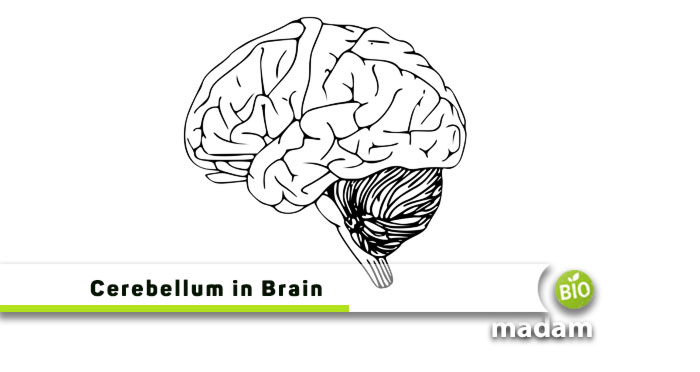
The brain is the primary component of your nervous system that carries out all bodily functions. Different parts of your brain perform specific roles, including memory, homeostasis, cognitive functioning, regulating hunger, thirst, mood, etc. Maintaining balance is another important, monitored and regulated by the cerebellum in the brain. But there’s more to this part of the brain that we will tell you in this article.
What is Cerebellum?
The cerebellum, also called the “little brain,” is one of the smallest brain components but the largest one in the hindbrain. It is present in the lower back of the brain between the cerebrum and the brain stem. Cerebellum accounts for only 10% of your total brain weight, yet it contains approximately 80% of the total neurons in the brain.
Brain anatomy shows it at the posterior cranial fossa, behind the fourth ventricle, the medulla oblongata, and the pons. The two main parts of the cerebellum in the brain are:
Cerebellar Cortex: It is a layer of folded tissues containing most of the neurons within the structure.
Cerebellar Nuclei: The cerebellar nuclei are the innermost part of the cerebellum comprising nerve cells that facilitate communication.
Functions of Cerebellum in the Brain
Researchers initially considered the cerebellum a motor structure as the cerebellum produces responses to parts of the motor system. However, the cerebellum does not initiate motor commands but modifies those commands to make movements more accurate and adaptive.
Cerebellum majorly contributes to coordinating voluntary movements, including motor skills such as posture, balance, and coordination. The main functions of the cerebellum in the brain are:
Maintaining Balance
Balance is the most critical task regulated by the cerebellum using special sensors that monitor changes in movement and balance. It receives input from proprioceptors and vestibular receptors modulating commands to motor neurons. It signals the body to change position and muscle load to fix the balance.
Motor Learning
This part of the brain also allows the body to learn and adapt to movements that require practice. It helps you understand movement through trial and error. Examples of motor learning include riding a bicycle or learning to hit a baseball.
Voluntary Movement Coordination
Cerebellum contributes majorly to voluntary movement and muscle group coordination. It coordinates the timing of these muscle movements to produce accurate and fluid body or limb movements.
Cognitive Functions
While the cerebellum assists motor functions, it also contributes to cognitive functions such as mood, attention, thinking, fear response, pleasure or reward response, and language processing. Moreover, it coordinates eye movements, allowing us to see things in our surroundings correctly.
Clinical Significance of Cerebellum
The cerebellum contributes to different bodily functions by communicating with various organs. It receives information regarding voluntary muscle movements from the muscles, tendons, ligaments, joints, and the cerebral cortex. It also catches information from the vestibular nuclei to maintain balance.
- Any changes in the anatomy or physiology of the cerebellum can lead to serious issues such as ataxia, which refers to disturbances in voluntary actions; it involves tremors with fine movements, including writing.
- Nystagmus is another similar condition, which results from ataxia in ocular muscles.
- Hypotonia refers to muscles losing resistance to palpation as the cerebellum’s influence diminishes on the gamma motor neurons.
What is the Difference between Cerebellum and Cerebrum?
People often confuse the cerebellum and cerebrum because of similar sounds, yet they perform different functions. While the cerebellum is between the cerebrum and the brain stem, the cerebrum is the brain’s largest part above the cerebellum. Cerebellum handles motor functions and voluntary movement. At the same time, the cerebrum regulates thinking, perceiving, producing, and understanding language.
How to Protect Your Cerebellum?

Protecting your brain keeps your cerebellum healthy to perform all the important functions. While you can’t prevent some neural issues, the following can help improve your brain’s health:
Eat Healthy
Eating healthy is one of the most important factors to keep your cerebellum healthy. Fish oil and walnuts are good choices to promote brain health. Coffee, eggs, and whole grains are also healthy food options.
Workout
Like other parts of the body, our brain also requires a workout. Working out physically stimulates blood flow to the brain, reducing stroke risk. Also, indulge in mental exercises to keep your brain working adequately.
Practice Safety
While healthy food and workouts promote brain health, protecting your head is critical to avoiding brain damage. Always wear a helmet while riding a bike and a seatbelt when driving.
Avoid Smoking and Drinking
Smoking and alcohol are detrimental not only to your liver and lungs but also to your brain. Smoking impacts brain function, and high consumption of cigarettes and alcohol increases the chances of a stroke.
The Bottom Line
The cerebellum (translating to “little brain”) is an important part of the brain, majorly responsible for motor functions. Cerebellum does not initiate motor commands but modifies those commands to make movements more accurate and adaptive. It contributes to motor learning and voluntary actions, besides a few cognitive functions; maintaining balance is another important function of the cerebellum in the brain. Eat healthy, work out, and avoid smoking to keep your cerebellum healthy.
FAQs
What are the 5 functions of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum contributes to voluntary movements such as walking and plays a major role in maintaining balance besides others. The five main functions are walking, balance, posture, motor learning, and eye movement.
What is the most important function of the cerebellum?
Maintaining balance and posture is the most critical part of the cerebellum. It monitors and regulates the posture and muscles to maintain balance through inputs from proprioceptors and proprioceptors.
What happens if the cerebellum is damaged?
Damage to the cerebellum can lead to various issues such as disturbances in voluntary movement (ataxia), loss of coordination of motor movement (asynergia), ataxia in ocular muscles (nystagmus), the inability to judge distance and when to stop (dysmetria), and muscles losing resistance to palpation (hypotonia).
What causes cerebellum damage?
Cerebellum damage may be due to numerous reasons, such as chain smoking, alcohol misuse, multiple sclerosis (MS), brain degeneration, stroke, cyst or tumor, genetic disorders, and certain medications.
Can you live without the cerebellum?
While the cerebellum is an important part of the brain, you can live without it. The cerebellum does not contribute to breathing, blood circulation, emotion, or any other function directly associated with life or death. Cerebellum contributes to processes that start somewhere else in your brain.
Can the cerebellum be repaired?
You can recover from cerebellum damage by engaging your brain’s neuroplasticity through therapy exercises. They help you regulate balance, motor movement, posture, eye movement, and cognitive skills.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.