Animals are highly organized organisms with complicated anatomy and physiology. They possess particular organ systems for different functions. The circulatory system pumps blood, the reproductive system helps reproduce, and the skeletal system facilitates movement. Similarly, other systems like the exocrine, endocrine and nervous systems exist. These are actively involved in producing hormones and neurotransmitters to regulate bodily functions. Neurotransmitters are essential for nerve impulse generation, while hormones regulate growth, movement, and reproduction.
Keep reading to learn all the differences between the endocrine and nervous systems.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Endocrine System | Nervous System |
| Components | Glands | Nerves |
| Parts | Pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, etc. | Brain, spinal cord, and neurons |
| Chemicals | Hormones | Neurotransmitters |
| Signal Transmission | Bloodstream | Nerve cells |
| Time for Transmission | More | Less |
| Function | Regulating sleep cycle, growth, homeostasis, reproductive cycle | Improving muscle movement, breathing, memory, senses, etc. |
| Disorders | Diabetes, Cushing’s disease, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism | Neuropathy, Bell’s palsy, & carpal tunnel syndrome |
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is one of the essential systems in the body, comprising different types of glands. The body starts producing the hormones as soon as the mother conceives the fetus and continues until old age. The formation, transport, and action of hormones take a long time to signal the target site. However, a sudden increase or decrease in the levels of particular hormones in the body can lead to complications. Thus, it is crucial to monitor the hormones regularly and report any signs and symptoms.
Functions of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system’s glands secrete different chemicals, including hormones that evoke target cell responses. The hormones secreted by endocrine glands travel to their target site through the bloodstream or intercellular fluid. These hormones facilitate the functions of different tissues and organs in the body. They play a significant role in nervous system development, growth and metabolism, homeostasis, blood sugar levels, and the reproductive system.
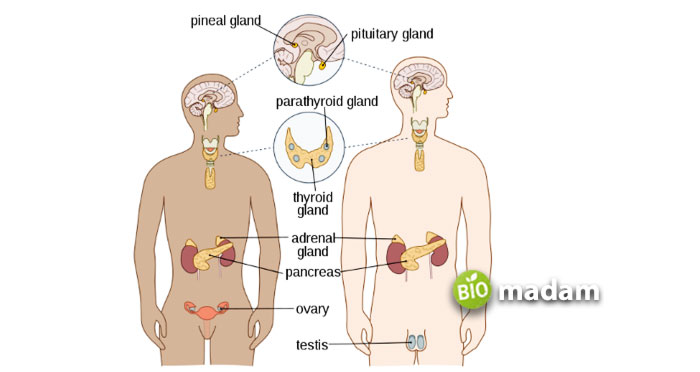
Parts of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system is made of various glands that perform a unique functions. The seven main endocrine glands in the body are:
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus is present in the lower central part of the brain and links the endocrine system to the nervous system. The neurons in the hypothalamus control the production of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus primarily helps manage your sleep, body temperature, mood, hunger and thirst, blood pressure and sex drive.
Pituitary
The pituitary gland is the size of a pea and is located at the base of the brain. It is the master gland that controls many other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland produces numerous hormones, including growth hormones, prolactin, thyrotropin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), corticotropin, and oxytocin. This gland is also responsible for controlling the menstrual cycle in women.
Thyroid
The thyroid gland present in the front lower neck is butterfly-shaped. It produces thyroxine and triiodothyronine that control metabolism. A higher amount of thyroid hormone catalyzes the hormones, while a lower amount reduces the reaction’s speed. Low or high levels of thyroid hormone can lead to hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Thus, it is vital to maintain normal levels of thyroid hormones.
Parathyroid
The parathyroid gland is attached to the thyroid hormone. They are a set of four tiny glands that control the calcium levels in the body. The thyroid hormone regulates the process by producing calcitonin.
Pineal
The pineal gland is found in the middle of the brain and plays the primary role in controlling the sleep cycle. It secretes melatonin that helps regulate your circadian rhythm, pushing you to wake up or sleep.
Adrenal Glands
The adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla are together known as the adrenal glands. They sit on the top of each kidney and can help control water balance and blood pressure. The adrenal cortex is on the outer side and produces corticosteroids that manage metabolism, stress, sexual function, and the immune system. Alternatively, the adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure under stress conditions.
Reproductive Glands
Reproductive glands comprise testes in males and ovaries in females. They also produce hormones that ensure normal sexual function and the development of secondary sex characteristics. Testes in males produce testosterone while ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone. These glands contribute to oogenesis and spermatogenesis essential for reproduction.
Endocrine Disorders
Fluctuations in the hormones produced by endocrine glands may lead to diseases and disorders like diabetes, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, Graves’ disease, Addison’s disease, menopause, etc.
