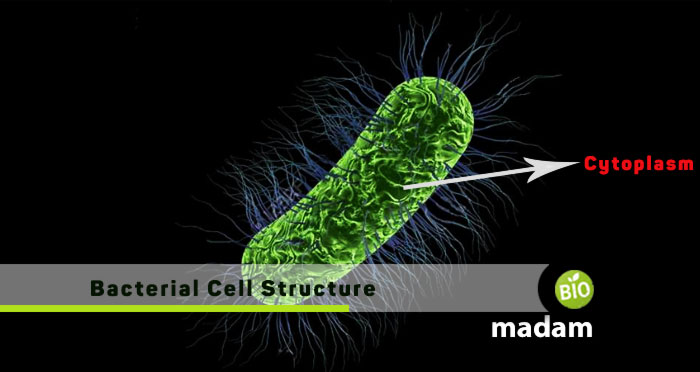
Bacteria, be it eubacteria or archaebacteria, are microscopic organisms invisible to the naked eye. Despite their small size, they have various organelles like other cells that perform specific functions. However, prokaryotic cells have fewer organelles than eukaryotic cells. The organelles in bacterial cells perform unique processes. Thus, the function of cytoplasm in prokaryotic cells also varies from eukaryotic cells.
Keep reading to learn everything about the function of cytoplasm in bacterial cells.
Bacterial Cytoplasm
Like other cells, bacterial cytoplasm is also a site for containing all the organelles. In a bacterial cell, cytoplasm refers to everything within the plasma membrane. It comprises different enzymes, amino acids, and inorganic ions. The bacterial cytoplasm also contains carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, RNA, and DNA. The watery part of the bacterial cytoplasm is called the cytosol; 80% of the total cytoplasm is water.
Cytoplasmic Organelles in Bacteria
The bacterial cytoplasm contains organelles that contribute to unique functions within the bacterial body. Some of the significant cytoplasmic organelles include:
- The nucleoid
- Ribosomes
- Plasmids
- Photosynthetic organelles
- Cytoplasmic inclusion granules
Functions of Cytoplasm in Bacterial Cell
Metabolism
The cytoplasm is the site of metabolism within the bacteria. Bacteria secrete enzymes to hydrolyze macromolecules for transportation across the plasma membrane. These reactions include catabolic and anabolic reactions collectively. The catabolic reactions help in the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones that further contribute to the formation of other molecules; the synthesis of new molecules takes place through anabolic reactions.
Cytoskeleton Formation
Bacterial cytoplasm contains various structural filaments that make up the cytoskeleton. These cytoskeletal filaments are critical to the shape formation and determination of bacteria. They also play a major role in bacterial cell division by binary fission.
Protein Synthesis
Cytoplasm also serves as a protein synthesis location as it contains ribosomes. Prokaryotic ribosomes are 60S comprising 50S and 30S subunits. They receive and decide on genetic instructions to produce unique proteins.
The Bottom Line
Bacteria are among the smallest organisms and are invisible to the naked eye. You can observe them under compound or electron microscopes to study their structure in detail. Microscopic examination of the bacterial cell shows it contains numerous organelles in its cytoplasm, including plasmids, nucleoids, and ribosomes. It is 80% water combined with various molecules such as DNA, RNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. The function of cytoplasm in bacterial cells is to provide a particular shape to the cell besides the cell wall. It also acts as the site for catabolic and anabolic reactions within the cell, including protein synthesis.
FAQs
Where is the cytoplasm in bacteria?
Everything within the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane is the cytoplasm. It comprises nutritional molecules and genetic information for the cell’s proper functioning. The bacterial cell cytoplasm is majorly water with some proteins, enzymes, and low-weight molecules.
Which process occurs in the cytoplasm of bacteria?
The bacterial cytoplasm is the site for all cellular processes within the cell. It contains enzymes that break down macromolecules. The smaller components are then used to manufacture other compounds required for bacterial survival. Thus, all kinds of cellular anabolic and catabolic processes occur within the cytoplasm.
Why do bacteria undergo respiration in the cytoplasm?
Cellular respiration is an important cellular process in bacteria to generate energy for other functions. Bacteria may use oxygen to perform respiration depending if they are aerobic or anaerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria respire with the help of oxygen, while anaerobic bacteria do not use oxygen.
Does bacterial transcription occur in the cytoplasm?
Bacteria do not possess a proper nucleus like in various types of eukaryotic cells, and thus all processes, including genetic division, occur within the cytoplasm. Its ribosomes in the cytoplasm are responsible for protein synthesis. Translation and transcription both take place in the cytoplasm of the bacteria. Bacterial ribosomes start the translation process of the mRNA before it transcribes completely.
What is the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol in bacteria?
Cytosol and cytoplasm are entirely different components of a cell. All liquid and solid substances within the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane make up the cytoplasm, whereas the cytosol is the fluid part of the cell components. Besides the cytosol, the cytoplasm also contains carbs, proteins, fats, inorganic molecules, DNA/RNA, and other lightweight molecules.

Hi, my name is Eva. I am currently practicing as a clinical social worker, that being my childhood desire. As a licensed therapist holding MPhil in Clinical Psychology, I am now on biomadam to provide the natives with the best family advice! Do you have any questions? See you in the comment section.