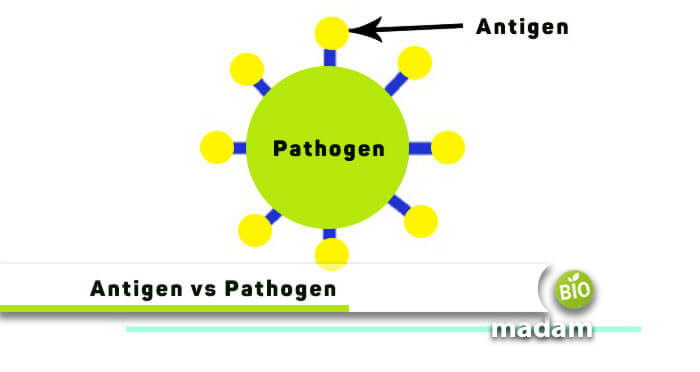
Are you familiar with the terms antigen and pathogen? As we are currently dealing with this severe pandemic disease, corona, you must have heard about these specific terms! Today we come up to elaborate you the differences between antigens and pathogens. It might seem a little subtle to grab the distinction between the two, but we’ll try our best to provide a complete understanding.
A pathogen is any microorganism that is the cause of sickness or disease. It includes all harmful bacteria, numerous viruses, many fungi, and protozoa. While on the counter side, an antigen is a describing characteristic of a pathogen. It is actually a molecule composed of complex carbohydrates and proteins that are further detected as foreign particles by a body’s immune system. Manifesting it with a familiar example! For instance, a person suffering from Tuberculosis is attacked by the whooping cough bacterium, which has significant antigens on it.
We’ll look into the differences between antigen and pathogen in detail, but let’s first check out the comparison table below!
Comparison Table
| Comparison | Antigen | Pathogen |
| Arrangement | Arranged as a molecule | Arranged as an entire microorganism |
| Specificity | Very specific | No specificity |
| Effect | Defining feature of a pathogen | Produces destructive effects |
| Types | Exogenous, endogenous, and autoantigen | Bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa |
| Composition | Mostly proteins or polysaccharides | Essential composition for a living micro-entity |
Describe an Antigen
The antigen is a unique structure present on the surface of a pathogen. We can’t call it an organism but a molecule that is the fundamental reason behind initiating an antibody immune response. It defines the character of a foreign particle that is most harmful to our body. As a result, the body activates itself and produces any of the five types of antibodies in defense. The foreign particles can be viruses, fungi, bacteria, or other parasites.
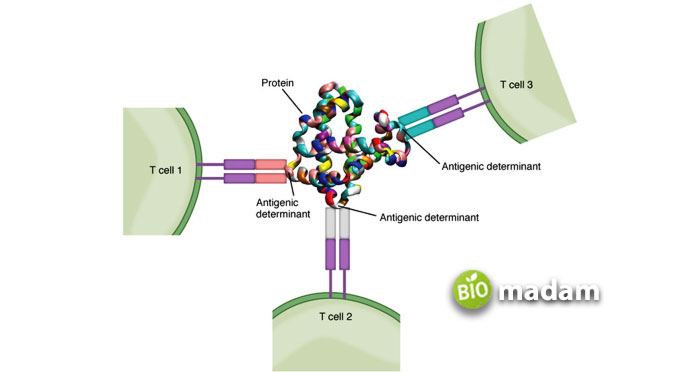
Antigens can be of many types, but the broader classification is as follow:
- Exogenous antigens
- Endogenous antigens
- Autoantigens
All those antigens attached at the surface of any pathogen/microorganism are known as exogenous antigens. On the other side, when antigens are produced inside a body due to some metabolic reactions, they are referred to as endogenous antigens. Last but not the least, autoantigens are the complex proteins in a body that is, unfortunately, recognized as foreign particles. Thus, they stimulate the immune response. All this mechanism ultimately causes self-destruction of a body, leading to different autoimmune diseases. Some example are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Describe a Pathogen
These are all those microorganisms that can harm a body and induce diseases and infections. Almost all pathogenic organisms have a particular origin with unique structures to attack a body. Pathogens include bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and other parasites. Although viruses come under non-living bodies, their transferable viral part is so strong that it can even kill a person. We are all familiar with one such disease that has prevailed these days, coronavirus!
Pathogens are interlinked with antigens. These molecular structures are present on microorganisms to initiate their induction process, and as soon as they enter a body, their immunity (humoral or cell-mediated) activates! In other words, these structures help a body detect this foreign particle, or pathogen, and prepare itself for a fight. Sometimes the body wins the race and kills a pathogen, and sometimes the case is entirely different!
Similarities Between Antigen & Pathogen
Apart from being distinct, there appears a few similarities between the two. Let’s find them below!
- Either it’s a pathogen or an antigen; both kicks start a body’s active immunity to protect it.
- Both of them are capable of inducing disease.
- These are often called immunogens.
Dissimilarities Between Antigen & Pathogen
Definition
Antigen
An antigen is a substance or a molecule attached to a pathogen, mostly as a defining property.
Pathogen
A pathogen can be a parasite that attacks a host cell and causes diseases.
Different Types
Antigen
An antigen is broadly categorized into three groups based on its location and function. These are exogenous antigens, endogenous antigens, and autoantigens.
Pathogen
While in contrast, pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi, molds, or protozoa.
Composition
Antigen
These are entirely the polysaccharides, proteins, or complex proteins to perform destructive function.
Pathogen
A pathogen is a complete microorganism with all principle functions to reside.
Effect on the Host Cell
Antigen
An antigen is a substance that works to identify its relative pathogen to a host cell, ultimately triggering the immune system.
Pathogen
A pathogen spreads its disease after attacking the host cell.
Specificity
Antigen
These are highly specific to its relative pathogen. Antigens of one microorganism can never be similar to the ones of another.
Pathogen
These are not so specific and can enter any living organism to produce its harmful effects.
Conclusion
Every human body has different types of immunities that activate themselves every time a foreign particle enters. Our body does the same when a pathogen invades! The article above might have cleared your conflicts about the two terms, so we hope the differences between antigen and pathogen are now understood. When a pathogen enters a body, the body detects it through the specific antigens and triggers its antibodies. In most cases, this antigen-antibody complex helps a body win against the harmful pathogen.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.