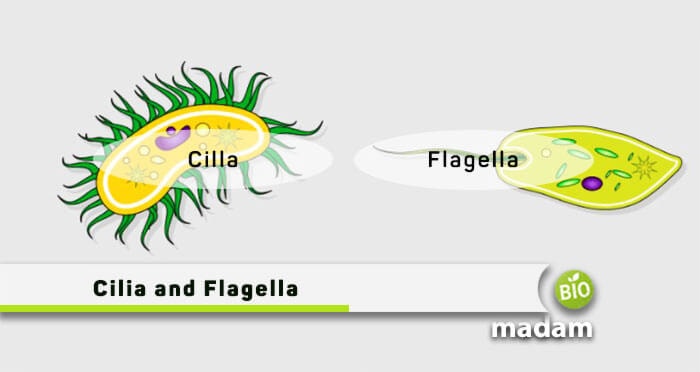
Cilia and flagella are the two cytoplasmic cells extending from the cell’s surface. The two cells have differences due to their structure, size, numbers, and functioning. Cilia are relatively shorter and can only be seen via a microscope, whereas flagella are large complex structures.
Their primary function is mainly associated with a cell’s locomotion, but they also help in other processes like circulation and respiration. Cilia and flagella are present on the cell’s surface, extending from the plasma, and are usually found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Let’s begin differentiating them through a comparison table.
Comparison Table
| Factors | Cilia | Flagella |
| Structure | Short & Hair-like | Long & Complex Hair-like |
| Length | 5 to 10 µm | 150 µm |
| Width | 1 µm | 0.02 to 0.025 µm thin |
| Presence | In Eukaryotic Cells | In Eukaryotes & Prokaryotes |
| Position | At the Cell Surface | At the Cell, Surface Extending from Plasma Membrane |
| Motility | Rotational & Fast-Moving | Rotatory Movement |
| Function | Locomotion & Circulation | Locomotion |
| Category | Two Types | Three Types |
| Numbers | Numerous | Less in Number |
| Density | Hundreds/Cell | Less than 10/Cell |
Explain Cilia
Cilia are short and hair-like microscopic structures extending from the surface of a living cell in single or multiple units. Cilia are responsible for moving the entire cells along its outer surface, thus aiding locomotion. Almost all eukaryotic cells comprise cilia that help develop the cell and body. These may vary from 5-10 µm, with a width of less than 1 µm. Such structures are usually present in hundreds of quantities on the cell surface in paramecium organisms.
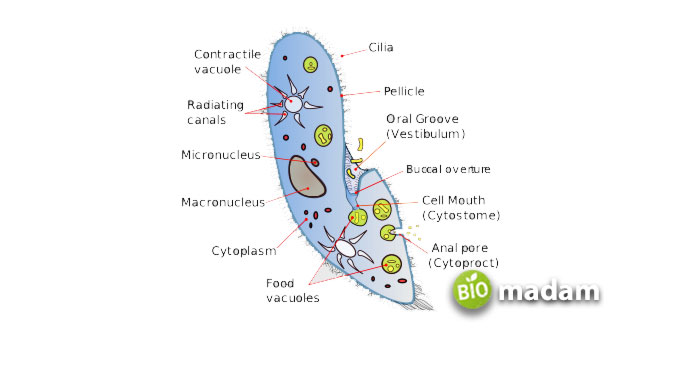
Cilia are chiefly active during cell cycle development and progression. It, however, allows only specific proteins for proper functioning. Moreover, cilia also play a vital role in molecular trafficking and cellular communication and participate in the vesicular secretion of exosomes. Scientists have broadly classified cilia into motile and non-motile structures.
Motile Cilia
Motile cilia are found in the respiratory tract, right and left lungs, and middle ear of the human body. It is the moving cilia that prevent mucus and dust along the airways. Furthermore, it has an essential role in facilitating the movement of sperm. This type of cilia is responsible for easy breathing and assures smooth functioning of the respiratory tract. Motile cilia have a 9+2 arrangement. Nine fused microtubules form a circle in this arrangement, whereas the two unfused microtubules are present in the circle’s center.
Non-motile Cilia
Non-motile cilia work as an antenna for the cells as they can receive signals from other cells. Non-motile cilia, also known as primary cilia, have a 9+0 arrangement in which nine fused microtubules form a circle.
