Disease and disorder are commonly used in pathology, anatomy, and physiology. But are disease and disorder the same thing? Although primarily being used interchangeably, they are not the same. They present similarly, yet the causes and influencing factors may vary. Diseases usually have a clear underlying internal or external cause. Contrary, disorders typically arise from lifestyle and genetic elements. Keep reading to know more about what is the difference between disease and disorder in detail for better understanding.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Disease | Diagnosis |
| Types | Infectious & non-infectious | Physical, mental, behavioral, emotional, structural, & genetic |
| Causes | Pathogenic, lifestyle | Genetic, lifestyle, environmental |
| Structural Changes | Yes | No |
| Transmittance | May be | No |
| Treatment | Curable | Manageable |
| Examples | Dengue fever, CVD, etc. | Thalassemia, PCOS, ASD, etc. |
What is a Disease?
A disease is a condition that has a known cause and may be treated. The oldest expression of disease goes back to 842 Circa when the French word ‘despise’ was used to represent disease. A combination of ‘des’ and ‘aise’ combined meant ‘without ease’.
The initial definitions of the disease have been explained as early as 1900. Disease results from a pathophysiological response to external or internal factors. It refers to changes in the normal functioning of cells, tissues, and organs by changes in the body due to internal or external factors.
Different Types of Diseases
There is no specific classification of diseases, and they may be categorized based on different characteristics. They may be caused due to various factors and thus classified in multiple ways. One of the most common categorizations is on the basis of causing entity, while others depend on the prognosis and effect of the disease on the body. Here are the fundamental types of diseases:
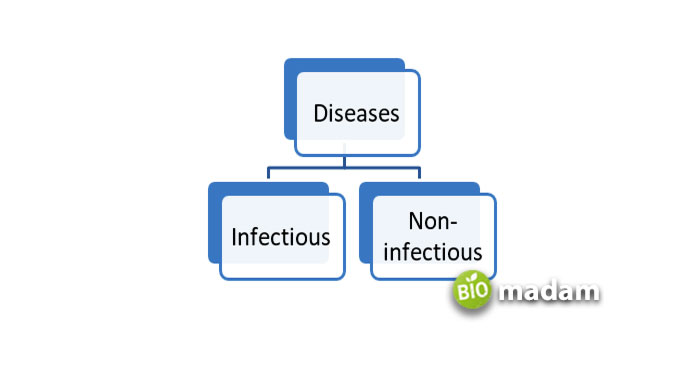
Infectious Diseases
Infections and diseases have been used for each other for a long time, especially by people who do not know much about disease types. Infections are diseases, but all diseases are not infections. Infectious diseases refer to changes in the body due to exposure to an antigen or pathogen. Pathogens like viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi, and bug bites may lead to infectious diseases.
Examples of infectious diseases include malaria, flu, poliomyelitis, etc.
Non-infectious Diseases
As the name suggests, non-infectious diseases are not caused by external pathogens like bacteria or viruses. Instead, non-infectious diseases may result from environmental and genetic factors. Malnutrition and poor lifestyle choices also contribute to non-infectious diseases.

Some non-infectious diseases are cardiac diseases, diabetes, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
What is a Disorder?
A disorder is a set of issues due to physiological factors leading to distress and impairment. Disorders may be physical or mental, leading to problems in daily life. One of the major differences between disease and disorder is the treatment and management of the conditions. Symptoms and signs of diseases may be treated with adequate medication. On the other hand, disorders may be managed using an adequate therapy regimen. Sometimes the causes of disorders are challenging to identify, and complications vary in individuals.
