of the peripheral nervous system comprises only a single neuron between the central nervous system and the particular organ.
Autonomic Nervous System
In contrast, the autonomic nervous system has two neurons with a single synapse working between the CNS and the effector organ.
Complexity
Somatic Nervous System
The functions of the somatic nervous system are not as complex as the autonomic nervous system.
Autonomic Nervous System
In contrast, the autonomic nervous system functions are complex because of sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways. It means this system has to take care of the rest and “fight and flight” responses.
Nerve Fibers
Somatic Nervous System
This type of nervous system has thick myelinated nerve fibers.
Autonomic Nervous System
On the other hand, the nerve fibers of the autonomic nervous system can be of thick or thin myelinated sheet.
Stimulus Detection
Somatic Nervous System
The sensory stimuli detected by the somatic nervous system are taste, touch, smell, noise, pain, and light.
Autonomic Nervous System
In contrast, the autonomic nervous system senses the involuntary stimulus, such as pH, blood pressure, heartbeat, sweating, etc.
Examples
Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system majorly helps in the movement of skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
However, the autonomic nervous system regulates smooth muscle and cardiac function apart from pupil dilation and contraction and respiratory function partially.
The Bottom Line
The somatic and autonomic nervous systems are divisions of the peripheral nervous system comprising nerves and neuromuscular junctions. It is responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body. The somatic nervous system regulates voluntary muscle function. Alternatively, the autonomic nervous system manages involuntary muscle function. In short, the key difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems is what type of body movement each controls.
FAQs
What is the weight of the brain?
The human brain weighs around three pounds. The weight and size of the brain reduce as we grow.
Is breathing somatic or autonomic?
The breathing mechanism naturally doesn’t require any thought process to start working; thus, it is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. To be precise, parasympathetic from the autonomic nervous system helps your breathing rate to slow down in rest conditions.
What are some examples of autonomic reflex vs somatic reflex examples?
Cardiac muscles and smooth muscles are examples of autonomic reflexes, whereas the knee reflex occurs by somatic reflexes.
Which part of the brain controls the autonomic nervous system?
The hypothalamus primarily acts to control the autonomic nervous system. This tiny brain part manages this nervous system from the dorsal longitudinal fasciculus.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.