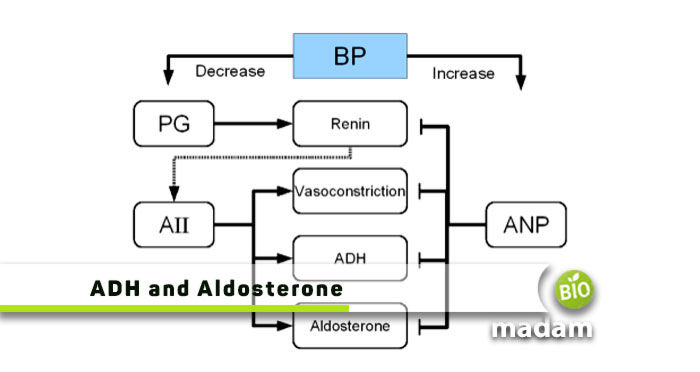
Hormones secreted by the endocrine and exocrine glands play a major role in maintaining anatomy and physiology of the body. ADH and aldosterone are two such critical hormones that are essential to the functioning of the body and its structure. Both are involved in water reabsorption in the nephrons. However, the most prominent difference between these hormones is the type of gland secreting them. They are also synthesized in different parts of the body. Let’s tell you everything about ADH and aldosterone.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | ADH | Aldosterone |
| Other Name | Vasopressin | Mineralocorticoid |
| Type of Hormone | Peptide | Steroid |
| Synthesis | Hypothalamus | Zona glomerulosa |
| Secretion | Pituitary Gland | Adrenal Cortex |
| Mechanism of Action | Opens pores in kidneys | Increases sodium pump activity |
| Function | Control blood volume and blood pressure | Absorption of sodium to maintain salt and water balance |
| Effect on Distal Tubules | Increases permeability to water | Increases permeability to sodium ions |
| Effect on Water Absorption | Directly increases absorption | Creates osmotic pressure to increase water absorption |
| Blood Pressure | Increases | No effect |
| Regulation | Osmotic pressure | Renin, angiotensin, and blood pressure |
What is ADH?
ADH (antidiuretic hormone), also known as vasopressin, is a peptide hormone. It performs the job of retaining water in the human body by concentrating urine. Vasopressin is a combination of “vaso” and “pressing,” translating to squeezing blood vessels.
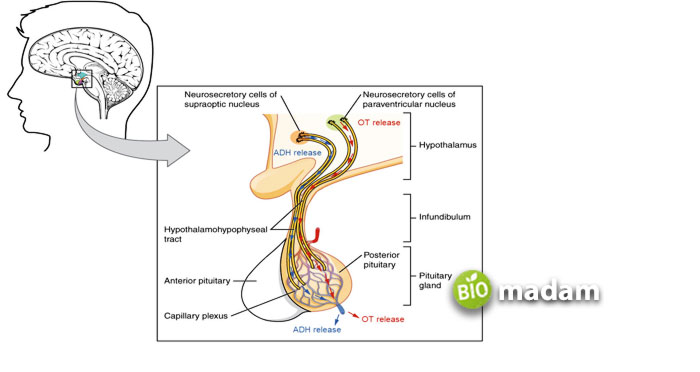
The osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus monitor the osmolarity of the blood. The hypothalamus is responsible for maintaining water balance in the body. It synthesizes ADH when the osmolarity of the blood decreases. It travels to the posterior pituitary gland, which secretes the hormone into the bloodstream. The pituitary gland acts as a storage space for the hormone and releases it when the blood pressure increases or decreases. When your body has low blood pressure, ADH comes into play to constrict arteries and veins and increases blood pressure. ADH helps you with different functions that manage blood pressure, including:
- Increasing the volume of blood pressure by facilitating the reabsorption of water by the kidneys.
- Increasing blood volume when a person is suffering from hypovolemia
- Reabsorbing water and lowering the levels of ADH to dilute blood highly concentrated with sodium.
What is Aldosterone?
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid of the adrenal cortex. It is produced in the zona glomerulosa in the adrenal gland and helps in the conservation of sodium ions. Aldosterone is a part of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. The renin angiotensin system plays a role in renal physiology. It works on the collecting ducts and distal tubules to preserve water. The process takes place through nephrons.