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is another crucial system in the body that ensures all functions by transmitting impulses. Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. The nervous system receives information and sends commands to the action site through sensory and motor neurons. They secrete neurotransmitters that contribute in the transmission of electric impulses and transfer of action potential.
Functions of Nervous System
It collects information and reacts to that information with the help of electrical impulses. It enables coordination between different body parts. The nervous system is responsible for decision-making, emotions, and how you respond to different stimuli. It also lets you interact with and understand your habitat and ecosystem.
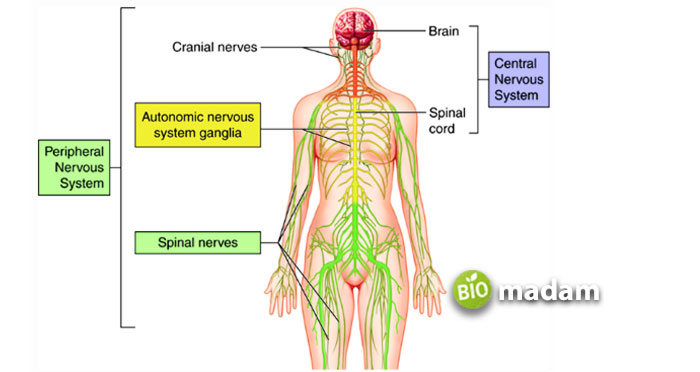
Parts of Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into two basic categories: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central nervous system comprises the brain and the spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system comprises the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
Central Nervous System
The brain is the central nervous system’s main component that functions with the spinal cord. It resides in the skull that gives the shape of a mushroom. The brain has four parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, the diencephalon, and the brainstem. The nerves from the brain are known as cranial nerves and are 12 in number.
On the other hand, the spinal cord is the tube-like structure that runs from the base of your head to the pelvis. It is also known as the vertebral column, comprising 31 vertebrae or segments. The spinal cord contains the sensory and motor nerves. Nerves arise from each segment in the spinal cord giving rise to 31 spinal nerves.
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system, as discussed above, has two significant subdivisions called autonomic and somatic nervous systems. The autonomic is further classified into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems that help the body during emergencies or rest conditions. The PNS overall has three main functions in your body. It is a key element of how your brain receives information about your surroundings. The PNS also contributes to delivering command signals to the muscles to control them consciously. Moreover, it also regulates critical processes that do not require ‘thinking’ or brain involvement. The somatic nervous system regulates sensory and movement functions. Meanwhile, unconscious thinking occurs in the autonomic nervous system.
Nervous System Disorders
Any changes in the normal functioning of the nervous system can lead to different diseases and disorders. Common nervous system disorders include Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, Parkinson’s, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.
Similarities Between Endocrine and Nervous Systems
- The endocrine and nervous systems enable body functions by responding to stimuli.
- They use chemical substances to transfer cells from one region to another in the body.
- They transmit signals to the effector organ.
Differences Between Endocrine and Nervous Systems
Definition
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is made up of different glands that secrete hormones.
Nervous System
The nervous system comprises neurons and neurotransmitters to transfer impulses throughout the body.
Parts
Endocrine System
The endocrine system comprises various glands, including the pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, reproductive glands, pancreas, etc.
Nervous System
The nervous system comprises the central and peripheral nervous systems consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Chemicals
Endocrine System
The endocrine system secretes hormones to carry information to target cells.
Nervous System
While the nervous system uses neurotransmitters to transmit signals throughout the body.
Signal Transmission
Endocrine System
The endocrine system transfers information through the bloodstream.
Nervous System
Alternatively, nerve impulses are transmitted to the target cells through nerve cells.
Transmission Time
Endocrine System
The endocrine system takes more time to reach the effector organ through blood.
Nervous System
On the other hand, nerve impulses travel to the target organ within a very short period.
Function
Endocrine System
The endocrine system regulates sleep cycle, growth, homeostasis, glucose, reproductive cycle, etc.
Nervous System
At the same time, the nervous system manages all bodily functions through nerve impulses, improving muscle movement, breathing patterns, memory, senses, etc.
Disorders
Endocrine System
Changes in the level of endocrine hormones may lead to menopause, Cushing’s disease, prolactinoma, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and diabetes that is opposite to hypoglycemia.
Nervous System
Whereas peripheral neuropathy, Bell’s palsy, and carpal tunnel syndrome are common nervous disorders.
The Bottom Line
Endocrine and nervous systems are crucial systems in the body that contribute to different functions. The main difference between the endocrine and nervous systems is that the former has glands while the latter comprises neurons. The endocrine system secretes hormones while the nervous system transmits impulses through neurons. Both these systems ensure and facilitate movement, thinking, growth, and reproduction. However, the nervous system transmits signals faster than the endocrine system.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.