The human brain is a fascinating organ that controls every aspect of our daily lives, from basic functions like breathing and digestion to more complex tasks such as decision-making and creativity. At the very base of the brain lies the brain stem, a small but mighty structure that is responsible for regulating some of the most critical functions of the body. Despite its relatively small size, the brain stem is a complex and essential component of the human brain that plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of the body.
This article will help you explore the main functions of the brain stem, besides highlighting its location, structure, and causes of brain stem damage.
Location of the Brain Stem
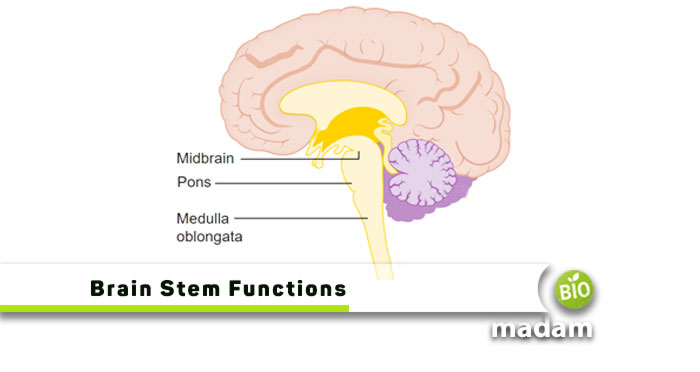
The brain stem is located at the base of the brain, between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. It sits just above the spinal cord and connects to the cerebellum, diencephalon, and cerebral cortex. The brain stem is divided into three main parts: the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain, each with its specific functions and structures. Its location is essential as it acts as a bridge between the spinal cord and the brain, regulating many vital functions that are necessary for the body’s proper functioning.
Functions of the Brain Stem
The various cranial nerve nuclei and tracts found in each area of the brain stem dictate the specific functions of that area. Let’s glance at the vital functions mentioned below:
Controls Breathing
The medulla oblongata is responsible for controlling breathing. It regulates the rate and depth of breathing by monitoring the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood. The medulla oblongata sends signals to the muscles involved in breathing to ensure proper oxygenation of the body.
Regulation of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
The medulla oblongata also regulates the heart rate and blood pressure. It sends signals to the heart to increase or decrease its rate depending on the body’s needs. The medulla oblongata also regulates blood pressure by adjusting the diameter of blood vessels.
Controls Digestion
The medulla oblongata controls digestion by regulating the muscles in the digestive system. It coordinates the movement of food through the digestive tract and controls the secretion of digestive enzymes.
Balancing Consciousness
The reticular formation, located in the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, plays a critical role in regulating consciousness. It receives sensory input from the body and filters out irrelevant information. The reticular formation also helps in maintaining wakefulness and alertness.
Monitoring Reflexes
The brain stem is responsible for several reflexes, including the gag reflex, cough reflex, and sneeze reflex. These reflexes protect the body from potential harm.
Regulation of Sensory and Motor Control
The brain stem plays a crucial role in regulating sensory and motor functions by involving sensory and motor neurons. It receives sensory input from the body and relays it to the appropriate parts of the brain. It also controls motor functions by sending signals to the muscles involved in the movement.
Sleep and Arousal
The brain stem is responsible for regulating the sleep-wake cycle and maintaining consciousness.
To sum up, this part of the brain has three fundamental functions:
- It serves as a pathway for ascending and descending neural pathways that travel to and from the brain.
- It houses the nuclei responsible for the control of the cranial nerves.
- It integrates the functioning of multiple vital systems.
Structure of the Brain Stem
The brain stem is a complex structure that is divided into three main parts. Each of these parts has specific structures and functions contributing to the overall function of the brain stem.
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brain stem and connects to the spinal cord. It is in charge of vital activities such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. The medulla also contains centers that control reflexes such as coughing, sneezing, and swallowing. It also contains cranial nerve nuclei, which control the sensory and motor functions of the face, head, and neck.
Pons
The pons is located above the medulla and is responsible for connecting the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating sleep, arousal, and consciousness, and also helps in the coordination of breathing. The pons has centers for the regulation of certain reflexes and cranial nerve nuclei that control facial muscles, hearing, and balance.
Midbrain
The midbrain is the uppermost part of the brain stem and is located between the pons and the diencephalon. It contains special structures that play a crucial role in the regulation of movement, including the substantia nigra, which produces dopamine, a neurotransmitter and a hormone, to helps in the control of voluntary movement. The midbrain further has the colliculi, which are involved in visual and auditory reflexes.
Common Causes of Brain Stem Damage

Brain stem damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Traumatic Injury: Trauma to the head, such as a concussion or severe blow, can result in brain stem damage.
Stroke: A stroke occurs when there is a disruption of blood flow to the brain, which can damage the brain stem.