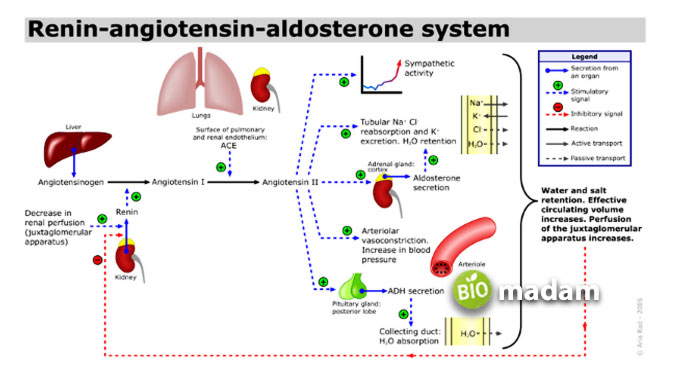
The nephrons in the kidney secrete renin that travels to the liver and converts renin into angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is then converted into angiotensin II in the lungs. Angiotensin II moves to the adrenal glands to produce aldosterone.
An increased amount of potassium in blood or plasma signals the release of aldosterone. A low renal perfusion decrease in sodium concentration may also stimulate hormone production. Aldosterone influences sodium and potassium pumps to reabsorb sodium and excrete potassium. As a result, it impacts blood pressure, blood volume, and water retention.
Similarities Between ADH and Aldosterone
- These hormones work in the collecting ducts and distal tubules in the kidney.
- ADH and aldosterone facilitate the reabsorption of water in the kidneys.
- They are secreted under the stimulus of low blood pressure.
Difference Between ADH and Aldosterone
Definition
ADH
ADH prevents the production of dilute urine from retaining water in the body.
Aldosterone
Aldosterone stimulates the absorption of sodium to maintain water and salt balance in the body.
Other Name
ADH
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is also known as vasopressin.
Aldosterone
On the other hand, aldosterone is also called a mineralocorticoid because of its function.
Type of Hormone
ADH
ADH is a peptide hormone contributing to water retention.
Aldosterone
But, aldosterone is a steroid in nature, maintaining salt and water.
Production and Secretion
ADH
ADH is synthesized in the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland.
Aldosterone
While, aldosterone is produced in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex and secreted from the adrenal gland.
Mechanism of Action
ADH
ADH works by increasing the permeability by opening pores in kidney epithelial tissues.
Aldosterone
Alternatively, aldosterone performs by increasing the activity of sodium pumps in the cells.
Function
ADH
The main function of ADH is to control blood volume and blood pressure in the body by retaining water.
Aldosterone
At the same time, aldosterone contributes to the absorption of sodium to maintain salt and water balance in the body.
Effect on Distal Tubules
ADH
Increases the permeability of DCT and collecting tubules to water.
Aldosterone
Conversely, it makes the collecting tubules and distal collecting tubules more permeable to sodium ions.
Effect on Water Absorption
ADH
Increases the water absorption from distal tubules directly.
Aldosterone
But, aldosterone increases water reabsorption by creating an osmotic pressure.
Blood Pressure
ADH
ADH impacts blood pressure by constricting blood vessels leading to increased blood pressure.
Aldosterone
Whereas, aldosterone does not have any effect on blood pressure.
Regulation
ADH
ADH is regulated through osmotic pressure in the blood vessels.
Aldosterone
Contrarily, aldosterone regulates through renin, angiotensin, and blood pressure.
The Bottom Line
ADH and aldosterone are important hormones in the body that contribute to water retention in the body. Despite their similar function, the main difference between ADH and aldosterone is their mechanism of action. ADH increases permeability by opening pores in kidney cells. Alternatively, aldosterone increases the activity of sodium pumps in the body. Moreover, ADH or vasopressin contributes to blood pressure, while aldosterone does not impact arteries, veins, or capillaries.
FAQs
What is the relationship between ADH and aldosterone?
ADH contributes to water reabsorption, whereas aldosterone also plays a role in sodium reabsorption. Aldosterone increases blood pressure and blood volume by stimulating water and sodium reabsorption.
Does aldosterone stimulate ADH release?
Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to increase fluid and sodium retention. It also stimulates the release of ADH from the posterior pituitary gland, which helps increase fluid retention.
How do ADH and aldosterone affect urine output?
ADH and aldosterone both work to retain water in the body. However, the mechanism of action is different. ADH opens pores in kidney tissues, while aldosterone increases the activity of sodium pumps.

The Biomadam Content Team develops and manages educational and informational articles published on Biomadam. Content is prepared using standard reference materials and follows internal editorial guidelines to ensure clarity and consistency.