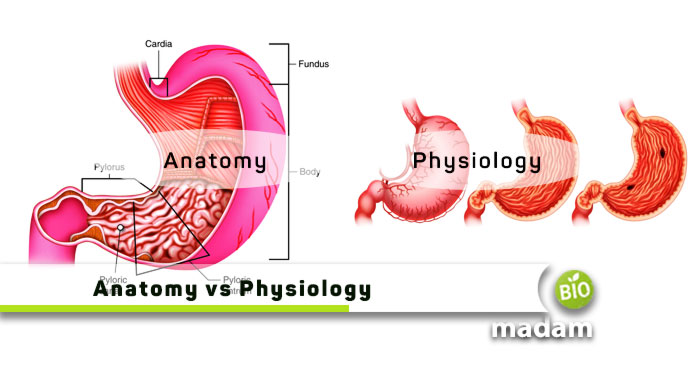
Anatomy and physiology are important aspects of medical studies, and many people think they are the same. While some colleges teach them as a combined subject, their exact contents are not the same. Anatomy refers to the structure or morphology of an organism, whereas physiology describes the functions and processes within the body. Anatomy and physiology together ensure the proper functioning of the body and enable the organism to develop and reproduce. Besides the basic definition, there are multiple other differences between the anatomy and physiology of organisms that contribute to an in-depth understanding of an organism’s characteristics.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Anatomy | Physiology |
| Definition | Structure | Function |
| Types | Regional/systematic, and micro/macro | Environmental, human, animal, plant, etc. |
| Analysis | Dead & alive organisms | Alive organisms only |
| Analytical tools | X-ray, CT scan | Ultrasound |
| Examples | Heart, lungs, kidneys, etc. | Digestion, excretion, circulation, etc. |
What is Anatomy?
Anatomy means “cutting” and refers to cutting an organism’s body to study the parts. Anatomy refers to the structure of the body that helps in performing different functions involved in the growth, development, and movement of the body.
Besides cutting and surgery, body parts are now studied through other means like MRI, CT scans, X-rays, etc.
Anatomical Divisions
Anatomy is divided into four categories on the basis of different features and studied accordingly.
According to the Area of Study
While the whole body of an organism is its anatomy, it is studied based on different parameters. One of the divisions is into regional and systematic anatomy.
Regional Anatomy
Regional Anatomy is the anatomy of a particular organ. It includes the structure and parts of that particular organ that contribute to a physiological function.
Systematic Anatomy
This part of anatomy explains the structure of more than one organ that combine to make a system involved in a particular function in the body. The function of these organs relies majorly on the anatomy of the organ.
According to Size
The other classification of anatomical structures is on the basis of their size. They are classified as macroscopic and microscopic structures.
Macroscopic Structures
You can see these structures with your naked eye through dissection or imaging techniques like X-ray. Common examples of macroscopic structures include eyes, muscles, kidneys, etc.
Microscopic Structures
On the other hand, the cell organelles that make up your whole body are not visible to the eye and need to be observed under a compound, electron, or student microscope. They comprise histological studies that focus on cells and tissues on a microscopic level.
Examples of Anatomical Structures
The whole body itself is an example of an anatomical structure as it contains all other organs. Bones are the most important skeletal parts of a body as they help support the framework and enable movement with the help of muscles. Other examples include
- Lungs
- Kidneys
- Heart
- Blood vessels (veins and arteries)
- Small and large intestines
What is Physiology?
Physiology is the branch of science that explains the functions performed by the body structures. It involves the function of the organs and organelles individually and their function with other body parts to form a system. Physiology is a vital aspect of studying an organism or diagnosing a pathological condition or disease, as most health problems usually arise from disturbed physiology.
Physiology basically majorly focuses on maintaining the homeostatic function of the body, but almost all processes occurring within the body are physiological (some are biochemical). Examples of physiological processes are excretion, digestion, active, and passive transport, etc., Whereas Krebs’s cycle and glycogenolysis are examples of biochemical processes.
Physiological Divisions
Physiology is divided into different categories, just like anatomy, yet on particular parameters. The most commonly studied branches of physiology are animal physiology, plant physiology, environmental physiology, evolutionary physiology, comparative, and exercise physiology. Here’s everything in detail about them:
Human and Animal Physiology
As the name suggests, this branch of physiology deals with studying the functions of human and animal bodies. As humans are mammals and belong to the kingdom Animalia, their internal structure majorly resembles each other. It helps understand the body’s functioning to diagnose and treat ailments in humans and animals better.
Plant Physiology
Like animals and humans, understanding plant physiology plays a major role in maintaining their health. Plant physiologists study the processes of evaporation, transpiration, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, etc.
Comparative Physiology
Comparative physiology focuses on the diversity in the ecosystem and the difference in their functioning. Researchers find comparative studies to be of critical importance as they allow you to understand how some organisms adapt more easily to some environments than others.
Environmental Physiology
Environmental Physiology may seem like an amalgam of comparative and plant studies. They are based on the impact of the environment on a plant’s health and how it alters its normal functioning. It includes observing the temperature, humidity, heat, wind, etc., In the plant surroundings.
Evolutionary Physiology
Evolutionary physiology is used to study the evolutionary behavior of organisms and how their physiology has modified over the years.
Exercise Physiology
The domain of exercise physiology studies the effect of exercise on an organism’s body, primarily the human body. It involves the study of heart rate, respiratory function, and other factors like muscle strain during and after physical activity.
Examples of Physiological Functions
Examples of physiological functions in the human body are
- Cardiovascular system
- Skeletal system
- Muscular system
- Digestive system
- Respiratory system
- Reproductive system
- Renal system
- The immune system, including humoral and cell-mediated immunity
- The endocrine system, including different hormones
- The nervous system, including SNS and PNS
Difference Between Anatomy and Physiology
Definition
Anatomy
Anatomy is the branch of science that deals with the structure and morphology of the body and its organs.
Physiology
Whereas physiology is the study of functions performed by different parts and systems of the body.
Types
Anatomy
Anatomy is divided into four types. If classified based on the region, it is categorized as Regional and Systematic anatomy. And if classified based on size, researchers study macro and microanatomy.
Physiology
Physiology is divided into multiple branches; environmental, animal, human, plant (vascular and non-vascular), evolutionary, and exercise physiology.
Analysis
Anatomy
Anatomy is analyzed in living organisms as well as dead beings.
Physiology
Physiology is only studied in living organisms as the body loses all of its function once dead.
Analytical Tools
Anatomy
The anatomy of a living or dead body can be analyzed through dissection or imaging techniques that do not require cutting.
Physiology
You can observe the physiology of body parts through microscopic studies and other techniques like ultrasound
Key Role
Anatomy
The anatomy of a body helps you understand the parts of the body and how they perform their specific role.
Physiology
Understanding physiology allows you to observe how processes on the cellular level contribute to systematic functions eventually.
Examples
Anatomy
Examples of Anatomical Structures include the parts of the digestive system and respiratory system, such as the stomach, esophagus, trachea, left and right lungs, etc.
Physiology
The most common examples of body physiology are the respiratory system, muscular system, and cardiovascular system, in which organs perform their individual function that combines to create a systematic effect.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, we now understand that anatomy and physiology are two important science subjects. In anatomy, we study body movements through particular organs, whereas, physiology helps us understand their functioning. We are afraid to say that abnormal changes in anatomical or physiological functioning can lead to disturbances in the ecosystem and community.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.