Kidneys are essential components of the body’s anatomy and physiology in getting rid of waste materials from the body. A healthy human has a pair of kidneys that work together to remove wastes through urine. However, a disease or condition may lead to the failure or removal of one of the kidneys. But, the good news is that humans can survive with one kidney. Let’s tell you about the structure and functions of the kidney in detail.
What are Kidneys?
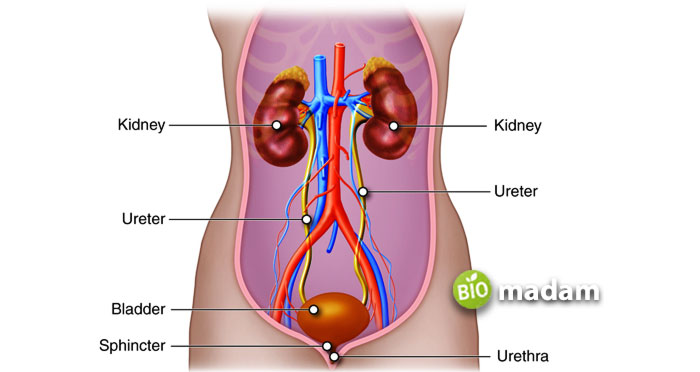
Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, one on each side of your spine, just below the rib cage. Each kidney is 10 to 15 centimeters long and weighs around 160 grams. They eliminate one to one and a half liters of urine per day. Despite removing only one liter, the kidneys filter about 200 liters of fluid daily.
The urine travels to the urinary bladder from the kidneys through two thin muscular tubes called ureters. One ureter emerges from each kidney and travels to the urinary bladder that stores urine until elimination. Thus, your kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder are the urinary system organs, comprising of essential tissues for proper functioning.
Functions of Kidneys
The main function of the kidney is to filter blood and form urine to ensure all toxins get out of your body. Nephrons, the building blocks of kidneys, perform this function. The nephrons filter the blood through their network of tiny blood vessels called the glomerulus. The filtered fluid passes via tubules to process it further and produce urine. The body can store urine between 1 to 8 hours before excretion. Further functions of the kidneys include:
Controlling Acid-Base Balance
The kidneys play a major role in controlling acid-base balance within the body. The pH of the bodily fluids such as blood, plasma, and urine depicts the acid balance. When the blood enters the kidneys to remove wastes, the kidneys remove acids and bases from the blood if they are in excess. Alternatively, they allow these molecules to reabsorb if the blood lacks them. Thus, urine formation also ensures that your body has all important acids and bases in adequate amounts.
Controlling Water Balance
You might have noticed that sometimes your urine is concentrated while other times it is comparatively diluted. This minor yet critical detail is also attributed to kidneys. Kidneys control the volume of urine produced while preventing dehydration. If you are dehydrated, your body will produce concentrated urine to avoid losing more water. On the other hand, you will have a higher urinary output when you drink more water. It is recommended to consume 3-4 liters of water daily, for men and women.
Maintaining Electrolyte Balance
The kidneys help manage the electrolyte balance within the body the same way it regulates acid-base balance. If your body lacks particular ions, the kidneys will stop them from passing through the filtration process. The main electrolytes managed by the kidneys include sodium and potassium.
For example, when you take excess salt (sodium chloride) in your diet, the blood becomes overloaded with sodium, and you feel like drinking more water. When you drink more water, more urine is produced, and your body pushes out the sodium in the urine. Similarly, if you intake high amounts of potassium, your urine will have a high potassium concentration.
Removing Toxins and Waste Products
Removing waste products and toxins from the body is the main function of the kidneys – why urine is produced!
The kidneys filter the water-soluble toxins and waste products to remove them from the body. The most common waste products secreted in the urine include creatinine and urea, along with others. When removing wastes, the kidneys send back hormones, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals into the bloodstream if needed.
Malfunction in the kidneys affects their ability to remove waste, and your organs may get intoxicated with unwanted waste products.
Controlling Blood Pressure
The kidneys also contribute to controlling blood pressure by producing renin which is a part of the RAAS (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System). Renin facilitates the production of angiotensin I from angiotensinogen that converts into angiotensin II in the capillaries of right and left lungs. Angiotensin II constricts blood vessels to increase blood pressure.
Meanwhile, urine formation acts as an outlet to remove electrolytes from the body and lower blood pressure when it is too high.
Erythropoietin Production
Kidneys act as both endocrine and exocrine glands in different roles. Like all types of glands, kidneys also secrete hormones that help in different bodily functions. Kidneys produce erythropoietin which signals the production of red blood cells that transport oxygen to bodily organs.
Vitamin D Activation
The kidneys convert calcifediol into calcitriol (active Vitamin D). Calcitriol is vital in regulating phosphate and calcium in the body and facilitates healthy bone development by the action of osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
Learning the Functions of Kidneys
Remembering so many functions of Kidneys can be challenging, but you do not have to worry anymore. If you notice, all the words in italic in the functions of kidneys form “A WET BED.” So, you can easily recall all the functions by remembering this simple mnemonic.
The Bottom Line
Kidneys are critical organs in the body, present deep in the abdomen, one on each side of the spinal cord. They are widely known for their role in urine production to eliminate toxins from the blood. The kidneys control the urine concentration according to the acids, bases, potassium, sodium, and other molecules and compounds in the body. Thus, they regulate acid-base and electrolyte balance besides controlling blood pressure. The kidneys also contribute to vitamin D activation and erythropoietin production.
FAQs
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
Nephrons are the structural and functional units of kidneys. They contain a vascular network of capillaries called the glomerulus. They also have a coiled renal tubule comprising different regions within the tubule that perform specific functions.
Why do we have 2 kidneys?
The human body is designed in an amazing way. Many people donate their kidneys to their relatives to save their lives in case of kidney failure. Having two kidneys allows you to save lives without sacrificing yours. An extra kidney also ensures you do not die if one of your kidneys gets damaged.
Can you pee without kidneys?
The kidneys are the center of urine production, and you cannot pee without your kidneys. If you do not have both kidneys, you will not produce urine. That is why people with renal failure go through dialysis to remove toxins from the body artificially.
What are the three main waste products in urine?
The urine comprises everything your body does not need and may become toxic. The glomerulus filters large molecules, and the renal tubules remove harmful materials. The three main nitrogenous wastes in urine include creatinine, urea, and uric acid.
How many nephrons are in each kidney?
Each kidney contains around one million nephrons made of various other structures. When blood passes through the kidneys, a million nephrons filter hundreds of liters of blood.
Can a kidney grow again?
Like many other organs in the human body, kidneys cannot grow again as they lack the ability to regenerate. This is because kidneys have a low basal cellular regenerative potential to grow again after injury.
What is the normal urine color?
Normally urine is either clear or has a pale hue. Sometimes, you may have colored urine due to medicines or food. The presence of red droplets in the urine may indicate blood which must be addressed immediately.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.