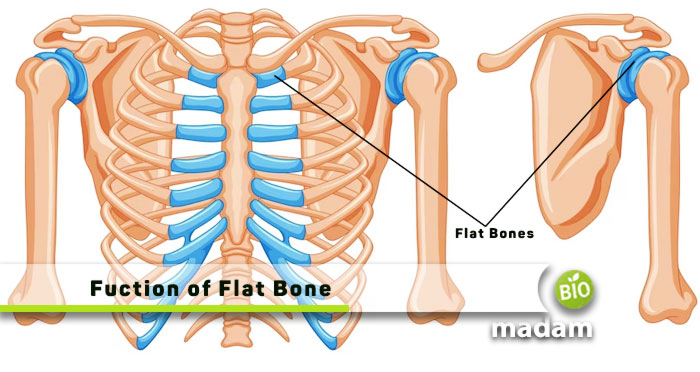
The musculoskeletal system is an important element of the human anatomy and comprises various types of bones. Bones provide a structure to the body and facilitate movement. Flat bones are one of the many types of bones in the body that contribute to different functions within the body. Flat bones are present in many parts of the skeleton, including the ribs, skull, pelvis, etc. Let’s delve into the function of flat bones and learn about their locations in the body.
What is a Flat Bone?
As the name suggests, flat bones are flat compared to other bones in the body, such as those in the legs and arms. Flat bones are more in length and width than thickness. They develop from a thin layer of spongy bone tissue containing the bone marrow, not a bone marrow cavity. The spongy layer has two sheets on the outer layer on each side of the compact or cortical bone tissue.
Functions of Flat Bones
Flat bones are found in various body regions, which we will discuss further in the article. They perform multiple functions, including:
Protection
The flat bones in the body protect sensitive body parts. The most prominent function of these bones includes protecting the brain from the external environment.
Strength
Another important role of the flat bone in the body is providing strength to the structures and enabling motility to the areas they are a part of.
Attachment
The flat bones also act as a space for attachment for large muscle groups. The muscles attach to the bones through tendons and ligaments help in holding two bones together.
Hematopoiesis
Flat bones, like other bones, are a site of hematopoiesis that refers to the production of blood cells. These cells include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Mineral Storage
These bones also act as a space for mineral storage, including calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and sodium. The minerals are essential for body functioning as they contribute to physiological mechanisms.
Where are Flat Bones Found in the Body?
Now that you know the functions of flat bones, studying their locations in the body will make it easier to understand the functions in relation to anatomical positioning.
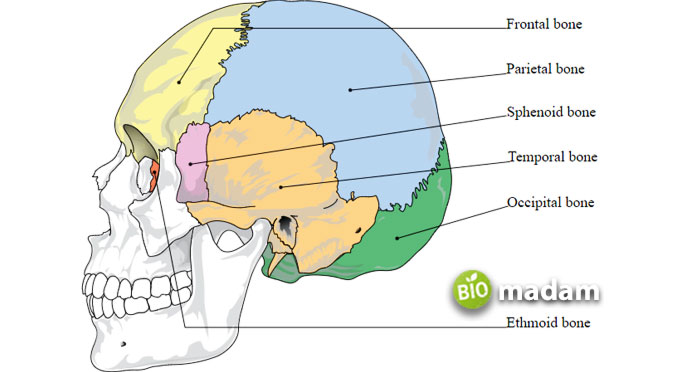
Skull
The bones of the skull are the most fundamental example of flat bones. While they are not exactly flat and are slightly curved, they have a flat shape. The skull also contains other types of bones except for flat bones. The flat bones in the skull include:
Parietal Bone: The parietal bones are present on either side of the skull and form the top as well.
Frontal Bone: As the name indicates, this bone forms the front of the skull, including the upper portion of eye sockets and the forehead.
Occipital Bone: This bone comprises the back of the skull and provides space for the spinal cord to connect to your brain.
Lacrimal Bone: The lacrimal bones are present in the eye socket.
Vomer Bone: The vomer bone forms the space between the nostrils, also known as the nasal septum.
Nasal Bone: Two nasal bones form the bridge of your nose and give it a definite appearance.
Ribs
Another structure in the body containing the flat bones is the rib cage. Opposed to common perception, the ribcage bones, forming the ribs, are also flat. Humans have twelve ribs or flat bones on either side that protect their internal organs.
Sternum
The sternum is present close to the ribs and is pivotal in protecting both lungs and the heart. It is made of flat bones and found in the middle of the chest.
Scapula
The scapula, or the shoulder bone, is also a flat bone that connects with the humerus and collarbone to form the shoulder joint. Humans have two triangle-shaped scapulae in the upper back to enable arm movement.
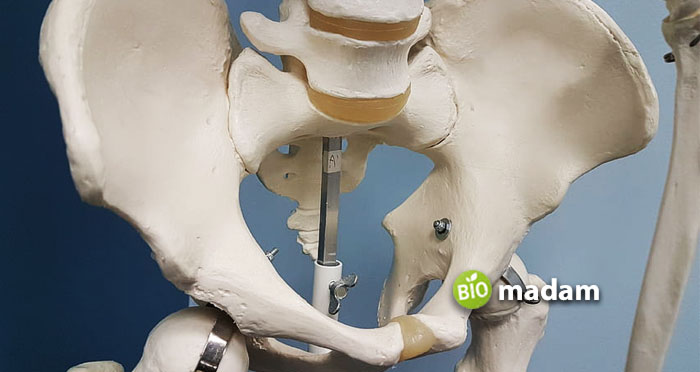
Pelvis
The coxal bone in the pelvis is also a large, flat bone comprising three bones: Ilium, Pubis, and Ischium. Ilium is present near the top of the pelvis and is the widest bone. At the same time, the pubis is at the back, while ischium forms the bottom of the pelvis.
The Bottom Line
Flat bones are one of the three types of bones in the body that contribute to structure, protection, and movement. They are present in the skull, pelvis, shoulder region, and ribs. The main function of flat bones in the skull is to protect the brain from the external environment and damage. At the same time, they provide the location for the attachment of large muscles and enable movement in joints.
FAQs
Do flat bones allow movement?
Flat bones are integral to the movement as they allow ligaments and tendons to attach and connect other bones and muscles.
Are flat bones strong?
Flat bones provide strength and structure to different parts of the body. The skull is also made of flat bones that protect the brain from the external environment and damage.
Is femur a flat bone?
The femur is not a flat bone because of its shape. Instead, it is a long bone that provides support and mobility to the legs.
What is the function of flat bones in sport?
It is important to keep your bones and joints healthy as athletes. Flat bones allow movement and flexibility while ensuring protection.
What is flat vs short bone?
Flat bones are flat in shape due to the difference in width and thickness. On the other hand, the short bones have almost equal length, width, and height.
How do flat bones grow?
The formation of flat bones of the skull takes place through intramembranous ossification that facilitates the proliferation of neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells that condense into compact nodules.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.