The world consists of millions and trillions of organisms, including both living and non-living entities. Today we are here to explain the differences between autotrophs and heterotrophs, comprehending the importance of food for living organisms. Living creatures all depend on food, water, and air to enjoy a healthy life. There are these two fundamental modes of nutrition for all living bodies, namely autotrophs and heterotrophs.
If we look at autotrophs, they are producers able to prepare their own food through natural processes. Whereas on the other side, heterotrophs live by depending on others for their nutrition. These entities are mostly called consumers, being able to consume food from producers. We will grab the discriminating differences between the two below, but first, let us catch a quick comparison table.
Comparison Table
| Basis of Comparison | Autotrophs | Heterotrophs |
| General Definition | Organisms able to fetch nutrition by preparing it themselves are autotrophs. | Organisms that rely on other living or dead organisms to get energy are heterotrophs. |
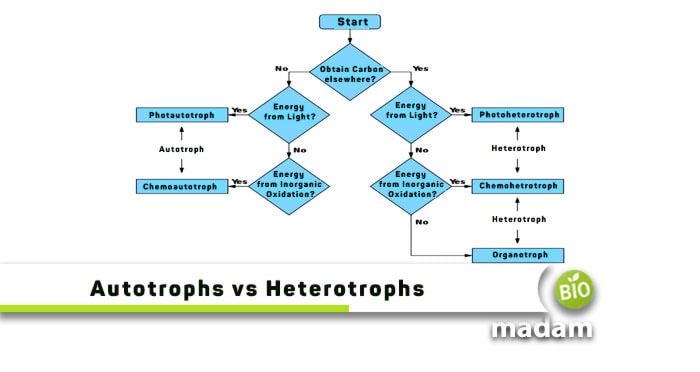
| Types | Chemoautotrophs & photoautotrophs | Chemoheterotrophs & photoheterotrophs |
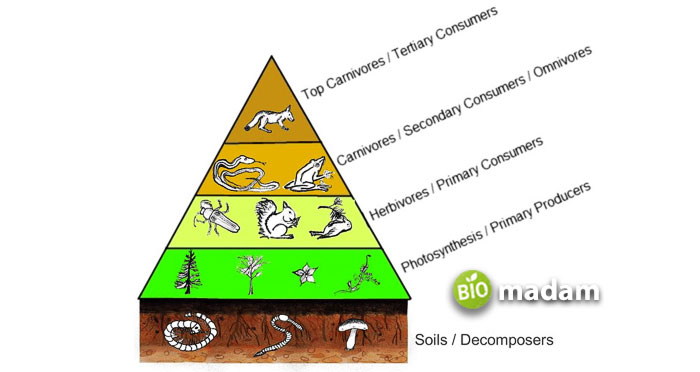
| Rank in a Food Chain | Autotrophs stand at the primary level. | Heterotrophs stand at secondary and tertiary levels. |
| Act as | Producers | Consumers |
| Photosynthetic Pigments | Utilizes these pigments | No role of photosynthetic pigments |
| Type of Carbon Source | Inorganic (CO2) | Organic (carbohydrates) |
| Examples | Plants and most algae | Animals and many fungi |
Briefly Explain Autotrophs
An autotroph is a Greek word combined from two individual words, “auto” and “trophe.” As the word itself suggests, auto means self, while trophe means food or nourishment. Therefore, autotrophs relate to all those organisms who dress their nutrition themselves. These are often called primary producers that grab energy from water, sunlight, and air and follow the photosynthesis path to make up the meal.
Most plants acquiring green leaves, enormous trees, phytoplankton, algae, and many bacteria fall under autotrophs following photosynthesis for their food. Now the question arises that how they utilize photosynthesis to bring forth their food. The procedure initiates when these organisms fetch a high amount of solar energy and employ it to alter carbon dioxide gas from air and water into a molecule called glucose. This compound is the fundamental source of energy for these producers. Besides this, the natural processes also cover a phenomenon called chemosynthesis. This procedure requires energy through different chemical reactions, which then transfer to autotrophs as food.
Briefly Explain Heterotrophs
This word also originated from the Greek language, similar to autotrophs, composed of two individual terms, “hetero” and “trophe.” Hetero indicates being different, and trophe is the same as before, meaning food or nourishment. It states that heterotrophs are all those organisms relying on other animals, plants, (be it vascular or non-vascular), or decomposing substances to gain energy for their survival. Heterotrophs are further classified into two fundamental categories, called chemoheterotrophs and photoheterotrophs.
The living organisms, that gain energy through oxidation in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), are called chemoheterotrophs. They invade to eat surrounding organisms, no matter if they are dead or alive! Some common examples of chemoheterotrophs are fungi, many animals, bacteria, and numerous pathogens Another type of heterotroph is the photoheterotroph.
As it is referred from the name, these organisms utilize sunlight to get food. The only difference between photoheterotrophs from autotrophs is that these creatures use carbohydrates, alcohol, or fatty acids to meet their carbon needs instead of using CO2. Some common examples include green non-sulfur bacteria, non-sulfur bacteria, heliobacteria, etc.
Catch the Contrast Between Autotrophs & Heterotrophs
Alternate Names & Dependency
Autotrophs
These are also called primary producers that are independent to prepare their nourishment.
Heterotrophs
These are the consumers who always rely on other organisms for their food.
Major Types
Autotrophs
The two distinct types of autotrophs are photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs.
Heterotrophs
The two distinct types of heterotrophs are photoheterotrophs and chemoheterotrophs.
Energy Source
Autotrophs
These organisms grab energy from two prominent sources, including chemical reactions and sunlight.
Heterotrophs
These organisms are consumers that directly or indirectly get energy from autotrophs.
Trophic Level in Food Chain
Autotrophs
In a food chain, autotrophs acquire the lowest position as producers.
Heterotrophs
Heterotrophs attain the second and third levels in a food chain as consumers.
Role of Solar Energy
Autotrophs
These organisms store solar energy, being producers, to proceed with photosynthesis.
Heterotrophs
There is no specific role of solar energy in heterotrophs. However, they can indirectly get this energy.
Role of Photosynthesis
Autotrophs
These living organisms mainly utilize photosynthesis, with the essential photosynthetic pigment, for their living.
Heterotrophs
There is no direct role of photosynthesis in the lives of heterotrophs, hence, no photosynthetic pigment is involved.
Organisms Included
Autotrophs
All the green plants, big trees, different bacteria, and all types of algae fall under autotrophs
Heterotrophs
These organisms are all animals, some bacteria, decomposing organisms, and groups of fungi having a distinct nucleus.
Organic/Inorganic Carbon Sources
Autotrophs
These organisms use carbon from inorganic carbon dioxide to prepare food.
Heterotrophs
These organisms indirectly utilize carbon from organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, fatty acids, etc., to prepare food.
Time to Prepare Food
Autotrophs
As these organisms depend on sunlight for their food, they are confined to the daytime to gain nutrition.
Heterotrophs
Consumers can prey on primary and secondary producers at any time, so there is no time restriction to get food.
Bottom Line
So, we concluded from the article above that either of the two modes of nutrition holds its own significance. You will observe autotrophs and heterotrophs keeping up the food chain to attain equilibrium on the Earth. The principal difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs is that the former is free to feed themselves whereas, the latter is fed by others.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.