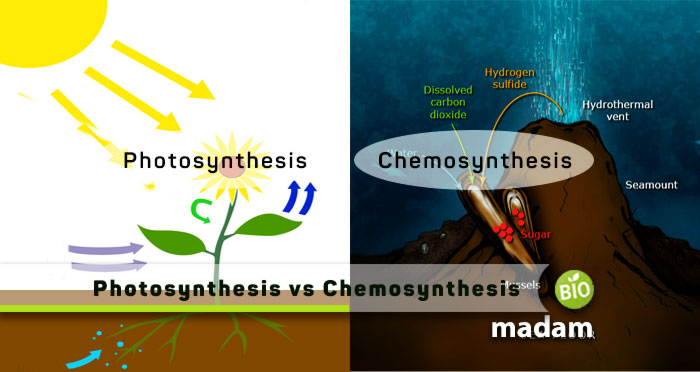
Chemosynthesis and photosynthesis help bacteria, plants, and algae produce food by utilizing different forms of energy. Both are vital for different species as some cannot do photosynthesis while others cannot perform chemosynthesis. While they both are food-producing processes, they differ in many ways, like their energy source, by-products, rate of the process, etc.
Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are a gift of nature to organisms to meet their food needs by utilizing available resources. Photosynthesis makes the use of light energy for the process, while chemosynthesis occurs through energy generated by inorganic reactions. They utilize carbon dioxide to fuel the process and produce oxygen and sulfur as by-products.
To understand these processes in detail, here are the primary differences between Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis.
| Basis of comparison | Photosynthesis | Chemosynthesis |
| Organisms | Plants, green algae, cyanobacteria | Deep-sea creatures |
| Source of energy | Sunlight | Chemical reactions |
| By-product | Oxygen | Sulfur |
| Pigments | Chlorophyll, Carotenoids, Phycobilins | No pigments |
| Plastids | Chloroplasts | Not involved |
| Occurrence | Daytime | Day and Night |
| Process rate | Rapid | Slower |
| Contribution to biospheric energy | Higher | Lower |
Photosynthesis
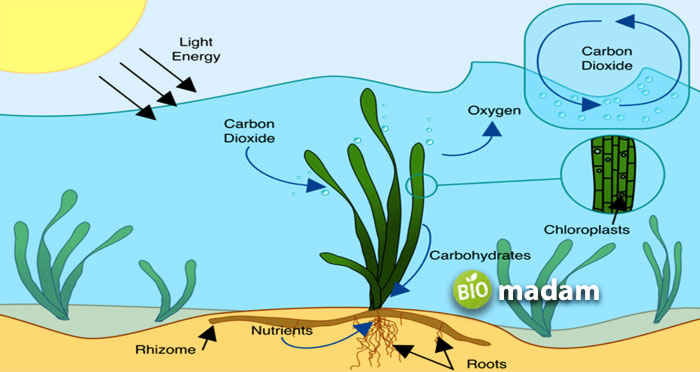
By definition, “Photosynthesis is the process of converting Carbon Dioxide and Water to Oxygen and Glucose in the presence of Sunlight and Chlorophyll.”
Photosynthesis is essential for plants to manufacture food as they cannot obtain energy from other sources.
Sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis; thus, the process occurs during the day in the presence of the sun. Photosynthesis occurs in two forms; aerobic/ oxygenic and anaerobic/ anoxygenic. Oxygenic photosynthesis is the most common type of photosynthesis occurring in green plants, different types of algae, and cyanobacteria. On the other hand, anoxygenic photosynthesis occurs in green and purple sulfur bacteria. While oxygen is considered a by-product of photosynthesis, purple and green sulfur bacteria do not produce any amount of oxygen.
Photosynthesis is an essential process for the sustenance of the environment as oxygen released as a by-product is vital for humans and animals, unlike any fungi Green plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria exhibiting this behavior are called photoautotrophs. They contribute highly to maintaining the Earth’s oxygen content.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis is defined as “The production of organic compounds through the energy obtained from oxidizing inorganic matter.”