Types of Disorders
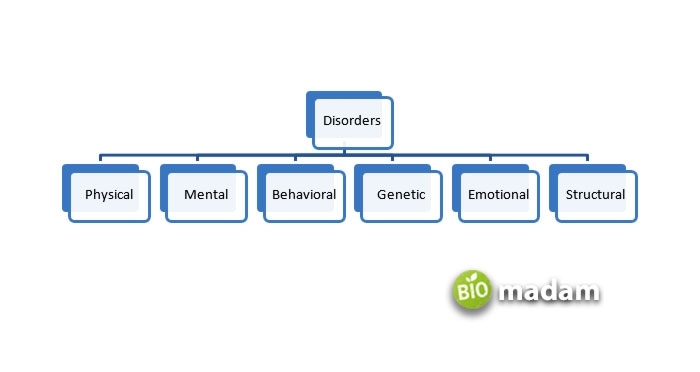
Physical Disorder
Physical disorders refer to problems that affect the bodily systems and can be identified using blood tests, CT scans, X-rays, etc. They typically exhibit physical symptoms like nausea, pain, headaches, etc.
Mental Disorder
Mental disorders refer to fluctuation in the nervous system that influences your emotional well-being. Unattended mental disorders like ASD, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder may lead to aggravated symptoms.
Behavioral Disorder
Behavioral disorders may arise from different underlying causes and affect day-to-day comprehension and function. ADHD is one of the common behavioral disorders in children and adults nowadays.
Genetic Disorder
Genetic disorders result from mutations in DNA and genes affecting normal functions. They may present physical or mental symptoms. Genetic disorders include thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, cleft lip, palate, etc.
Structural Disorder
Structural Disorders refer to physical damage to bodily organs or tissues due to mental or physical trauma. Damage to tendons and ligaments restricting movement may also be classified as a structural disorder.
Emotional Disorder
Emotional disorders may arise from various underlying factors and lead to emotional symptoms like anxiety symptoms, depression, panic attacks, etc.

Difference between Disease and Disorder
There is a clear difference between disease and disorder in medicine that is explained below:
Definition
Disease
The disease is characterized by specific signs or symptoms altering the body’s normal functioning.
Disorder
A disorder, on the other hand, is a disruption in physical or mental function that may lead to impairment and unease.
Types
Disease
Diseases are divided into infectious and non-infectious, depending on their causes.
Disorder
On the contrary, disorders may be categorized as physical, mental, behavioral, emotional, structural, and genetic.
Causes
Disease
External factors like pathogens or internal issues usually cause diseases.
Disorders
Disorders may arise from fluctuations in normal body physiology and genetic and environmental factors.
Structural Changes
Disease
Diseases may lead to structural changes in the body.
Disorder
Disorders do not cause any changes to the body structure.
Transmittance
Disease
Diseases are communicable if caused by pathogens. Other diseases are non-transmittable.
Disorder
Infectious entities do not cause disorders; thus, they are not communicable.
Treatment
Disease
Diseases can be treated using the right set of medications and physical therapy.
Disorder
On the other hand, disorders are not entirely curable generally and may be managed through adequate therapy.
Examples
Disease
Examples of diseases are malaria, kidney disease, atherosclerosis, etc.
Disorder
Physical and mental disorders include thalassemia, arrhythmia, bipolar disorder, etc.
The Bottom Line
Disease and disorder are often used interchangeably, yet they are not entirely the same. External factors may cause diseases, whereas disorders typically result from lifestyle, genetic or environmental factors. The most notable difference between disease and disorder is the causative agents and treatment. Disorders may be managed through medication and therapy, while diseases are completely curable if treated adequately.
FAQs
What is the difference between disease and condition?
Condition or illness is a broader term for different ailments resulting from various factors. When identifying a specific pathological situation, conditions are divided into disease or disorder.
Is cancer a disease or disorder?
Cancer is a disease that can be developed due to several causes, where the cells divide uncontrollably, leading to tumors. Benign tumors may become malignant when they spread to neighboring tissues. Changes in the DNA of the cell lead to cancer.
What is the difference between syndrome and disease?
Diseases usually have specific causes and indicate symptoms that may be treated through proper treatment. However, a syndrome may not always have a definite cause and exhibits a group of multiple symptoms.
What are the differences between disease and disorder in plants?
Plants may suffer diseases caused by elements like infection by a pathogen, insect feeding, injury, etc. Nevertheless, growth disorders may rise when plants are not grown under adequate conditions and provide inadequate light, water, or nutrients.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.