Recently updated on March 4th, 2023 at 07:21 am
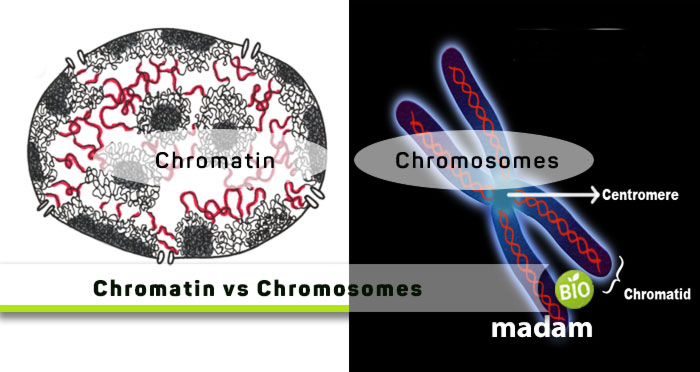
Chromatin and chromosomes carry the hereditary material, called DNA, of an organism. The only fundamental difference between them is the structure. Chromatin is a rather unorganized form of genetic material. Alternatively, chromosomes are highly organized and directly involved in reproduction. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have these structures, but these are dispersed in the cytosol of cytoplasm in the latter. Chromatin and chromosomes carry essential genetic information regarding the structure and function of an individual. They appear during different stages of cell division. Let’s tell you everything about chromosomes and chromatin and what differentiates them.
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Chromatin | Chromosome |
| Nature of Genetic Material | In long strings | A condensed form |
| Composition | Nucleosomes | Chromatin fibers |
| Structure | DNA wrapped around histone proteins | Condensed structure with two chromatids |
| Appearance | Long, uncoiled structure | X-shape with p and q arm |
| Condensation | 50 times | 10,000 times |
| Presence | Interphase | Metaphase & anaphase |
| Function | Packaging of gene material | Equal distribution of genetic material |
| Microscopy | Electron microscope | Light microscope |
| Pairing | Absent | Present |
| Metabolism | Gene regulation and cell division | No metabolic activity |
What Is Chromatin?
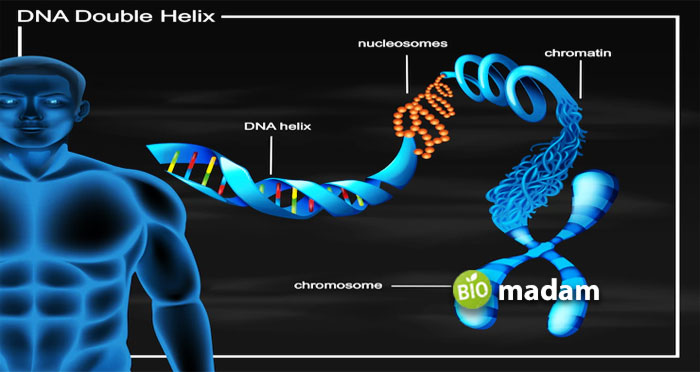
Chromatin is a complex present in different types of eukaryotic cells. It comprises DNA, RNA, and proteins. Nucleosomes make up chromatin. They are a complex of DNA and histone proteins.
Chromatin packages the DNA double helix. It allows DNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and promotes gene expression. Chromatin saves the DNA from entangling and prevents damage. The genetic material in the cell typically appears in the form of chromatin. Chromatin is of two types; euchromatin and heterochromatin. Heterochromatin is the inactive form and offers structural support to the genome. On the other hand, euchromatin is the active, expressive form of genes.
Structure of Chromatin
Chromatin is found in the nucleus and is a thread-like form. The chromatin fiber has a diameter of 10 nm. It is made of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are DNA strands wrapped around histone proteins. There are usually 150 to 200 strands of DNA around eight histone proteins to form nucleosomes. Linker DNA interconnects the nucleosomes. The linker DNA has between 20 and 60 base pairs. It contains H1 histones. Nucleosomes along with histones proteins are termed chromosomes. Chromatosome formation gives its particular form to chromatin. It looks like beads on a long string in a condensed form.
What are Chromosomes?
Chromosomes carry the genetic material and are involved in the replication and transcription of DNA. They consist of DNA and packaged proteins. They are characteristic of eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes have several chromosomes. Some organisms have more than one chromosome set. Humans contain 46 chromosomes or a pair of 23. 44 chromosomes are 22 homologous pairs with the same chromosomes, called autosomes, while two are sex chromosomes. These two sex chromosomes are X and Y chromosomes, with Y present only in men.
