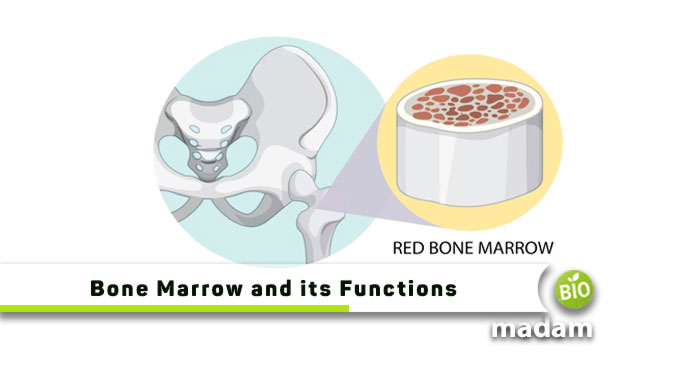
Bone marrow, widely known as the body’s blood-producing factory, is a critical element of human anatomy and physiology. The primary function of the bone marrow in the body is the production of cells that contribute to immunity and other bodily systems. Keep reading to learn the types of bone marrow and their functions.
What is the Bone Marrow?
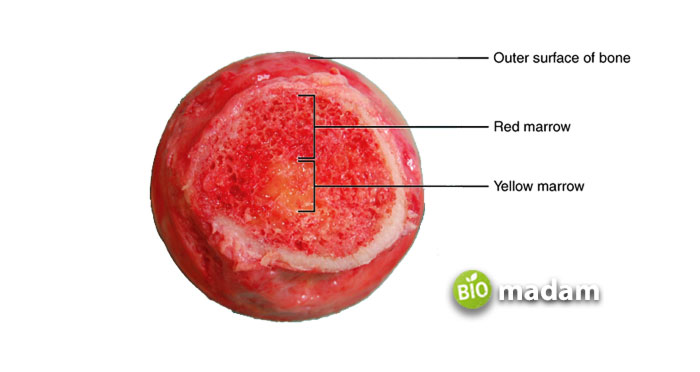
Bone marrow is a fatty tissue in bone cavities that produces red and white blood cells. It is one of the three bone components besides compact and spongy bones. Spongy bone forms the ends of the bones, while the compact bone is the stronger outer layer. Meanwhile, bone marrow is present in the center of bones and on the tips of spongy bones. Bones contain blood vessels and bone marrow, where they store stem cells and fat to produce blood. The fat cells are used as an energy reserve per need. The bone marrow also contributes to the production of platelets.
Types of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow in the human body has two types: red and yellow. Both these kinds of bone marrow perform particular functions and weigh around 2.5 kg.
Red Bone Marrow
The red bone marrow has stem cells that produce red blood cells, giving it its characteristic red color. It also contributes to the production of white blood cells and platelets, playing a critical role in the formation of blood and plasma. All of your bone marrow is basically red bone marrow until the age of seven.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Opposed to red bone marrow, the yellow bone marrow does not give rise to red or white blood cells. Instead, the two types of stem cells in the bone marrow (mesenchymal stem cells and adipocytes) store fat. This preserved fat is used to produce the energy required to develop bones, cartilage, fat cells, and muscles. The yellow bone marrow functions to replace the red bone marrow as you grow.
The Function of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow has a central role in birds and mammals by producing blood cells and taking part in the lymphatic system. Let us discuss these functions in detail below:
Immune Cells Production
Bone marrow helps produce cells of the immune system, including the B and T cells. These main types of lymphocytes are responsible for fighting antigens and pathogens to protect your body from several diseases. Once the bone marrow produces them, they migrate to the target sites. Lymphoid cells also develop in the bone marrow. They move to the thymus to mature into T cells. The B cells mature and contribute to producing antibodies that act on specific antigens. Later, they move toward the peripheral lymphoid tissues. The multipotential stem cells form the lymphoid cells.
Platelet Formation
The function of red bone marrow in the body is the production of platelets essential for the blood clotting process. It prevents excessive loss of blood in case of cuts and injuries.
Fat Storage
The yellow bone marrow performs the function of storing fat. The stored fat is later used as a source of energy per need.
Bone Marrow Pathologies
The role of bone marrow is critical to normal body functioning, and any changes may lead to diseases and disorders. The pathologies due to improper functioning of the bone marrow include:
Anemia
Anemia refers to an insufficient amount of red blood cells in your body. A malfunctioning bone marrow stops the production of red blood cells, leading to aplastic anemia.
Leukemia
Leukemia arises from the abnormal production of white blood cells, altering the normal form and function of the blood.
Myeloproliferative Disorder
Some of the myeloproliferative disorders include primary myelofibrosis, chronic myelogenous leukemia, essential thrombocytopenia, polycythemia vera, and chronic eosinophilic leukemia. They impact the production of blood cells and platelets in the body.
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that results from malignancies in the lymphocytes. It eventually affects the immune system.
Keeping the Bone Marrow Healthy
You can keep your bone marrow in good health by taking care of it, as it is the base of all the functions in your body. We would not be able to survive if there was no blood. So, how can you keep your bone marrow healthy for a healthy life?
- Maintain your vitamin and mineral levels to ensure the proper production of blood cells. Doctors emphasize the intake of iron, B9, and B12 particularly.
- Take a protein-rich diet to promote the production of healthy bone marrow cells. You can obtain different types of proteins from beans, lean meat, nuts, eggs, and milk.
- Ensure proper treatment of diseases that may lead to bone marrow abnormalities.
- Avoid the causes of cancer, such as smoking, genetic disorders, and carcinogenic chemicals, to prevent leukemia.
The Bottom Line
The bone marrow is the cell-producing factory of the body. There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow, which produce blood cells and store fats for energy production. The red bone marrow forms red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. However, the function of the bone marrow is not limited to cell production only. The yellow bone marrow is involved in the storage of fats. The fats are processed and used as an energy source when needed.
FAQs
Can you live without bone marrow?
Bone marrow is a primary lymphoid organ in your body involved in producing all blood components. White blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets are critical to keeping your body healthy. They fight bacterial and viral infections, carry oxygen, and prevent blood loss. Thus, you cannot live without bone marrow.
Can I donate bone marrow?
A bone marrow transplant helps maintain a healthy life when one’s bone marrow does not work properly. You can donate healthy bone marrow cells to treat people with blood cancers such as leukemia.
What does bone marrow look like?
The bone marrow comprises soft, spongy tissues with a texture similar to a jam or jelly. The red and yellow bone marrow fills the cavities of your bone and produces blood cells.
What are common symptoms of bone marrow conditions?
Your physician may recommend you get some tests done to evaluate bone marrow conditions on presenting specific signs and symptoms. Common symptoms of bone marrow issues may include frequent infections, frequent bleeding, fatigue, bruising, and muscle weakness.
What protein is found in bone marrow?
The bone marrow and all connective tissues are rich in the fibrous protein collagen. It has a unique amino acid profile that helps give the bone marrow a specific structure while keeping it pliable.
What is hematopoietic marrow?
A hematopoietic bone marrow refers to an immature stem cell that develops into various types of cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Where is red bone marrow found in adults?
The red bone marrow is present in the flat bones, including the skull, hip bone, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum. Other locations include spongy or cancellous bones such as the humerus, tibia, and femur.
What is myeloid?
Myeloid refers to anything related to or resembling the bone marrow. It may also include certain types of hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.