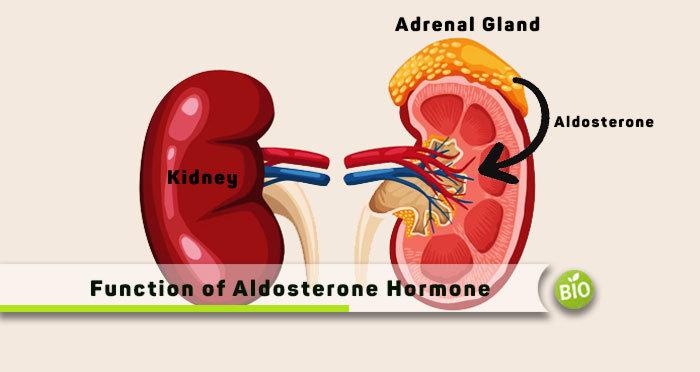
The endocrine and exocrine glands produce hormones that contribute to different bodily functions. Each contributes to a specific job, from the thyroid gland to the liver and the pancreas. For example, the thyroid hormone regulates metabolism, and an excess or deficiency may lead to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Similarly, aldosterone is a critical hormone essential for maintaining blood pressure. It regulates the uptake and elimination of salt and water. There are various other functions of the aldosterone hormone in the human body.
What is Aldosterone?
Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone secreted by the adrenal gland, which is an endocrine gland. The hormone travels through the bloodstream and contributes to the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Eventually, it plays a significant role in controlling water and electrolyte balance within the body. The electrolyte balance comprises potassium, sodium, and water content through the circulatory and excretory systems. A high aldosterone level can lead to fluid build-up in body tissues and elevated blood pressure.
Function of Aldosterone Hormone
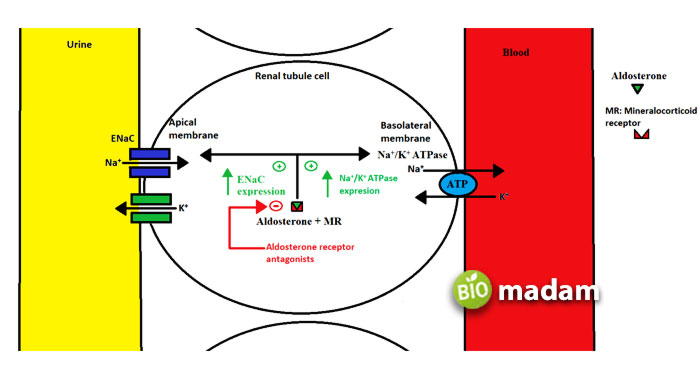
Aldosterone’s main function is to help regulate blood pressure by signalling the kidneys and colon to increase the potassium in your urine. It may also increase the amount of sodium in your bloodstream. Like ADH, aldosterone also increases blood volume due to water retention. Keep reading to learn the functions of aldosterone in detail.
Fibrosis
Studies have shown fibrosis and hypertrophy in perivascular and cardiac interstitial tissues by the aldosterone hormone. Hypertrophy may result from arteriovenous fistula and chronic anemia without fibrosis. Activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, or RAAS, leads to myocardial fibrosis in cardiac hypertrophy. Thus, a higher level of aldosterone in the bloodstream is believed to be related to myocardial fibrosis with cardiac hypertrophy besides angiotensin. The high aldosterone levels are also thought to contribute to synthesizing fibrous proteins like collagen.
Further studies showed that administering aldosterone could prevent cardiac fibrosis without directly affecting hypertension. Recent studies have also shown a relationship between cardiac left ventricular mass and increased aldosterone levels. Aldosterone transcribes collagen I mRNA due to increased type I and III with salt treatment and aldosterone.
Cerebrovascular Impact
Studies have shown the connection between aldosterone in vascular stroke and remodeling. Spironolactone has proved to help prevent cerebral infarction. It also reduces the size of cerebral infarcts. Moreover, mineralocorticoid treatment is seen to increase vascular expression receptors for epidermal growth factors. Thus, researchers mention that aldosterone increases vascular remodeling by boosting the vascular epidermal growth factor.