Explain Flagella
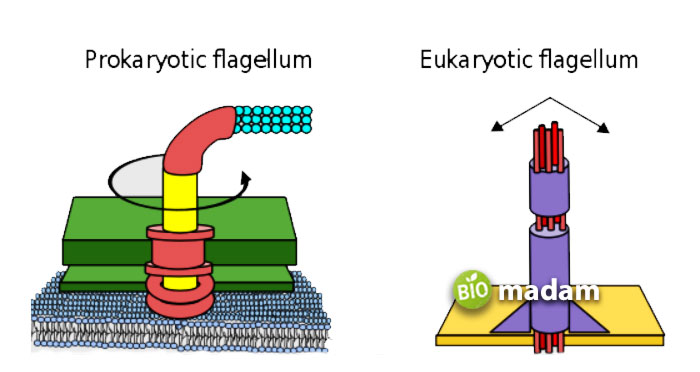
Flagella are long and complex hair-like structures present on the cell’s surface extending from the plasma membrane. The primary function of flagella in a body is to move an entire cell from one place to another. Flagella consists of a hook in the cell envelope, a filament that is the outer part of the cell, and a basal body attached to the cytoplasmic membrane. These structures are entirely flagellin protein, a globular protein, fixed in the cell envelope. Flagella are comparatively longer than cilia, with 150 µ length and 0.02 to 0.025 µm width.
These structures are further categorized into three types i.e., bacterial flagella, archaeal flagella, and eukaryotic flagella.
Bacterial Flagella
These have a helical filamentous structure rotating like screws. Bacterial flagella are typically found in Salmonella typhi, E. coli, etc. This type of flagella is responsible for the motility of bacteria through rotatory movement. Besides, bacterial flagella can be single or many per cells.
Archaeal Flagella
Archaeal flagella comprise similar properties and characteristics as that bacterial flagella, with the only difference in the lack of a central channel. This type of flagella is also responsible for motility and is present as single or many per cells.
Eukaryotic Flagella
Such flagella are a complex type that has difficult projections. Eukaryotic flagella beat back and forth, which means that the flagella return to their original position multiple times.
Similarities between Cilia and Flagella
Cilia and Flagella share some similarities as well, such as:
- Both outgrow the plasma of the cell.
- Either its cilia or flagella, both arise from the basal body.
- They consist of an axoneme which is a central filament.
- Both structures have a 9+2 microtubule arrangement.
- Last but not least, both help in cell locomotion.
Differences between Cilia and Flagella
Below are the detailed differences between the two to help you better comprehend these structures.
Brief Description
Cilia
These are the tiny, slender, short hair-like structures found all over a cell’s surface. Cilia are seen supporting the locomotion of a cell.
Flagella
On the other side, flagella are relatively longer, complex hair-like structures that extend throughout the cell surface.
Presence
Cilia
Cilia are only present in eukaryotes, short in length but enormous in quantity.
Flagella
In contrast, flagella naturally occur in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. These are comparatively long but few in quantity that have the locomotory function in the prokaryotic cells.
Structure
Cilia
A typical cilium has a 9+0 axoneme structure, but when explicitly discussing motile cilia, it has a 9+2 axoneme. However, both do not contain nexin.
Flagella
On the contrary, flagella have a 9+2 axoneme structure with nexin present between microtubules.
Leading Role
Cilia
These play a leading function in the movement of a cell, respiration, circulation, and excretion.
Flagella
In contrast, flagella help only in locomotion.
Nature of Movement
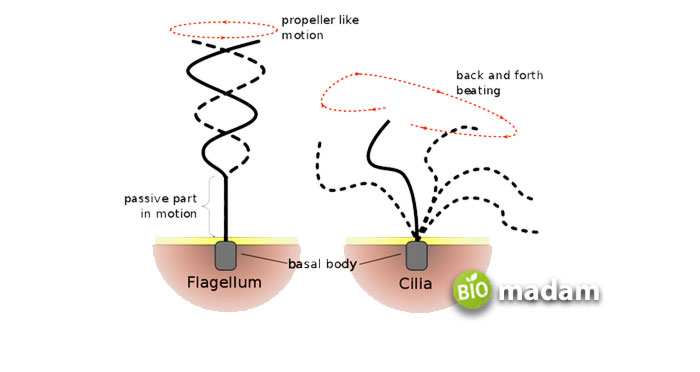
Cilia
Cilia are observed showing coordination through rotational movement. Moreover, these structures move at a pretty rapid rate.
Flagella
On the other hand, flagella present a sinusoidal, whip-like, independent movement that is slow compared to cilia.
Examples
Cilia
These microscopic structures are naturally present in the lining of various body tubes, such as reproductive organs in mammals and the intestinal lining.
Flagella
In contrast, numerous archaea and bacteria contain flagella. Besides, the euglena is a famous flagellated eukaryote.
Conclusion
As we know that cilia and flagella are majorly found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes, so they have a similar structure with differences only in numbers. The cells mainly function for locomotion but, in some cases, help in respiration, circulation, and excretion.
The cells also differ in their movement as cilia rotate while flagella have rotatory movement. Overall, cilia comprise a simple structure, whereas the flagella structure is complex, which is key in differentiating the two cells and their way of functioning.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.