Proteins are made of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body. They are present around the body in all organisms to provide structural and functional support. Proteins are complex molecules that carry out different bodily functions besides contributing to the structure of the body.
Fibrous and globular proteins are one of the many types of proteins like structural proteins, transport proteins, hormonal proteins, and others. They play a major role in regulating body functions with the help of enzymes. The primary difference between fibrous and globular proteins is their involvement in synthesizing cells and tissues.
Fibrous proteins form connective tissues, tendons, and fibers, whereas globular proteins produce enzymes and amino acids.
Let’s discuss fibrous and globular proteins for a deeper understanding. Keep reading to find out a simple method for you to remember the differences effortlessly.
Comparison Table
| Factors | Fibrous proteins | Globular proteins |
| Other Names | Scleroproteins | Spheroproteins |
| Structure | Narrow, wire-like | Spherical/ Globular |
| Function | Maintains structure | Regulates metabolism |
| Categorization | Structural proteins | Functional proteins |
| Solubility | Soluble in strong acids | Soluble in water, bases, and acids |
| Acid Sequence | Regular | Irregular |
| Sensitivity | Less sensitive | More sensitive |
| Examples | Keratin, collagen | Hormones, antibodies |
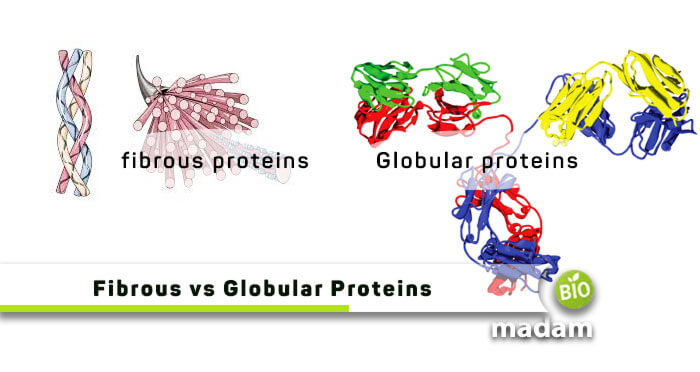
What are Fibrous Proteins?
Fibrous proteins are in the form of fibers or rods and are also called Scleroproteins. They are made of polypeptide chains resulting in the formation of a sheet-like structure of the proteins. Fibrous proteins comprise multiple units or a single unit that repeats multiple times. The protein chains are connected to each other through strong hydrogen bonds. The insolubility of fibrous proteins in water distinguishes them from other protein types.
Characteristics of Fibrous Proteins
- Soluble in strong acids only
- Insoluble in water
- Do not easily de-nature
Functions of Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins are mainly involved in producing or repairing tendons and muscle fibers. They help in the formation of tough tissues that offer support and strength to other tissues, like connective or epithelial.

What are Globular Proteins?
Globular proteins are globe-like or spherical and thus are also called spheroproteins. While fibrous proteins are mainly responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of the body, globular proteins have their role in producing enzymes and messengers besides performing regulatory functions in the body.
They contain primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structures of straight-chain polypeptide chains that may change directions. Globular proteins contribute to the transportation of molecules across membranes.
Characteristics of Globular Proteins
- Globular proteins are soluble in all solvents like water, bases, and acids
- Forms colloids with water
- Sensitive to temperature and pH change
Functions of Globular Proteins
Globular proteins also participate in the structural formation of the body and perform many other functions. They facilitate the transmission of messages in the body for regulating body processes. Such proteins are also involved in catalyzing enzymes for organic bioreactions. Their major function is the involvement in metabolism. Furthermore, antibodies are the structures existing as globular proteins to produce humoral immunity response, whenever a pathogen (denoted through an antigen). Fibrous proteins help in the structural maintenance of the body in organisms enters.

Differences Between Fibrous And Globular Proteins
Definition
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins help in the maintenance of body structure through the formation of fibers and connective tissues.
Globular Proteins
Globular proteins are involved in different metabolic functions by producing catalyzing enzymes.
Other Names
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins are also called scleroproteins.
