Photosynthesis and respiration are important plant processes that are critical for the survival of human beings in biomes and ecosystem. Plants produce their food through photosynthesis and act as producers to run the food chains and food webs. The main difference between chlorophyll A and B is their role in the process. Chlorophyll A is the main pigment in photosynthesis, while Chlorophyll B facilitates the former. Let’s tell you about the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis and further differences between chlorophyll A and B.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Chlorophyll A | Chlorophyll B |
| Definition | Photosynthetic pigment | Accessory pigment |
| Present in | Algae, plants, and cyanobacteria | Plants and algae |
| %age in Plants | 75% | 25% |
| Color | Blue-green | Olive green |
| Absorbed λ | 430 nm to 660 nm | 450 nm to 650 nm |
| Absorbed Color | Red-orange and violet-blue | Red-orange |
| Reflected Color | Blue-green | Yellow-green |
| Rate of Absorption | Stronger | Weaker |
| Structure | Chlorin ring with a CH3 group in 3rd position | Chlorin ring with R-CH=O in 3rd position |
| Formula | C55H72MgN4O5 | C55H70MgN4 O6 |
| Mol. Weight | 839.51 g/mole | 907.49 g/mole |
Role of Chlorophyll in Photosynthesis
Plants produce their food through photosynthesis as opposed to chemosynthesis, adopted by several bacteria. Plants use water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide to manufacture glucose. Plants convert light energy into chemical energy, and oxygen is released. Photosynthesis is essential to life as it maintains the oxygen levels in the environment critical for sustaining life.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in all eukaryotic green plants and is vital to the process of photosynthesis. Plants have four types of chlorophyll, including chlorophyll A, B, C, and D. Chlorophyll A and B are abundant in green plants. In contrast, chlorophyll C and D are found in marine algae and cyanobacteria, respectively.
Keep reading to learn all about Chlorophyll A and B in detail.
What is Chlorophyll A?
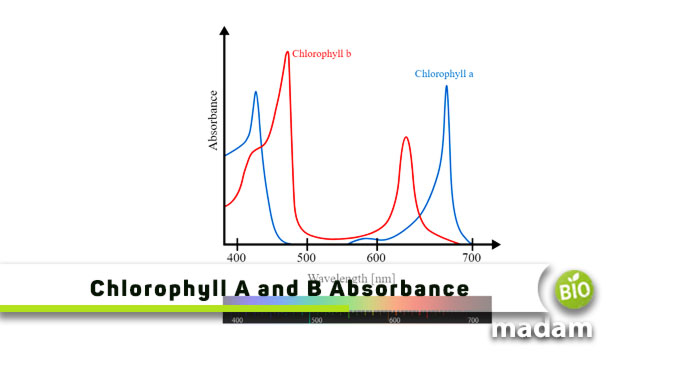
Chlorophyll A is the primary green pigment responsible for light absorption and provides energy for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll A reflects blue-green light, giving leaves the characteristic green color. It absorbs visible light of wavelengths 429 nm and 659 nm most effectively. They depict violet-blue and orange-red colors.
Chlorophyll A transfers the trapped energy into P680 andP700. It is the primary electron donor in the photosynthesis electron transport chain.
What is Chlorophyll B?
Chlorophyll B is the accessory pigment that contributes to photosynthesis in algae and green plants. It collects energy in the form of light and passes it to Chlorophyll A. Chlorophyll B reflects yellow-green color compared to chlorophyll A. Chlorophyll B increases the absorption spectrum by offering a broader range of the light spectrum. It absorbs 455 nm and 642nm, the most efficiently that exhibits violet and red colors.
When enough light is not present, plants produce more chlorophyll B instead of chlorophyll A. The production of chlorophyll B allows them to increase their photosynthetic ability. Plant cells pass the captured light from one pigment to the other until it reaches chlorophyll A.