Infections: Certain infections, such as meningitis or encephalitis, can cause inflammation and damage to the brain stem.
Tumors: Brain tumors or cysts can grow and cause damage to the brain stem.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Certain neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy, can cause damage to the brain stem over time.
Genetic Disorders: Some genetic disorders or diseases, such as Leigh syndrome or mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, can cause damage to the brain stem.
Chemical Exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as carbon monoxide or lead, can cause damage to the brain stem.
It is essential to look for a doctor’s help promptly if there are any signs or symptoms of brain stem damage, as it can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening conditions.
Symptoms of Brain Stem Damage
The symptoms of brain stem damage can vary depending on the location and extent of the injury. Some of the common symptoms of brain stem damage include:
- Difficulty with basic life-sustaining functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure
- Weakness or paralysis of the face, arms, or legs on one or both sides of the body
- Problems with balance and coordination
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Loss of sensation or numbness in the face or limbs
- Vision or hearing loss
- Changes in consciousness, such as drowsiness or coma
- Severe headaches
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
A thorough evaluation by a medical professional is necessary to determine the cause of the symptoms and appropriate treatment options.
What can be the Consequences of Brain Stem Damage?
The brain stem is a crucial component of the human brain, and any damage to it can have severe consequences. Damage to the brain stem can lead to several conditions, including:
Coma: Damage to the reticular formation can lead to a coma, a state of unconsciousness.
Breathing Difficulties: Damage to the medulla oblongata can cause breathing difficulties, leading to respiratory failure.
Dysautonomia: Dysautonomia is a condition that results from damage to the autonomic nervous system, which is regulated by the brain stem. It can lead to several symptoms, including lightheadedness, low blood pressure, and fainting.
Movement Disorders: Damage to the midbrain can result in movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement control.
Sensory and Motor Deficits: Damage to the brain stem can lead to sensory and motor deficits, including weakness or paralysis on one side of the body.
Is it Possible to Recover from Brain Stem Damage?
The recovery from a brain stem injury depends on several factors, including the extent and severity of the injury, the location of the damage, the age and overall health of the patient, and the timeliness and effectiveness of the medical intervention.
In some cases, the brain stem can recover partially or completely from the injury. The recovery process may involve a combination of medical treatments, rehabilitation, and lifestyle changes to manage the symptoms and support the recovery process.
However, in severe cases, the damage may be irreversible, leading to permanent disabilities or even death. The most severe injuries to the brain stem can result in a condition called “locked-in syndrome,” in which the person is fully conscious but unable to move or communicate. It is crucial to seek medical attention immediately if there are any signs or symptoms of a brain stem injury to increase the chances of recovery. In some cases, early intervention can help prevent further damage and improve the outcome.
Treatment for Brain Stem Damage
In cases of mild brain stem injury, rest and observation may be enough, while more severe injuries may require hospitalization and intensive treatment.
Here are some of the treatment options for brain stem damage:
Medications
Medications may be given to control symptoms such as pain, inflammation, or seizures. In some cases, medications may also be used to help improve brain function and reduce the risk of further damage.
Surgery
Surgery may be necessary in cases where there is bleeding, swelling, or pressure on the brain stem. The type of surgery will be determined by the location and severity of the damage.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is an essential component of treatment for brain stem damage. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy may be used to help patients recover lost function and improve their quality of life.
Supportive Care
Patients with severe brain stem damage may require supportive care, such as mechanical ventilation or feeding through a tube.
The treatment of brain stem damage is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The goal of treatment is to minimize the damage and promote recovery to the fullest extent possible.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Brain Stem

Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy brain stem:
Stay Physically Active: Regular physical activity has been shown to improve brain health and reduce the risk of cognitive decline. Exercise moderately for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
Eat a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in macro and micronutrients can help keep your brain stem healthy. Include foods such as whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables in your diet.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can have negative effects on the brain stem and other parts of the brain. Engage in relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
Get Enough Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for brain health. Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep each night, and establish a regular sleep routine.
Protect your Head: Wear protective headgear during sports and other activities that may pose a risk of head injury.
Avoid Harmful Substances: Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, which can damage the brain stem and other parts of the brain.
Keep your Mind Active: To keep your brain active and healthy, engage in cognitively challenging activities such as reading, puzzles, or learning a new skill.
Takeaway
The brain stem is a crucial part of the central nervous system that is responsible for controlling various vital functions of the body. The brain stem is involved in controlling respiratory and cardiovascular functions, swallowing, and sensory and motor functions. It also contains cranial nerve nuclei that play a significant role in vision, hearing, and facial movements.
Damage to the brain stem can have severe clinical implications, including life-threatening conditions. Therefore, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any symptoms of brain stem damage. While we cannot control all the factors that can lead to brain stem damage, we can take steps to maintain a healthy brain stem. With proper care and treatment, many people can recover from brain stem injuries and regain lost function.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.