Structure of Chromosomes
Chromosomes form chromatin fibers. It is the highest form of structural condensation of genetic material. The chromosomes contain multiple genes packed in the double-stranded DNA. The DNA molecules are tightly wrapped around the histone proteins to fit them inside the cell. If you uncoil the histones and DNA in a human cell to form a long chain, they will be as long as six feet.
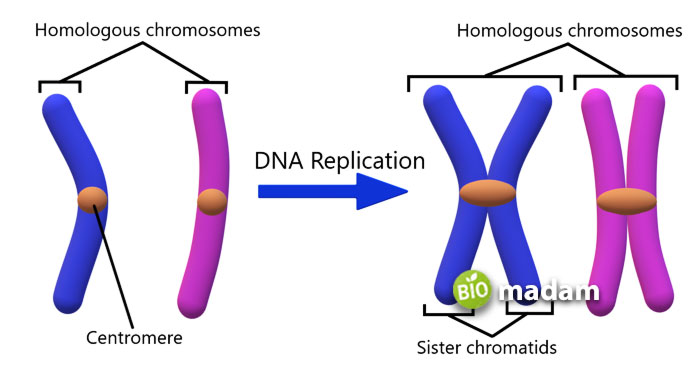
Chromosomes only appear in the dividing phase and are not visible under a student microscope in the non-dividing phase. Chromosomes have two strands called sister chromatids. They join at a central point called the centromere giving rise to four arms. The short arm is the “p arm” while the long arm is the “q arm.”
As chromosomes have a vital function in reproduction, they perform their task accurately. However, sometimes mutations may occur. Mutations in genes during replication can lead to health issues. For example, sickle cell anemia develops as a result of a mutation. Furthermore, people with Down syndrome have three Chromosome 21 copies instead of two.
Similarities Between Chromatin and Chromosomes
- Chromatin and chromosomes carry genetic information.
- They are both found in eukaryotic cells, and to some extent, in prokaryotic cells.
- They comprise DNA and histone proteins.
Differences Between Chromatin and Chromosomes
Definition
Chromatin
Chromatin is the genetic material in the cell made of DNA wrapped around histone proteins.
Chromosomes
Whereas, chromosomes are the condensed form of chromatin and appear during cell division.
Composition
Chromatin
Chromatin is composed of nucleosomes.
Chromosomes
Yet, chromosomes comprise chromatin fibers.
Structure
Chromatin
Chromatin has helical DNA strands wrapped around histone proteins.
Chromosomes
On the contrary, chromosomes have a condensed and thick structure with two chromatids.
Appearance
Chromatin
It has a thread-like, long, thin uncoiled structure.
Chromosomes
However, chromosomes contain two thick strands joined together in the form of an X with p arms shorter than q arms.
Condensation
Chromatin
Chromatin is 50 times condensed compared to the normal DNA strands.
Chromosomes
In comparison, chromosomes are 10,000 times more folded and condensed than the normal DNA double-helix.
Presence
Chromatin
Chromatins appear in the interphase of the cell cycle.
Chromosomes
Conversely, chromosomes form during the metaphase of the cycle and are present in the anaphase.
Function
Chromatin
It allows the packing of the genetic material into the nucleus and regulates gene expression.
Chromosomes
However, chromosomes enable the proper arrangement of genetic material during cell division.
Microscopy
Chromatin
Chromatin can only be observed under an electron microscope.
Chromosomes
Unlike, chromosomes appear only during division. You can see them under a light or compound microscope.
Pairing
Chromatin
Chromatin is in free form and not present in pairs.
Chromosomes
In contrast, chromosomes are found in pairs. They can be homologous.
Metabolism
Chromatin
Chromatin is involved in gene expression regulation and cell division.
Chromosomes
Alternatively, chromosomes do not exhibit any metabolic activity.
The Bottom Line
Chromatin and chromosomes contain the genetic material of the cell. Chromatin is a less organized form, whereas chromosomes are highly condensed. Chromosomes are not present in the cell all the time. They form during cell division. They ensure equal distribution of DNA in daughter cells. A significant difference between chromatin and chromosome is their observation. Chromatin is only seen under an electron microscope. Alternatively, you can observe different types of chromosomes under a light microscope. They do not have metabolic activity.
FAQs
What is the relationship between chromatin and chromosomes?
Histone proteins and DNA combine to form chromatin. Chromatin forms chromosomes on further condensation. Chromosomes are a higher level of organization than chromatin.
In which phase are chromatids pulled apart?
Chromatids split during anaphase, where they move to different cells eventually.
Why do chromosomes look like an X?
When chromatin condenses into chromosomes, they join at a central point. It results in the formation of an X shape.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.