Recently updated on June 1st, 2023 at 07:46 am
The nucleus is known as the brain of the cell and the most important part of the cell besides mitochondria. While mitochondria are the cell’s powerhouse, the nucleus is responsible for growth and reproduction. It is the largest component of the cell, taking up 10% of the total volume.
What is Nucleus?
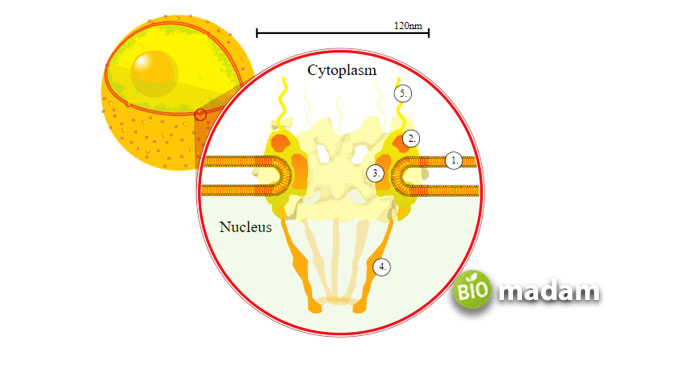
The nucleus is the information center of the cell. It contains all data for the organism’s growth, development, and sexual reproduction. It has a double-membrane that separates it from the rest of the cell and prevents the mixing of nuclear material with other components of the cell. The porous nuclear membrane enables material transport in and out of the cell.
Parts of Nucleus
The nucleus comprises four major parts:
Nuclear Envelope
It is a double-layered membrane that encloses the nucleus’ contents. The nuclear membrane is also made of a lipid bilayer that allows the entrance and exit of materials from the nucleoplasm to the cytosol or cytoplasm. Molecules that go in and out of the nucleus include RNA, performing its various functions, and proteins.
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is an important nucleus component that helps synthesize ribosomes by assembling and transcribing ribosomal RNAs. It does not have a membrane but may contain up to four nucleoli. The nucleolus has an eminent role in cell division.
Nucleoplasm
You may call the nucleoplasm the cytoplasm of the nucleus. It is gelatinous and semi-aqueous and composed of water, different enzymes, salts, and other organic molecules. The nucleoplasm helps protect the components of the nucleus. It provides a space for the transport of materials.
Chromatin/Chromosomes
They consist of DNA that carries all genetic information of the cell. Chromosomes, including this DNA, carry instructions for development, growth, and reproduction. When no cell division occurs, chromosomes are present in a free form called chromatin. It is composed of histone proteins and DNA. Chromosome is further divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin according to its looks and function.
Function of Nucleus
The nucleus performs numerous functions relating to growth and reproduction in plants, animals, and other eukaryotes. Some of which include:
- It is responsible for growth, differentiation, protein synthesis, and cell division.
- It contains the cell’s hereditary material in the form of chromatin and chromosomes.
- The nucleus is the site of DNA replication in eukaryotes.
- The semipermeable envelope allows the transport of materials from the cytoplasm to the nucleoplasm and vice versa.
- Proteins and RNA is present in the nucleus and contribute to reproduction and differentiation.
- Ribosomes are produced in the nucleolus.
- The nucleus allows chromatin to arrange into chromosomes for cell division.
- The nucleus regulates metabolism in the cell through the synthesis of enzymes.
- The presence of a nuclear envelope helps keep the information content safe in the nucleus.
- It provides a space for transcription (conversion of DNA into mRNA).
The Bottom Line
The nucleus is the site of cell division and transcription within the cell. It consists of four parts, out of which the chromatin carries the genetic information. At the time of division and differentiation, the chromatin material packages itself into highly structured forms known as chromosomes. It is the main site for the regulation of metabolism, ribosome production, and cell division.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.