The red nucleus is not a part of eukaryotes or prokaryotes on the cellular level. Instead, it is an organelle in the brain contributing to the extrapyramidal motor system. The structure of the red nucleus has been a point of debate among scientists and anatomists. While there is information about its role in the body’s movement, there is still discord regarding the structure of the red nucleus. Studies also suggest that the structure has evolved, and researchers are working to find out more about the function of the red nucleus. Keep reading to learn all that anatomists know.
What is the Red Nucleus?
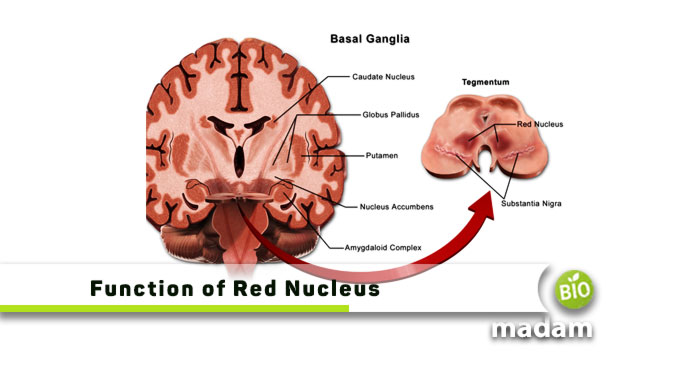
The red nucleus is a structure in the midbrain. It is present in the tegmentum of the midbrain at a similar level to the superior colliculi. The tegmentum is present posterior to the crus cerebri and anterior to the cerebral aqueduct. The substantia nigra is the point of transition from the tegmentum to the crus cerebri. The pars reticulata part of the substantia nigra is proximal to the red nucleus.
It is an oval-shaped paired structure that has a bright red color, leading to its name, “red nucleus.” The bright red color of the structure comes from the strong vascular system in the organ. It also contains a high level of iron pigments in the neural cytoplasm.
The Function of Red Nucleus
The main function of the red nucleus is its role in controlling movements via axon projections as a motor control pathway. These axons are known as the rubrospinal tract, which ends in the cervical region. The signals from the red nucleus contribute majorly to the movement of the upper limbs than the lower limbs. These axons have lower projections compared to the corticospinal tract. It shows that the red nucleus does not play a significant role in directing motor output. It also represents that the red nucleus regulates fine motor control and muscle movements.
Structure of Red Nucleus
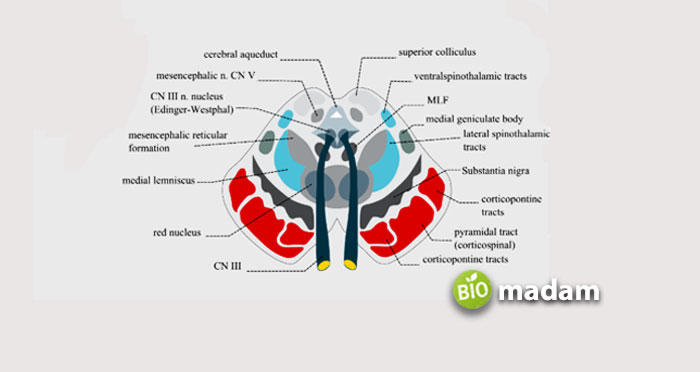
The structure of the organ is around 5mm in diameter from the subthalamic part of the diencephalon to the inferior extent of the superior colliculus. They have the rostral parvocellular and caudal magnocellular, leading to the formation of efferent tracks. The CN III oculomotor nerve pierces the red nucleus before it passes through the interpeduncular fossa. Besides the oculomotor nerve, the retroflex fasciculus and superior cerebellar peduncle also pass through the organ. This also explains the red perforated appearance on staining.
The red nucleus contains the medial third of the pars reticulata of the substantia nigra, anterior tegmental decussation, and interpeduncular nuclei to the anterior side. The medial lemniscus tract and cerebellothalamic fibers are seen on the lateral side. Furthermore, each red nucleus has the central tegmental tract on the posterior end, besides the trigeminothalamic and periaqueductal gray region. The oculomotor nuclei, medial longitudinal fasciculi, and mesencephalic nuclei are also found on the posterior side.
As mentioned, the neurons in the structure of the red nucleus contain iron pigments and are of two types. The large multipolar neurons are present in the caudal end, whereas the smaller counterparts disperse throughout the red nucleus. They contain a fibrous layer that restricts the corticobulbar and superior cerebellar regions.
The Bottom Line
The red nucleus is a structure in the midbrain present in the tegmentum of the midbrain at a similar level to the superior colliculi. Researchers have been working to find the exact anatomy and physiology of the structure. Latest studies show it as an oval-shaped paired structure that has a bright red color, leading to its name, “red nucleus.” It is around 5 mm in diameter from the diencephalon’s subthalamic part to the superior colliculus’s inferior extent. The main function of the red nucleus is its role in controlling movements via axon projections as a motor control pathway.
FAQs
What happens if the red nucleus is damaged?
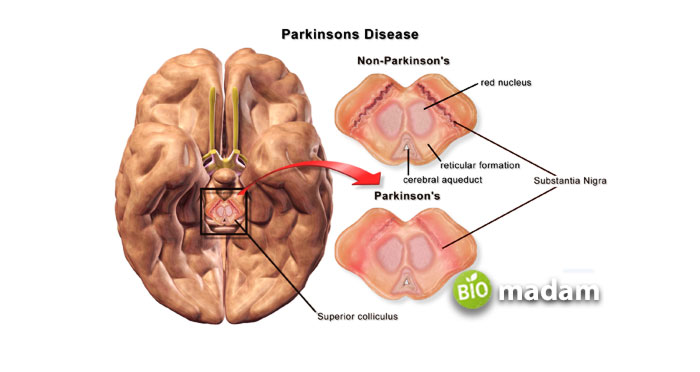
As the red nucleus is involved in regulating motor function and movement of upper limbs, damage to the red nucleus may result in choreiform movements, contralateral tremor, and ataxia.
Why is it called the red nucleus?
The red nucleus gets its name from its vascular structure and a high amount of iron in the form of ferritin and hemoglobin. The hemoglobin especially contributes to the red color of the organ.
What is the function of the rubrospinal tract?
The rubrospinal tract is responsible for transmitting signals from the cerebellum and motor cortex to the red nucleus. The tract stimulates the flexor muscles by connecting to the alpha and gamma motor neurons.
Is the red nucleus white matter?
The red nucleus comprises round masses of gray matter. It is present in the tegmentum of the midbrain at a similar level to the superior colliculi. So, it is not the white matter in the brain.
Does rubrospinal tract control movement?
The rubrospinal tract regulates and controls large muscle movements besides fine motor control. It controls the upper limb response as the tract terminates in the thoracic and cervical regions.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.