Globular Proteins
Alternatively, globular proteins are widely known as spheroproteins.
Structure
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins have fiber or wire-like, narrow and long shapes.
Globular Proteins
Whereas globular proteins have a globe-like or spherical shape.
Function
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins help in the structural maintenance of the body in organisms by forming ligaments, tendons, connective tissues, and fibers.
Globular Proteins
Whereas globular proteins help regulate metabolic functions and produce messenger proteins for exchanging messages throughout the body.
Categorization
Fibrous Proteins
As their function in maintaining structure is evident, they are called structural proteins, having secondary structure.
Globular Proteins
On the other hand, globular proteins are functional proteins and help in regulating body functions.
Solubility
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins are insoluble in water and weak bases and acids. They only solubilize in strong acids.
Globular Proteins
Contradictorily, they are soluble in water and all bases and acids.
Acid Sequence
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins are made of repetitive amino acid sequences, which could be the same or different sequences.
Globular Proteins
In contrast, they have an irregular amino acid sequence with changing direction.
Sensitivity
Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous proteins are not immediately influenced by environmental changes and do not de-nature easily.
Globular Proteins
While globular proteins are sensitive to changes in the surroundings like temperature and pH.
Examples
Fibrous Proteins
Some common examples of fibrous proteins include elastin, collagen, keratin, etc.
Globular Proteins
Examples of globular proteins are enzymes, insulin, hemoglobin, myoglobin, etc.
The Secret Trick
Remembering the difference between two different proteins can be confusing. You can conveniently remember six differences between fibrous and globular proteins through SPADES.
SPADES is an acronym that helps you remember the key factors that define the differences between the two proteins. SPADES stands for
- Shape
- Purpose (categorization/ function)
- Acid sequence
- Durability (sensitivity)
- Examples
- Solubility
By remembering a simple word, you can recall what the differences are based on; and score well in exams.
FAQs
Should you reduce proteins while dieting?
If you are willing to lose weight, it is very unlikely for a dietician to recommend cutting down on proteins unless there is an underlying health condition. Proteins are the body’s building block and contribute to bodily structures instead of accumulating like fats. Instead of reducing protein intake, it is better to minimize carbs and calories through unhealthy foods.
Is there anything like “too many proteins”?
Yes, anything in excess is harmful to the body. While you need to take proteins as a major part of your diet (around 10% to 15% of your daily nutrition intake) to regulate body structure and functions, taking more than the required amount can lead to health issues.
What happens when you take too many proteins?
Taking a high-protein diet helps you lose weight but only as suggested by your nutritionist. If you keep increasing the protein content in your daily diet, it can lead to indigestion and kidney problems.
How long can our bodies store protein?
While our body is designed to store nutrients like fats and carbs, but not proteins, for later use, it does not store proteins. They stay for as long as 24 hours in the body and need to be replenished every day. That is why malnourished people have less muscle mass as the body starts consuming proteins from the muscles.
Do plant-based proteins have the same goodness as animal-based proteins?
Yes, plant-based proteins like soy proteins have been seen to decrease the chances of developing breast cancer that can be developed though genetic mutation. You can take soy protein through soy milk and tofu besides other sources. It is a perfect choice for vegans and people who avoid animal-based products.
The Bottom Line
Fibrous and globular proteins are essential for the functions and structure of living organisms and contribute in different ways. Fibrous proteins are structural proteins, while globular proteins are functional proteins. The former have strong bonds and do not easily dissolve in solvents other than strong acids. Alternatively, the latter is easy to solubilize in water and acids or bases. Taking an adequate amount of proteins in your diet ensures proper body functioning and may cause health issues otherwise.
Sabrina is a licensed pharmacist with extensive knowledge of physiology and pharmacology. She gained distinction in pharmacology and quality management. Her research on the need for Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) and improving compliance for diabetic patients through effervescent granules gained wide recognition. She loves to work on innovations and research to learn something new regarding medicine every day. She has been writing for many years now and aims to improve the quality of life by imparting adequate information to the readers.