Recently updated on March 3rd, 2023 at 12:05 pm
DNA and genes are a part of the cell of a human body. DNA is made up of nucleotides, whereas genes are a short section of DNA. These are responsible for carrying the hereditary material from parents to the child. They are microscopic and only visible under a microscope such as compound or electron microscope.
DNA and genes differ entirely from each other. The two things are completely different in structure, composition, and functionality. This article explains DNA and genes in detail and highlights the key differences between the two.
What is DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as DNA, was first discovered by Johannes Friedrich Miescher, a Swiss biologist, in the year 1869.
DNA contains genetic information in living organisms. It is a double helix, made up of two long and thin twisted strands, and holds the blueprint. It also comprises nucleotides, including nitrogen bases, sugar, and phosphate groups.
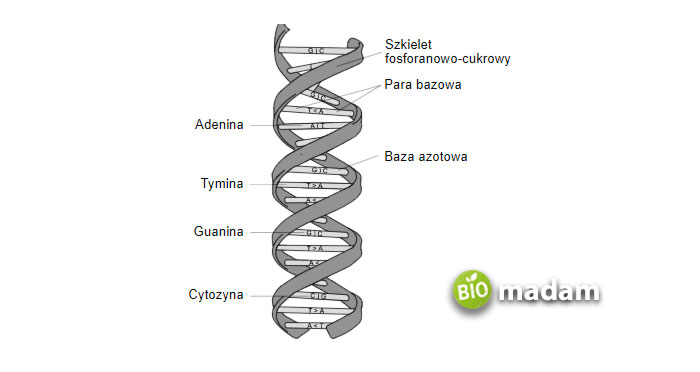
The structure of DNA looks like a ladder, twisted at both ends. It is responsible for carrying the genetic information, mutations, replication, and transcription processes. During cell division, DNA is accountable to assure equal distribution of DNA.
A DNA molecule has four types of basis:
- Adenine
- Thymine
- Guanine
- Cytosine
There is a specific way the basis follows, such as C always pairs with G and A always pairs with T.
DNA replicates and doubles during cell division, and thus it is inherited by two daughter cells from one cell. It has information stored and, therefore, during cell division, transfers the information to consecutive generations.
What is Genes
Genes are made up of DNA and are functional units of heredity. It is a subpart of DNA and is transferred from parents to their children.
In the human body, there are about thirty thousand genes in every cell. These genes are responsible for controlling different types of RNA, and of course, DNA.
Genes are organized and packed in a component called chromosomes. There are 46 chromosomes paired in two in a human body. The 23 pairs of chromosomes are passed in sets from mother and father to child. Therefore, each individual has two copies of genes, one inherited from the father and one from the mother.
Some genes work by giving information to make proteins; however, not all genes code this. The primary function of genes is to decide almost about everything in the human body. They affect a certain trait possessed by an individual.
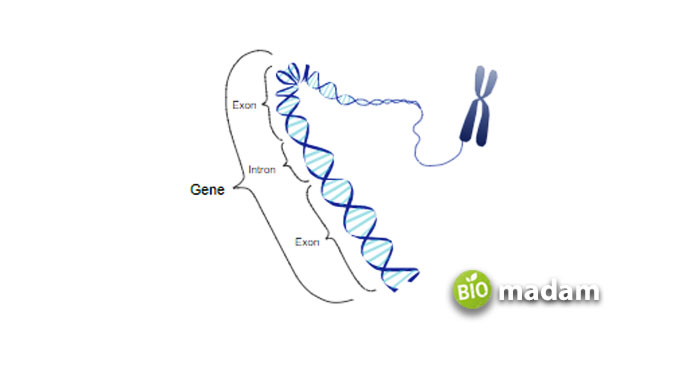
From the color of the child’s eye to the disease, it may inherit, such as sickle-cell anemia, all the things in a human body are managed and affected by genes.
Just like DNA, genes also comprise four nucleotides; Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T). However, unlike DNA, Genes can have different combinations of ACGT and gives people other characteristics.
The Difference Table
| Characteristics | DNA | Genes |
| Composition | Long-chain of polynucleotides | Made up of DNA |
| Functionality | Regulates genes | Regulates traits |
| Structure | Two long chains of polynucleotides joined together | Present on DNA’s short stretch |
| Presence | In a cell’s nucleus | On a chromosome |
| Codes | Encodes genetic instruction | Coded with hereditary information |
| Nucleotides | Pairs with T and C pairs with G | Different combinations of ACGT |
| Trait | Transfers all information of all traits | Transfers information for a specific trait |
| MicroRNA | Non-coding DNA can not transcribe into RNA | Gene can transcribe into RNA |
| Packing | DNA is tightly packed | Genes are loosely packed |
| Repetitiveness | Repetitive | Less Repetitive |
Chromosomes
DNA molecules are packed tightly around proteins called histones in the nucleus of the cell to form a thread-like structure called chromosomes.
Chromosomes contain genes that help them in determining the traits and characteristics of a child. Chromosome 1, the largest chromosome, contains about 8000 genes, whereas the smallest chromosome, chromosome 21, contains 3000 genes.
Chromosomes are only visible during cell division in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA makes the chromosomes tightly packed during cell division and hence can be seen through a biological microscope for students.
Chromosomes are divided into two sections or arms. The division is done by the centromere, which is a constriction point in the chromosome. The short arm is labeled as the ‘p’ arm, whereas the long arm is called the ‘q’ arm.
Centromere location in each chromosome determines the chromosome’s characteristic shape and helps in describing the location of specific genes.
Chromosomes vary in shape and number. Humans have linear chromosomes arranged in pairs inside the nucleus of the cell. The only cell that does not contain a pair of chromosomes is the reproductive cell.
The reproductive cells consist of only one copy of each chromosome. The two reproductive cells unite and become a single cell, containing two copies of each chromosome. One copy of the chromosome is inherited from the father in the child, while one is inherited from the mother.
Conclusion
DNA and genes are an essential part of a body and help specifically in reproduction. Genes, however, are made up of DNA, but still, the two components differ entirely from each other. DNA and genes are important parts of chromosomes. DNA is responsible for making chromosomes, whereas genes help it in determining the traits of the child.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.