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Activity
Aldosterone is also seen to have a role in regulating plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). It enhances the effect of angiotensin 2 on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity. Spironolactone decreased sclerosis and the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 mRNA expression level in Radiation-induced glomerulosclerosis.
Vascular Modulation
Aldosterone regulates vascular tone by increasing vasoconstrictive effects of catecholamines. It results from decreased catecholamine uptake in the tissues and impaired vasodilation. Moreover, the uptake of angiotensin 2 and adrenergic receptors may also contribute to vascular tone modulation. It impacts the vascular smooth muscle cells through mineralocorticoid receptors leading to an intake of sodium. It also potentiates the incorporation of angiotensin 2-induced leucine into smooth muscle cells, causing hypertrophy.
How is Aldosterone Controlled?
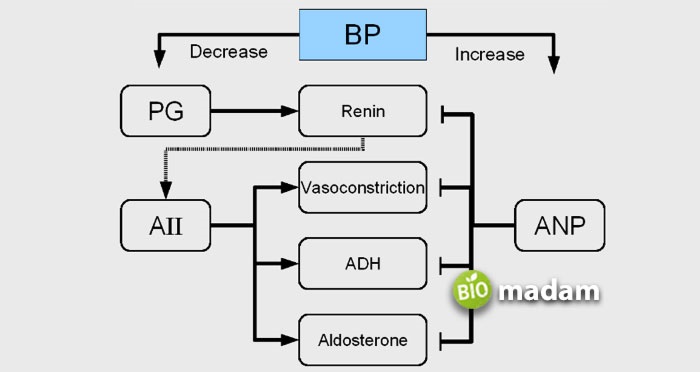
Aldosterone is a part of the RAAS (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system), which regulates the water and electrolyte content in the body. A decrease in blood pressure stimulates the activation of RAAS to signal the kidneys to increase it. Renin in the pathway contributes to the series of chemical reactions leading to angiotensin II production. It causes an increase in the production of water and salt reabsorption from the kidney. Thus, it elevates blood volume by restoring salt levels and blood pressure.
The Bottom Line
Hormones from different types of glands in the body perform various functions. Aldosterone is an important hormone that regulates the water and electrolyte balance to control blood pressure. It is also seen to have a prominent role in the nervous system and fibrosis in connection with myocardial hypertrophy. An increase or decrease in aldosterone levels can lead to serious health consequences.
FAQs
What happens when aldosterone increases?
The increase in aldosterone in the blood is known as hyperaldosteronism. It caused fluid retention and increased blood pressure. A high aldosterone level may also lead to paralysis or a cyst or tumor in the adrenal gland.
Is aldosterone a diuretic?
Aldosterone is a diuretic that stimulates the production and excretion of urine from the body. So, if you are taking it as a medication, you will observe an increase in your urinary output.
Does aldosterone increase potassium?
Aldosterone reduces potassium levels and leads to an increase in blood pressure. The potassium is excreted into the lumen while sodium is absorbed. The potassium and hydrogen ions exchange occurs in the late distal tube and collecting duct.
Is aldosterone used for hypertension?
Aldosterone leads to an increase in blood pressure. And thus, aldosterone antagonists are used to managing patients with resistant hypertension.
Does aldosterone increase blood sugar?
Aldosterone increases hepatic glucose production by inhibiting the effect of insulin. Even one dose of aldosterone has been seen to increase fasting blood sugar in clinical trials.
What hormone is renin?
Renin is not a hormone but a type of enzyme. It is produced in the kidneys and contributes to aldosterone production as a part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. The production of aldosterone contributes to blood pressure management.
Does salt increase aldosterone?
Studies show that high salt intake impacts aldosterone production, which may cause malignant hypertension. It also increases the expression of AT1R mRNA in the cardiovascular tissue in salt-loaded SHRSP.
What are the 3 stress hormones?
Cortisol is the main stress hormone in the body. Vasopressin and catecholamines including norepinephrine and adrenaline are also stress hormones in their capacity.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.