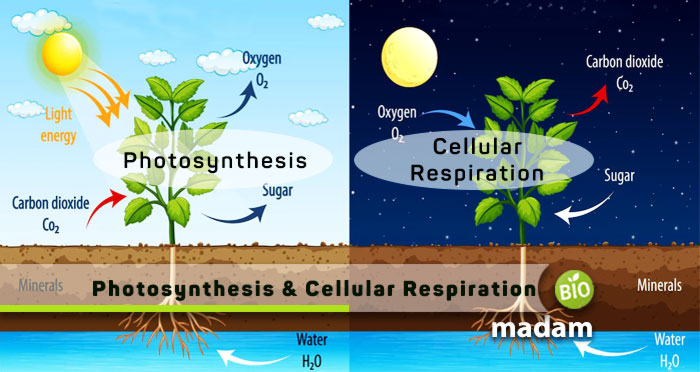
Respiration is an essential process in all organisms, whereas photosynthesis occurs in green plants, algae, and a few types of bacteria only. The process of respiration takes place in plants and animals at alternative times. Animals breathe during the day. But, plants photosynthesize during the day and respire at night. Cellular respiration is one of the types of respiratory processes which occurs at the cellular level. It is a vital process to obtain energy for cellular functions. Both are essential for the survival of life. Here are all the differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration along with their definitions.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Photosynthesis | Cellular Respiration |
| Definition | Food manufacturing process | Energy liberation process |
| Chemical Equation | CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 | C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + ATP |
| Occurrence | Green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria | All prokaryotic & eukaryotic organisms |
| Location | Chloroplasts | Cytoplasm, mitochondria |
| Time | Daytime | All day & night |
| Steps | Light-dependent & Light-independent Reactions | Glycolysis, Pyruvate Oxidation, Kreb’s cycle, Oxidative Phosphorylation |
| Process Type | Anabolic | Catabolic |
| Reactants | CO2, water, sunlight | Oxygen & glucose |
| Products | Oxygen, water, glucose | Water, ATP, CO2 |
| Coenzymes | NADP | NAD + FAD |
| Pigments | Chlorophyll | No pigments |
| Reaction Type | Endothermic | Exothermic |
| Phosphorylation | Photophosphorylation | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| Carbohydrates | Produced | Consumed |
| Energy Conversion | Light energy to potential energy | Potential energy to kinetic energy |
| Dry Weight | Increased | Decreased |
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is an energy-producing process carried out by plants in the presence of chlorophyll to produce sugar molecules (energy). It uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and sugar. These sugar molecules act as an energy source in various molecular and cellular functions. Plants, like mosses, and other organisms, such as algae, and some cyanobacteria also perform photosynthesis to obtain energy. Herbivores utilize the energy stored in different leaves of green plants to fulfill their nutrient demands.
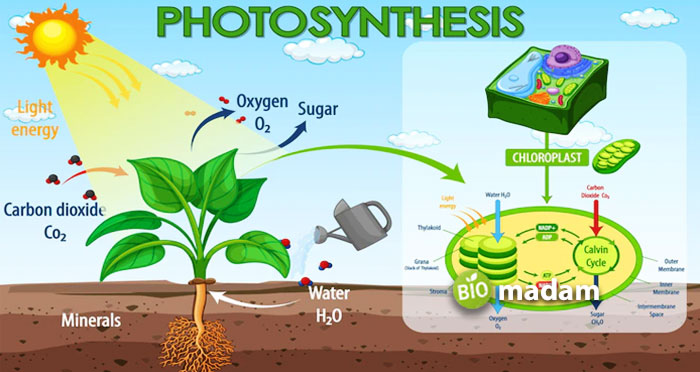
Photosynthesis is either oxygenic or anoxygenic, depending on the organism’s requirements. The process only takes place in green plants because of chlorophyll a and b in chloroplasts. It consists of two stages; light-dependent and light-independent. The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane in the presence of sunlight. The energy absorbed from the sunlight converts to NADPH and ATP molecules. The other part of the process is glucose production in the stroma without sunlight. It uses the energy from NADPH and ATP. This stage is also called the Calvin Cycle. The equation for the process is
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 (sugar) + 6O2
While plants use photosynthesis to manufacture sugar, algae convert solar energy into chemical energy. The process also utilizes light and liberates oxygen as a by-product.
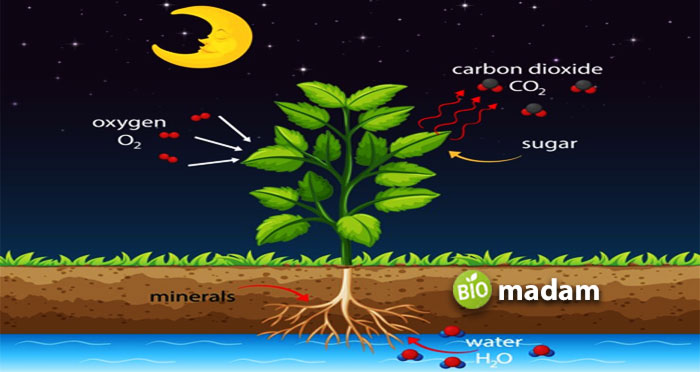
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration works conversely to fermentation and photosynthesis and breaks down glucose to produce energy for body functions. Organic substances break down to provide biochemical energy. Each glucose molecule liberates between 30 and 32 ATP molecules. Cellular respiration is vital for an organism as many functions cannot take place without usable energy.
