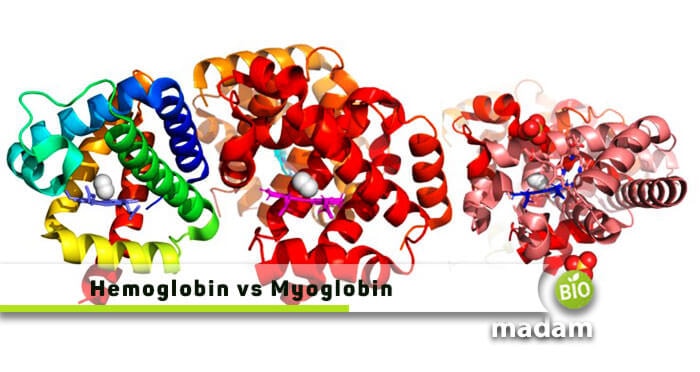
The human body comprises millions of different elements and essential structures, including globular and fibrous proteins. Do you want to know the difference between hemoglobin and myoglobin? Both of these are the necessary globin proteins that help in binding and transferring oxygen inside a body. Most vertebrates and a few invertebrates acquire hemoglobin and myoglobin to enhance the amount of oxygen transported in them.
Hemoglobin is chiefly present in erythrocytes, where it helps transport oxygen from one part to another in the human body. It is hetero-tetrameric molecule. On the other side, myoglobin is the muscle protein that supports storing oxygen in muscle tissues and is monomeric.
We will discuss more differences between the two later on that will directly link them with their various functioning. Before that, let’s have a look at the brief comparison table between hemoglobin and myoglobin.
Comparison Table
| Basis of Comparison | Hemoglobin | Myoglobin |
| Structure | This globular protein exhibits a quaternary structure. | This globular protein exhibits a tertiary structure. |
| Polypeptide Chains | Four chains (2 alpha & 2 beta) | Single chain |
| Function | Carries oxygen from the lungs to transfer it to the body. | Stores oxygen in muscles to be utilized as energy. |
| Binding Ability | Can bind with O2, CO, CO2, H+, and NO. | Can only bind with O2 |
| Formation of Curve | Sigmoidal shape | Hyperbolic shape |
| Molecular Weight | 64.5 kDa | 16.7 kDa |
| Occurs As | Hetero-tetrameric subunit | Monomeric subunit |
| Occurrence in Bloodstream | Higher concentration | Lower concentration |
Explain Hemoglobin
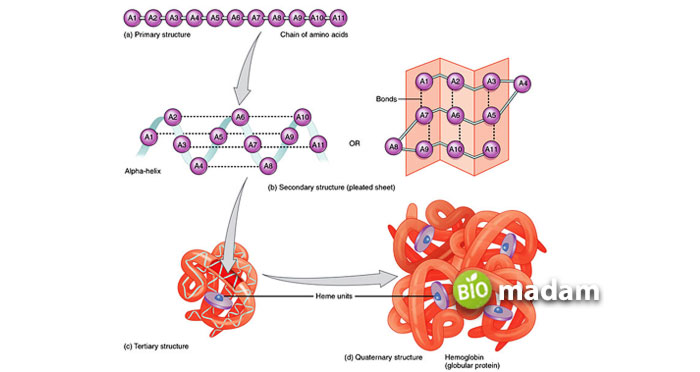
A globin protein, hemoglobin, is a naturally occurring molecule in the body often present in red blood cells. Its primary function is to transport oxygen from both lungs to other parts of the body. Similarly, it helps in returning carbon dioxide to the lungs. The molecule includes two primary portions, a heme part, and a globin part. Heme is the iron structure bound to four pyrrole rings, while globin is the central protein part, containing two alpha and two beta chains. The pyrrole rings in the heme group are attached to ferric ions through methylene bridges.
There is a unique porphyrin structure present in the globulin chain of hemoglobin, having to iron. The constituents of globulin rely on what type of hemoglobin it is. So, besides alpha structures (essential part), the other two can be beta chains, delta chains, or gamma chains. Hemoglobin usually contains two alpha and beta units with 144 amino acids in the former and 146 in the latter.
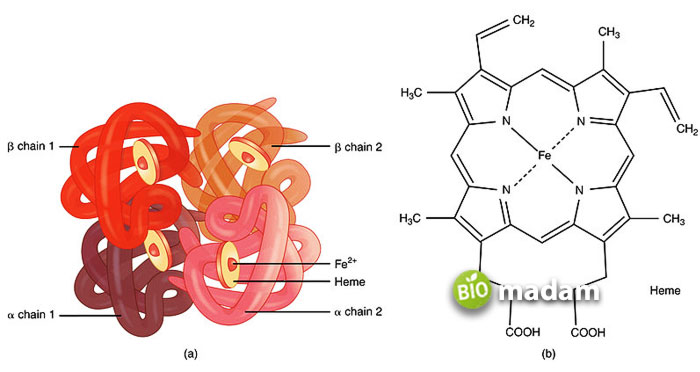
The binding capacity of oxygen with hemoglobin is lesser as compared to carbon monoxide. So whenever an oxygen molecule bonds with a hemoglobin subunit, it is convenient for other molecules to attack that protein. A human body has a Hb value, which can change with a person’s gender and age. When the RBC level falls with the decrease in hemoglobin, it causes a condition called anemia. The fall in RBCs can even lead to chronic diseases besides these mild conditions.
