Recently updated on March 2nd, 2023 at 06:31 am
Genes and alleles are important terms for studying gene expression and biological studies of animals and plants. You may know that genes are the hereditary material of an organism that determines its physical and mental characteristics, but what are alleles?
Alleles can be simply defined as variants of genes that exhibit different forms of the same characteristic. The difference between gene and allele is not at two extremes, but it is critical to understand that both are not entirely the same. Let’s talk about genes and alleles in detail.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Gene | Allele |
| Definition | Hereditary units | Gene variant |
| Determinant | Genotype | Phenotype |
| Types | Alleles | Dominant/recessive |
| Examples | Hair length, height, plant color, etc | IA, IB, and recessive i |
What are Genes?
Genes are known as the molecular unit of hereditary and contain all information on a chromosome (composed of DNA and protein), about the traits and characteristics of that organism. Genes are made of amino acid sequences that encode a particular trait. Each chromosome has multiple genes that have the gene sequence in the form of RNA that is translated into proteins. The genes and genotype depend on the type of organism.
What is a Genotype?
Genotype refers to the set of all genes present in an organism that carry different characteristics. There are around 20,000 genes in humans, and the genotype of humans contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. The human body has four types of genes. The genes on a chromosome are arranged in a particular manner that determines your physical traits and behavior.
What is a Phenotype?
Another term commonly heard along genotype is phenotype. While genotype is the set of information for different features of a person, the phenotype is how the genes express themselves. For example, if you have a genotype that determines your hair to be blonde, the blonde color of your hair that you see is the phenotype.
Example of Genes
All of your characteristics are examples of genes like; if you have brown eyes when one or both of your parents have brown eyes, you possess genes for brown eyes. Sometimes, genes may also contribute to hereditary diseases like thalassemia major. If you are a carrier of that particular disease, you are a thalassemia minor. But if both of you have a gene for thalassemia minor, there are chances that you may have a thalassemia major.
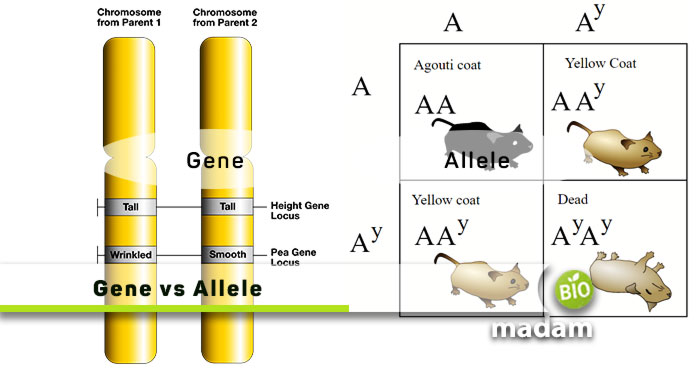
What are Alleles?
Alleles are the two forms of one gene that determine your characteristics. The genes or alleles could be heterozygous or homozygous. When two humans mate, they both give 23 chromosomes to the offspring. Each chromosome of one parent contains hereditary information the same as the counterpart chromosome of the other parent. If both the chromosomes have the same gene expression (both have long hair), it is a homozygous gene/ allele. Yet, if they both express a difference (one has long hair, one has short), the dominant gene decides the offspring’s characteristics.
What are Dominant Alleles?
Some phenotypes have more than one allele, like eyes (blue, brown, green, etc.), and when parents with heterozygous alleles mate, the alleles have to fight to determine the child’s trait.
But, how is it determined?
After extensive studies, one of these alleles has been seen to be dominant while the other is recessive. As mentioned above, in the case of blue and brown alleles, brown is dominant. It means that if one parent has blue eyes and the other has brown, the child will have brown eyes. On the other hand, if they are homozygous, the child can have blue eyes. In this scenario, blue eyes are the recessive allele.
What are Co-dominant Alleles?