Cellular respiration occurs in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. The site of cellular respiration in Prokaryotic cells in the cytoplasm. On the contrary, it takes place in cytosol and mitochondria in plant and animal cells. The process is divided into four fundamental stages in eukaryotes – glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration that produces two pyruvic acid molecules. It comprises ten steps and is also called the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway. The obtained energy is stored in ATP while NAD+ converts to NADH. This stage of the cycle holds significant importance as it gives the initial ATP molecules and facilities the process further.
Pyruvate Oxidation
The pyruvate molecules then move to mitochondria, transforming into the Acetyl coenzyme used in Krebs’ cycle. Sometimes you may see only three steps of Cellular Respiration in many places. Many researchers believe that it is not a distinct step of the process while others think otherwise.
Kreb’s Cycle
The third step of Cellular respiration is Kreb’s cycle. It is also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA (Tricarboxylic acid) cycle. Kreb’s cycle is a detailed process in itself with eight steps. Each of these steps uses eight specific enzymes to produce energy. FAD and NAD+ contribute majorly to the energy in the cycle, which later converts into ATP. One Kreb cycle produces three NAD+ molecules and one FAD molecule. These products are reduced to NADH and FADH2. Krebs’ cycle gives carbon dioxide as a by-product of respiration.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
It is the last step of the process in which each pair of hydrogen atoms from FADH2 and NADH provides an electron pair. They reduce oxygen atoms to produce water. The transport of electrons is also termed the electron transport chain. It enables a gradual reduction in the energy of the electrons. Every pair of electrons involved in the process gives three ATP molecules as the product. The chemical reaction of cellular respiration is
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Difference Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Definition
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process of manufacturing food in plants with the help of sunlight.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration refers to the breakdown of stored energy molecules to facilitate biological processes within the cell.
Chemical Equation
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is represented as CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Cellular Respiration
Whereas the chemical equation for cellular respiration is C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy
Occurrence
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in green plants, a large group of algae, and cyanobacteria.
Cellular Respiration
While cellular respiration takes place in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
Location
Photosynthesis
The location of occurrence is one of the most prominent differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The process of photosynthesis in plants takes place in chloroplasts.
Cellular Respiration
Conversely, it takes place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. In eukaryotes, for example, in plants, cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm and moves to mitochondria.
Time of Occurrence
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs only during the day as it requires sunlight to process.
Cellular respiration
Alternatively, cellular respiration happens throughout the day as it does not need sunlight.
Steps
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is primarily divided into two stages; light-dependent and light-independent processes.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration has four steps; glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, Kreb’s cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Type of Process
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is an anabolic process that utilizes energy to create products.
Cellular Respiration
On the other hand, cellular respiration is a catabolic process that liberates energy by the breakdown of the material.
Reactants
Photosynthesis
The reactants involved in photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
Cellular Respiration
Unlike, oxygen and glucose react to produce energy in cellular respiration.
Products
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis produces oxygen, water, and glucose as by-products.
Cellular Respiration
In contrast, the by-products of cellular respiration are water, ATPs, and carbon dioxide.
Coenzymes
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis uses NADP as the coenzyme.
Cellular Respiration
Conversely, cellular respiration uses FAD and NAD as coenzymes during the process.
Pigments
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis utilizes green pigments called chlorophyll present in chloroplasts.
Cellular Respiration
But, cellular respiration does not require any pigments.
Type of Reaction
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, unlike chemosynthesis and cellular respiration, is an endothermic process as it requires energy to manufacture food.
Cellular Respiration
However, cellular respiration is an exothermic process as it breaks down sugar to liberate energy.
Phosphorylation
Photosynthesis
Photophosphorylation takes place during photosynthesis.
Cellular Respiration
Whereas oxidative phosphorylation happens during cellular respiration.
Energy Conversion
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis utilizes light energy from the sun and converts it into potential energy.
Cellular Respiration
In comparison, cellular respiration converts potential energy into kinetic energy.
Carbohydrates
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis produces carbohydrates at the end of the process.
Cellular Respiration
Yet, cellular respiration utilizes carbohydrates during the process to liberate energy.
Dry Weight
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis adds to the dry weight of the organism.
Cellular Respiration
At the same time, cellular respiration reduces the dry weight of the organism as a result of energy breakdown.
The Bottom Line
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are important processes for the sustenance of life. Cellular respiration occurs in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. In contrast, photosynthesis occurs in green plants, algae, and a few bacteria. The main difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is their metabolic contribution. Photosynthesis uses energy to produce glucose. On the contrary, cellular respiration utilizes energy by breaking down molecules. While they are distinct in their mechanism and products, both are essential to life.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.