Explain Myoglobin
A comparatively small monomeric protein, myoglobin, is found in the skeletal muscles of all vertebrates. It functions as the storage unit for oxygen in muscle tissues and renders it a characteristic red color. Whatever oxygen enters the muscle tissues, myoglobin entraps it to produce energy and perform muscle contraction. Organisms having higher concentrations of myoglobin can control their breath for a long time as this macromolecule is the stash house for oxygen.
For example, marine animals like seals and whales have more muscles with enough myoglobin to survive in the water. As it is a protein, it contains similar heme as hemoglobin. The heme part of myoglobin consists of iron, responsible for the red/brown color of the protein.
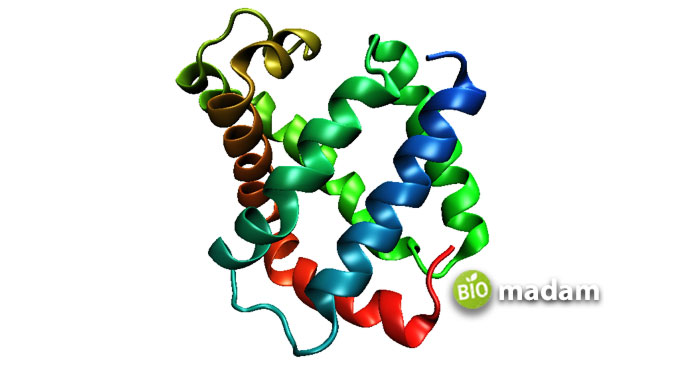
Myoglobin stands with its secondary structure, containing a linear amino acid chain. It comes with 154 amino acids of alpha-helical chains, being a monomeric unit. Myoglobin is further stabilized by the addition of hydrogen bonds.
Whenever a person’s skeletal muscles face injury (due to any issue), myoglobin starts functioning by releasing itself into the blood. It helps to provide stored oxygen, where one can observe the elevated levels of myoglobin in the blood right after a few hours. Thus, an injured person can fulfill their oxygen shortage through sufficient myoglobin in his body.
Grab the Similarities Between Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
- Both of these molecules have a prosthetic group called “heme.”
- Either hemoglobin or myoglobin, both serve as oxygen-binding macromolecules (proteins).
- They are accountable for the red color in their respective areas.
Find Out the Differences Between Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
Brief Denotation
Hemoglobin
This globular protein is present in red blood cells and works as an oxygen-binding molecule in the blood.
Myoglobin
This protein is specifically present in muscle tissues of almost all vertebrates and works as an oxygen-binding molecule.
Abbreviation & Molecular Weight
Hemoglobin
We usually write hemoglobin as Hb, which has a 64.5 kDa molecular weight.
Myoglobin
We usually write myoglobin as Mb, which has a 16.7 kDa molecular weight.
Occurrence
Hemoglobin
This molecule is present specifically in RBCs, so ultimately, hemoglobin occurs all around the body.
Myoglobin
This organic molecule is present in the muscle and heart tissues of almost all vertebrates.
Structure
Hemoglobin
It usually shows a quaternary structure.
Myoglobin
It usually represents the tertiary structure.
Number of Polypeptide Chains
Hemoglobin
It is a tetrameric molecule with four polypeptide chains named alpha, beta, delta, and gamma. The sequence of these chains depends on the type of globular protein.
Myoglobin
It is a monomeric organic molecule, and thus contains one polypeptide chain with 154 amino acids.
Activity with Oxygen Molecule
Hemoglobin
Hb binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to various other parts of the body.
Myoglobin
It is the storehouse for oxygen in muscle tissues. Myoglobin releases the stored oxygen in the tissues whenever necessary to fulfill energy requirements.
Types of Organic Macromolecules in Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
Hemoglobin
There are different types of this molecule, such as Hemoglobin A, Hemoglobin F, and Hemoglobin A2.
Myoglobin
This monomeric subunit has a single kind that is used in all skeletal muscles.
Curve Formed in the Molecule’s Saturated Condition
Hemoglobin
It forms an oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, exhibiting a sigmoid curve shape.
Myoglobin
It has more affinity to bind oxygen than hemoglobin, so it saturates earlier, forming a hyperbolic curve.
Oxygen-Binding Affinity
Hemoglobin
It has decreased affinity to bind with oxygen molecules.
Myoglobin
This molecule survives by having a higher oxygen-binding affinity.
Effect of CO2 and Ph. on Oxygen Binding
Hemoglobin
Carbon dioxide binds more quickly to hemoglobin than oxygen. Furthermore, CO2 and Ph. are inversely related to each other, so an increase in CO2 decreases the Ph. of blood and ultimately affects hemoglobin in RBCs.
Myoglobin
There is no significant effect of CO2 and Ph. on myoglobin.
Presence in Bloodstream
Hemoglobin
One can test hemoglobin that’s present all the time in the bloodstream
Myoglobin
Myoglobin is released into the bloodstream to satisfy oxygen needs only after an injury.
Bottom Line
After fetching the differences between hemoglobin and myoglobin, you should have learned the significance of both biological terms. Hemoglobin is vital for transporting oxygen throughout the body, while myoglobin is responsible for saving oxygen in muscle tissues. Both organic molecules relate to oxygen binding in one way or another. It’s just that hemoglobin exhibits a higher capacity for binding to oxygen than myoglobin. Overall, it’s a vast topic to be understood clearly, and we did our best to provide you with every detail of both these globular proteins.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.