Chlorophyll A requires Chlorophyll B to extend the absorption spectrum. On the other hand, Chlorophyll B cannot produce enough energy independently. Thus, they both are essential to photosynthesis in plants.

Similarities between Chlorophyll A and B
- Chlorophyll A and B are green-colored pigments in plants and almost all classes of algae.
- They are involved in photosynthesis.
- Both pigments absorb light energy to produce food.
Difference between Chlorophyll A and B
Definition
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll B
On the other hand, chlorophyll B is the accessory pigment that passes light to chlorophyll A.
Present In
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A is a component of all algae, plants, and cyanobacteria.
Chlorophyll B
Whereas chlorophyll B is found in green algae and plants only.
Percentage in Plants
Chlorophyll A
75% of all chlorophyll present in plants is Chlorophyll A.
Chlorophyll B
Conversely, chlorophyll B is found in around 25% of photosynthetic plants.
Pigment Color
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A is blue-green in color in the pure state.
Chlorophyll B
Alternatively, chlorophyll B gives an olive green hue in its pure state.
Absorbed Light
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A absorbs light between 430 nm to 660 nm.
Chlorophyll B
On the other hand, chlorophyll B absorbs light wavelengths ranging between 450 nm to 650 nm.
Effectively Absorbed Light
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A absorbs wavelengths 429 nm and 659 nm most effectively.
Chlorophyll B
Contrarily, it most effectively absorbs the light wavelength of 455 nm and 642nm.
Absorbed Color
Chlorophyll A
This pigment absorbs red-orange and violet-blue colors from the spectrum.
Chlorophyll B
However, chlorophyll B absorbs only red-orange light from the spectrum.
Reflected Color
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A reflects the blue-green color that gives leaves their characteristic green color.
Chlorophyll B
At the same time, chlorophyll B reflects yellow-green color compared to chlorophyll A.
Rate of Absorption
Chlorophyll A
The rate of absorption of chlorophyll A is stronger than other chlorophyll pigments.
Chlorophyll B
On the contrary, chlorophyll B has a weaker absorption rate than chlorophyll A.
Structure
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A comprises a chlorin ring with a methyl group in the third position.
Chlorophyll B
But, the chlorin structure of chlorophyll B has an aldehyde group in the third position.
Chemical Formula
Chlorophyll A
The chemical formula of Chlorophyll A is C55H72MgN4O5.
Chlorophyll B
Nevertheless, chlorophyll B is represented by the chemical formula C55H70MgN4O6.
Molecular Weight
Chlorophyll A
The molecular weight of chlorophyll A is 839.51 g/mol.
Chlorophyll B
Yet, chlorophyll B possesses a molecular weight of 907.49 g/mol.
The Bottom Line
Chlorophyll is essential to photosynthesis in autotrophic organisms. Photosynthetic organisms have chlorophyll A, B, C, or D, which helps produce food by capturing light. Green plants and algae have chlorophyll A as the primary and chlorophyll B as the accessory pigment. One of the major differences between chlorophyll A and B is that the latter does not directly play a role in food synthesis. Chlorophyll A captures light to convert it into glucose. At the same time, chlorophyll B passes the light to chlorophyll A. Chlorophyll A is abundant in plants (75%), while chlorophyll B is in lesser quantity (25%).
FAQs
What’s the role of chlorophyll A and B?
Chlorophyll A and B are green pigments involved in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is an essential pigment, while chlorophyll B is the accessory pigment. The former traps the light energy and emits electrons during the process. Chlorophyll B passes the trapped energy into chlorophyll A.
Why do plants have 2 types of chlorophyll?
While chlorophyll A is the primary pigment, chlorophyll B helps broaden the absorption spectrum. Thus, both pigments work together to produce enough food in the plant.
Do all plants have chlorophyll A and B?
All green plants have chlorophyll A and B compared to cyanobacteria with chlorophyll C or D. Chlorophyll A reflects orange-red and blue-violet light. In contrast, chlorophyll B reflects orange-red light only.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.