Recently updated on October 4th, 2023 at 06:26 am
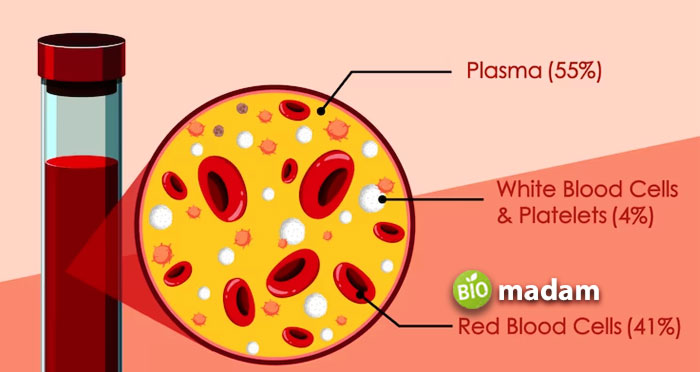
The human body consists of organs and organ systems. These organs carry out their functions through tissues to keep us alive. The human body comprises various substances to create these complex systems, where blood plays a major role. Blood consists of plasma, platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells. This blood flows throughout the body to provide oxygen. There are two systems regulating the flow of blood and other body fluids.
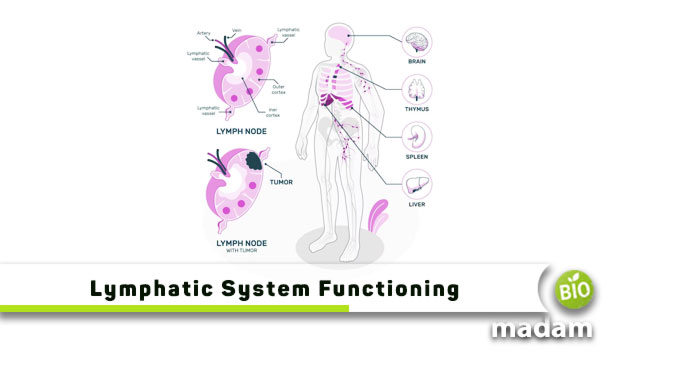
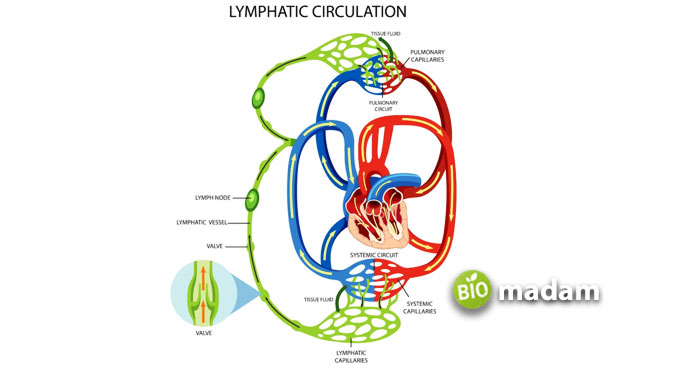
The circulatory system and lymphatic system regulate the blood flow throughout the body. The lymphatic system includes lymphatic vessels, bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. In this article, we will explore what bone marrow is and what are its functions in the lymphatic system.
What is Lymphatic System?
The lymphatic system is part of the immune system. It is complementary to the circulatory system. Both systems work together to regulate the blood flow in the body. The lymphatic system ensures optimal functioning of the immune responses. The lymphatic system consists of:
- Bone Marrow
- Thymus
- Lymph Vessels
- Lymph nodes
- Spleen
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
What is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow is the spongy and gelatinous substance found in the center of the bones. Blood cells that make up the blood are made inside this spongy bone marrow. The process of cell production is known as hematopoiesis. Blood cells first exist as stem cells which further mature to form blood cells. all types of blood cells including platelets, white blood cells, and red blood cells are formed within the bone marrow. Blood flows through the bone marrow, and takes these mature blood cells to flow them throughout the body.
Types of Bone Marrow
There are two types of bone marrow:
- Red Bone Marrow: Produces white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
- Yellow Bone Marrow: Produces fats, cartilage, and bones.
Function of Bone Marrow in the Lymphatic System
The following are the most important functions of bone marrow:
Delivering Oxygen and Nutrients
Red blood cells formed inside the red bone marrow are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients throughout the body tissues. They are able to carry oxygen due to the presence of a protein called hemoglobin present within them. Red blood cells also transport carbon dioxide from the rest of the body to the lungs.
Formation of Blood Cells (Hematopoiesis)
The main function of the bone marrow is hematopoiesis besides playing a primary role in the immune system. This term refers to the formation of blood cells. Red bone marrow is responsible for the production of stem cells that eventually mature to form blood cells. Three types of blood cells are formed within the bone marrow, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The functions of these cells indirectly become the functions of the bone marrow.
Preventing Infections
White blood cells are also formed within the red bone marrow. They actively play a role in fighting against viruses, bacteria, and other parasites present in the blood. They are also called immune cells, regulating the immune response of the body. Thus, bone marrow plays a role in preventing infections.
Controls Bleeding
The third type of cells formed within the red bone marrow are platelets. They are involved in stopping or preventing the bleeding. If an injury occurs, they actively move towards the wounded area to stop the bleeding by forming clot over the injured site.
Development of Bones and Cartilage
The yellow bone marrow is involved in the storage of fats in the adipocytes. It also contains mesenchymal stem cells that are involved in developing bones and cartilage.
Prevents Damage Caused by a Disease
Bone marrow regenerates itself to fight cancer. In the case of a genetic disease, bone marrow plays a role to prevent further damage from happening due to that genetic disease. Bone marrow can restore its function after damage has been caused by a certain treatment such as chemotherapy.
Final Takeaway
Our bodies are complex systems with intricate pathways. Blood and fluid flow through these pathways, and reach every part of our body. The circulatory system regulates the blood flow in the body, and the lymphatic system is complementary to the circulatory system. The lymphatic system is made of bone marrow, lymph vessels, lymph nodes, etc. It is a spongy substance found in the middle portion of the bone. The two types of bone marrow are responsible for hematopoiesis and absorbing and storing fat to form bones and cartilage.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.