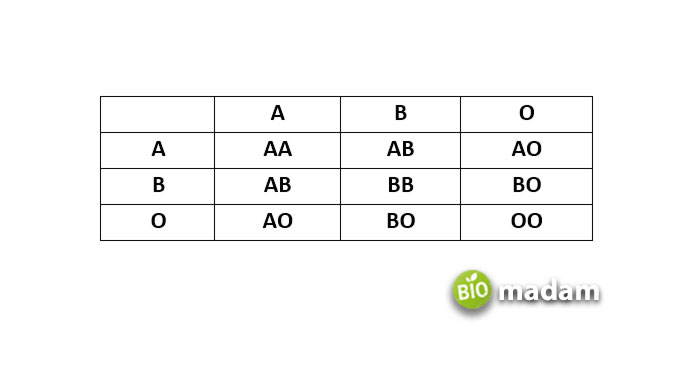
Besides dominant and recessive alleles, another type of allele is co-dominant alleles. One common example of co-dominant alleles is blood groups. For example, if one parent has an A blood group while the other has a B blood group, there is no particular answer to “What will be the child’s blood group.” The offspring may have A, B, AB, or O blood group. It is the same with all A, B, AB, And O blood types. You typically get an O blood group if no allele for a blood group is present on the chromosome, making it quite rare.
Examples of Alleles
Alleles are not only present in humans but also in plants and animals. Alleles are widely studied in plants to create new types of plants that benefit us. One of the alleles is P and p, which determine the color of the pea plant. P is the dominant allele with the phenotype of purple color, and p exhibits white color.
Similarities Between Gene and Allele
As alleles are a variant of a gene, they are quite similar to each other.
- Genes and alleles have genetic information about the characteristics of an organism.
- They are made up of DNA.
- They are present on different types of chromosomes and account for an organism’s particular appearance and behavior.
Difference between Gene and Allele
Definition
Genes
Genes are the hereditary units present on chromosomes.
Alleles
Alleles are variants of genes that exhibit particular forms of the same factor.
Determinant
Gene
They determine the genotype of an organism.
Alleles
Alternatively, alleles determine the phenotype of an organism.
Types
Genes
Alleles are types of genes offering variation.
Alleles
The types of alleles are; dominant and recessive.
Examples
Genes
Hair color, height, earlobes, bone structure, etc.
Alleles
On the contrary, examples of alleles include AABBCC for darkest skin tone and aabbcc for the lightest skin tone.
FAQs
What are wild and mutant alleles?
Wild genes are used to describe the phenotypic characters in the wild population, while mutant alleles result from a mutation in the genes. Mutant genes usually cause diseases in the population when they are in dominant form or homozygous alleles.
What are Allelomorphs and locus?
Allelomorph is another name for alleles that may occur in pairs on each counter chromosome and impact the phenotype of that organism. Locus is defined as the size or position of the presence of that allele.
Why do you only get one allele from each parent?
During the process of cell division, the chromosome pairs split and are distributed into gametes. Gametes contain one copy of each chromosome with an allele for every gene. This way, when each of the parents gives 23 chromosomes to the offspring, it contributes to one allele responsible for a particular characteristic.
What are mutations?
Mutations refer to permanent changes in the genes that may or may not cause disease. A well-known example of gene mutation is sickle cell anemia, which results in the irregular shape of the red blood cells.
How do genetics help in forensics?
Forensic studies are an important part of crime investigation as they help resolve different aspects of a crime. If forensics find the DNA of the culprit in the form of hair or skin flakes at the crime scene, they can be of great help to solve the case. They also enable investigators to find out the family of the victims.
The Bottom Line
Genes and alleles are essential for a person’s behavioral and physical characteristics. Every organism has a particular set of genes and alleles that determine its looks and features. Humans get 23 chromosomes from each parent with an allele for a particular characteristic. If both have the same allele, the offspring gets the same trait. However, if both are different, the offspring bears the dominant allele.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.