Recently updated on October 5th, 2023 at 05:52 am
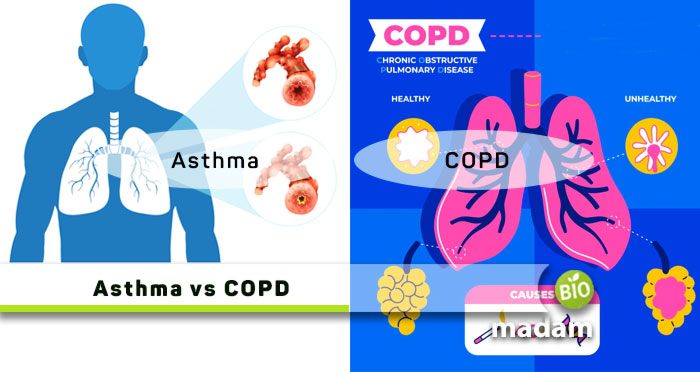
Asthma and COPD are respiratory system disorders that affect breathing. The symptoms of Asthma and COPD can be pretty similar and difficult to distinguish if one does not understand the difference between the two. Both diseases can cause airway infection and respiratory issues. A CRT or an RRT can conduct an accurate diagnosis of the condition that is vital to providing adequate treatment. For proper understanding, let’s talk about the differences between Asthma and COPD.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Asthma | COPD |
| Progression | Non-progressive | Progressive |
| Trigger | Allergens, cold | Fumes, smoke, and chemicals |
| Age | Any age | >40 years |
| Family History | Not necessary | Yes |
| Symptoms | Coughing, and breathing difficulties | Chronic cough, clearing throat |
| Occurrence | Symptomatic episodes | No symptom-free periods |
| Airway Obstruction | Reversible | Irreversible |
| Allergen Interaction | Yes | No |
| Smoking Influence | No | Yes |
| Sputum Microscopy | Increased eosinophil & cytotoxic T lymphocytes | Increase in neutrophils & helper T lymphocytes |
What is Asthma?
Asthma is typically characterized by breathing difficulties that may occur in episodes of sudden attacks. Asthma occurs as a result of swollen airways. The tightened muscles and increased mucus production cause difficulty in breathing, however you can overcome mild asthma through different breathing exercises. Allergens such as pollen are common asthma triggers. Yet, many other factors contribute to the condition. Some contributing factors include the common cold, upper respiratory tract infections, smoke, dry air, weather or climatic changes, pollution, excessive crying or laughing, strong smells, and anxiety symptoms.
Asthma does not present in the same way in each patient. Some might have more frequent asthma episodes, while others might have mild ones. Sometimes Asthma attacks can be fatal and require an inhaler. These inhalers typically contain corticosteroids that help improve respiration.
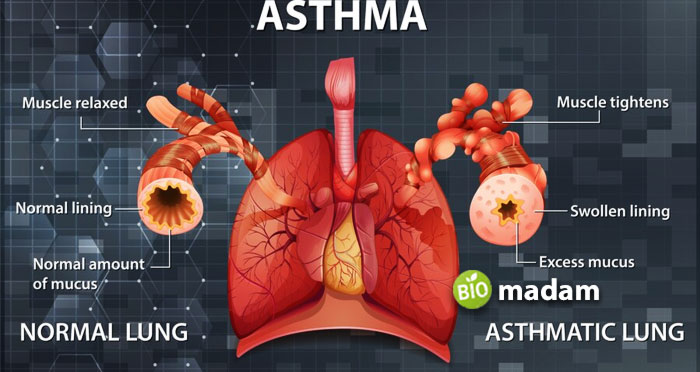
Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma may be caused by many triggers and exhibits itself through one or more of the following symptoms:
- Breathing difficulty
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Difficulty in talking
- A feeling of heaviness in the lungs or chest
- Anxiety
If any of these signs or symptoms occur, you might have asthma. Visit your physician to get a proper diagnosis. Though there is no permanent treatment for it, you can manage asthma by avoiding the triggers and keeping an inhaler at hand.
What is COPD?
COPD is a general term used to describe various respiratory system disorders like Bronchitis and Emphysema. Compared to asthma, bronchitis or COPD is a progressive disease. It does not occur in the form of spontaneous attacks. Instead, it affects the airway’s mucosal lining, which worsens over time. The presentation of COPD is similar to asthma. Bronchioles become stiff and inflamed, and more mucus is produced. The narrowing and tightening of the airway make it difficult to breathe with COPD.
Multiple factors like age and environment cause COPD. Like other bodily functions, the respiratory system also shows less disease resistance in old age. As you pass the age of 40, you become more susceptible to COPD. However, not everyone over 40 has COPD. It is also related to the lifestyle and surroundings. You are more likely to have COPD if you smoke regularly, which directly affects your lungs, or if you live in a polluted area.