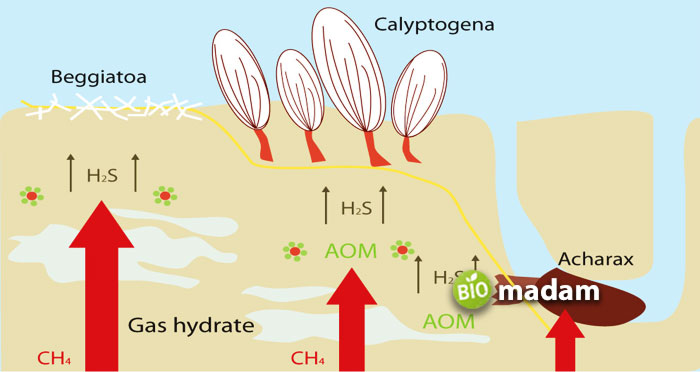
Chemosynthesis is usually utilized by organisms and bacteria living deep under the oceans and seas where the sunlight cannot reach them. Contrasting to photosynthesis, chemosynthesis produces sulfur as the by-product as a result of the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with oxygen and carbon dioxide. Organisms that perform chemosynthesis are called Chemoorganotrophs.
Chemoorganotrophs are typically present in hypothermal vents in deep water where no sunlight is present. They utilize the compounds from the seafloor as their energy source to produce food. The process of chemosynthesis is mainly a food-production mechanism for microbes living on the seabed. Some organisms like tube worms tend to have a symbiotic relationship with chemosynthetic bacteria. Their ability to utilize already present compounds as a source of energy allows them to thrive underwater.
18H2S + 6CO2 + 3O2 → C6H12O6 + 12H2O + 18S
Hydrogen Sulphide + Carbon Dioxide + Oxygen → Glucose + Water + Sulphur
Similarities between Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis
While both processes differ in the reactants and by-products, they possess some similarities, including;
- Chemosynthesis and photosynthesis help the plants produce food in the form of carbohydrates.
- They produce organic matter through the utilization of sunlight or chemical energy.
- Both processes use CO2 for the conversion of energy to organic material.
- Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis contribute to the sustenance of life on Earth.
Differences between Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis
Organisms
Photosynthesis
It usually occurs in plants with green pigments, like green plants, cyanobacteria, green algae, mosses, etc. Higher plants or vascular plants have pigment in their leaves for the process.
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis is carried out by underwater creatures living deep under the sea and ocean that utilize inorganic reactions as their energy source.
Energy Source
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis utilizes sunlight as the fundamental energy source to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis occurs through the reaction of hydrogen sulfide to release energy for carbohydrate synthesis. They use the present compounds underwater to produce energy.
By-product
Photosynthesis
Oxygen is produced as a by-product during photosynthesis and is essential for cellular respiration. However, some photosynthetic organisms like purple and blue sulfur bacteria do not produce oxygen as a by-product.
Chemosynthesis
Sulfur is produced as a result of chemosynthesis by organisms living in deep seas and oceans.
Pigment
Photosynthesis
Green pigments, including chlorophyll a and b, carotenoids, and phycobilins, are involved in the process.
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis does not involve pigments.
Plastids
Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are plastids in plants involved in photosynthesis. They are responsible for converting light energy into stable chemical energy through photosynthesis which produces oxygen.
Chemosynthesis
No plastids are present in Chemoorganotrophs, and they produce energy by utilizing chemicals in hypothermal vents.
Occurrence
Photosynthesis
As photosynthetic plants need sunlight to convert carbon dioxide, it occurs during the day only.
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis occurs during the day as well as at night because of the bacteria’s ability to obtain energy from inorganic chemical processes.
Process Rate
Photosynthesis
Provided with direct light, photosynthesis is a relatively rapid process.
Chemosynthesis
It is a slow process compared to photosynthesis.
Contribution to Biospheric Energy
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis mainly happens on land, providing oxygen to other living organisms and contributing to biospheric energy.
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis occurs in deep waters and does not play a major role in the sustenance of the atmosphere.
The Bottom Line
The differences between photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are dynamic as both processes are essential for the survival of different plants and bacteria, unlike yeasts that utilize cellular respiration and fermentation process. They use different energy sources and carbon dioxide to convert reactants into food and energy sources. However, photosynthesis contributes primarily to the sustenance of life by converting sunlight into carbohydrates and oxygen for respiration. Life on Earth would not be possible without photosynthesis, as humans need oxygen for proper body functioning.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.