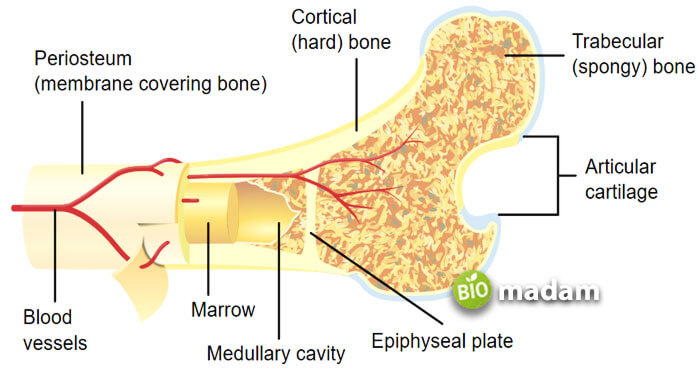
The skeletal system is the basic framework of all animals and plays a prominent role in maintaining the shape and form of the body. It is composed of various kinds of bones and connective tissues, including tendons and ligaments. All these, together, enable the functioning of body parts. The most prominent bones of the skeletal system include the sternum, femur, tibia, fibula, etc Bones are composed of two parts; the spongy bone and the compact bone.
What is the Spongy Bone?
The spongy bone is a less dense and lighter bone structure. It consists of bars and plates of bones with small cavities that contain red bone marrow. They may look haphazardly arranged when observed, yet they provide maximum strength and support to the bone. Spongy bones typically look like a honeycomb or sponge with pores in them. Bone marrow is present between the spaces. However, do not think they are mushy and light like a sponge.
Spongy bones are also rigid (less than compact bones) and help in support. They are highly vascularized and present at the end of long bones. They are also found in the skull, vertebrae, and bones of the joints. While these bones are not as strong as compact bones, they offer better flexibility and adapt easily to changes in line of stress.
Functions of Spongy Bone
The Spongy bones play a major role in different functions due to the presence of bone marrow between the spaces and their flexible, light nature. Let us tell you a few of them.
Erythropoiesis
One of the significant roles of the Spongy bone is in the production of red blood cells. Around 2 million RBCs are produced per second in the bone marrow inside the spongy bones. The highly vascularized spongy bones make it possible by delivering lipids, glucose, and amino acids required to produce red blood cells.
Storage of Minerals
Bones are mainly composed of calcium and store about 99% of the total calcium content in the body. They are also responsible for storing 85% of phosphorus. Spongy bones enable the regulation of minerals in the body by offering space for storage and releasing them with the help of hormones as per need.
Shock Absorber
They are the shock absorbers in our bones that eliminate the chances of serious injuries and prevent them. Though sometimes the damage may also reach the spongy bones, their basic function in the joints is absorbing shock and preventing injury.
Weight Reduction
Spongy bones help reduce the weight of the bones as they are light and less dense than compact bones. If your body were just made of compact bones, the shock absorption wouldn’t be the same, and you would feel heavier.
FAQs
What is the advantage of spongy bone tissue at the ends of long bones?
The lightweight of these bones enables them to follow the lines of stress and provide support to the bone framework.
What is the role of compact bones?
Compact bones are heavy and hard bones that support your body and muscles to walk, run and carry out all functions that require skeletal involvement. Around 80% of the bones are compact, protecting the spongy bone and bone marrow between the spaces.
What are the other names for spongy bones?
Spongy bones are also known as Trabecular and cancellous bones due to the presence of trabeculae.
The Bottom Line
Spongy bones are less-dense, lightweight bones enclosed within the compact bones and are involved in shock absorption besides providing support. They also act as a site for the storage and release of minerals according to need. These are found in vertebrates, joints, skulls, and at the end of long bones.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.