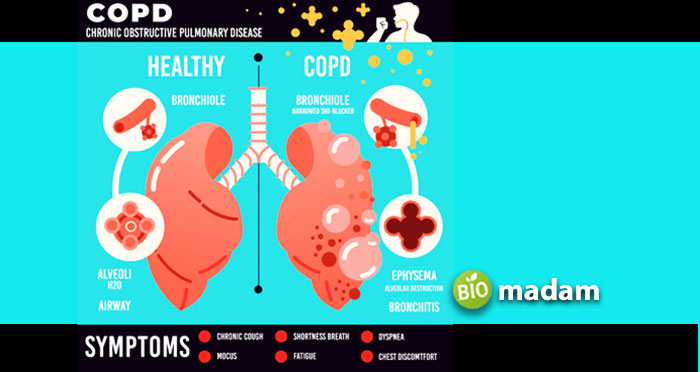
Symptoms of COPD
Symptoms of COPD are similar to asthma. The most widely exhibited symptoms of COPD include
- Recurrent coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Heaviness in the chest and lungs
Similarities Between Asthma and COPD
- Asthma and COPD are respiratory tract disorders.
- Both of them have similar symptoms like coughing, wheezing, breathing difficulties, etc.
- They cause inflammation in the airway, constricting the tract.
Differences Between Asthma and COPD
Definition
Asthma
Asthma is a non-progressive respiratory disorder causing breathing difficulties.
COPD
On the contrary, COPD is a progressive disorder of the respiratory system that may worsen over time.
Triggering Agents
Asthma
Asthma is typically triggered by allergens, the common cold, flu, smoke, etc.
COPD
Yet, COPD may result from working in fumes and chemicals, air pollution, or hereditary.
Progression
Asthma
Asthma does not worsen over time when the episodes are appropriately managed.
COPD
On the other hand, COPD is a progressive disease and may worsen depending on age and environmental factors.
Age
Asthma
Asthma is independent of age and may present in people of any age group.
COPD
In comparison, COPD is more common in people 40 years or more age.
Family History
Asthma
People with asthma may or may not have a family history.
COPD
Conversely, a person suffering from COPD is likely to have it in their family.
Symptoms
Asthma
Common asthma symptoms include coughing, abnormal breathing patterns, heaviness in the chest, etc.
COPD
Whereas, symptoms of COPD are chronic cough, clearing throat, and shortness of breath.
Occurrence
Asthma
Asthma presents itself in episodes exhibiting the above-mentioned symptoms. The patient does not show any signs meanwhile.
COPD
In contrast, there is no symptom-free period in COPD as it is a progressive disease.
Airway Obstruction
Asthma
Airway obstruction in asthma is reversible.
COPD
On the opposite, airway obstruction in COPD is irreversible.
Allergens
Asthma
Asthma typically occurs due to interaction with an allergen or a pathogen having antigen, besides other gene-environmental interactions.
COPD
However, COPD is not affected by allergens. Instead, other environmental factors like smoke and fumes contribute to it.
Smoking
Asthma
Smoking is not a primary causing factor in asthma.
COPD
But, the chances of COPD increase if you have been smoking for several years.
Sputum Microscopy
Asthma
Sputum microscopy in the case of asthma shows increased eosinophil and cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
COPD
Conversely, COPD sputum microscopy presents an increase in neutrophils, helper T, and B lymphocytes in the mucous.
The Bottom Line
Asthma and COPD are airway diseases that constrict the respiratory tract. They cause the narrowing of the airway by swelling the tract and increasing mucous production. Asthma is commonly attributed to antigen interaction, whereas COPD results from fume intake and old age. People over the age of 40 are more susceptible to COPD. They exhibit similar symptoms. You can observe the difference between Asthma and COPD by Spirometry. Airway obstruction in asthma is reversible and managed by inhalers. On the other hand, COPD is a progressive disorder. Asthma needs timely management, while COPD requires long-term treatment.

FAQs
What are the forms of COPD?
The two most common forms of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis progresses through increased mucus production in the respiratory tract, whereas Emphysema causes airway inflammation.
How do doctors know if you have asthma or COPD?
Asthma and COPD have similar symptoms differentiated through Spirometry. It is a simple, painless test and is considered the best way to diagnose COPD.
What is ACO?
Asthma-COPD overlap (ACO) refers to the coexistence of asthma and COPD. While asthma and COPD are specific diseases, they sometimes coexist. One may occur when the other exists already. It means that their airway reacts to allergens and triggers different stages of an allergic reaction. They also produce excessive mucus and swelling of the tract. It can sometimes be deadly.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.