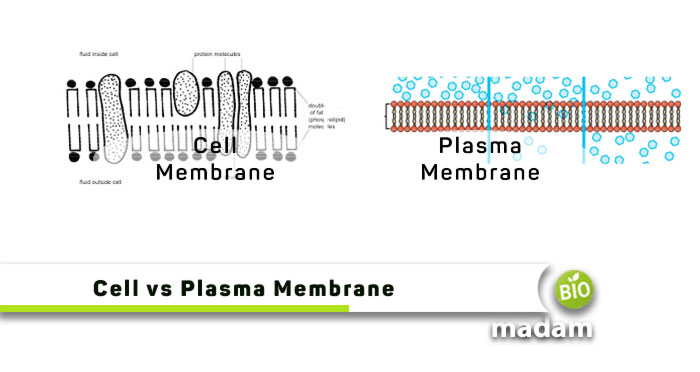
You must have visited this page after being baffled by the terms cell membrane and plasma membrane. Are you looking for a contrast between the two? These cell membranes and plasma membranes are muddled and applied most of the time synonymously. The key differentiating feature among these cellular terms is that the cell membrane bounds a complete cell, whereas the plasma membrane hops a particular organelle.
Let’s walk through this article to analyze more differences between these membranes, but before that, we have compiled a comparison table below.
Comparison Table
| Basis of Comparison | Cell Membrane | Plasma Membrane |
| Location | Surrounds a whole cell | Covers a cell’s internal structures |
| Composition | Composed majorly of phospholipid layers. | The composition can differ with organelles |
| Tonicity | Involves in maintaining tonicity of a cell | Doesn’t help in the tonicity of a cell |
| Function in Cytokinesis | Helps in cytokinesis during cell division | No function in cytokinesis |
| Presence of Cilia | Can consist of cilia for better movement | Cilia is never present on it |
| Fighting with Foreign Substances | Act as a barrier against harmful agents (types of bacteria) | Doesn’t necessarily fight with external particles. |
Explain Cell Membrane
Any layer bounding a complete cell and its internal structures is known as a cell membrane. Such membranes are made up of two phospholipid layers planted with essential proteins. All cell membranes are known to be selectively permeable because of their nature. The lipid tail present in them is hydrophobic, which means they are water-repelling and welcome the glycerol/cholesterol contents. Moreover, the integral proteins play an influential role in the transportation of several molecules, e.g., nitrogen, oxygen, CO2, CO, etc., in and out of the cell, just like the lipid bilayers.
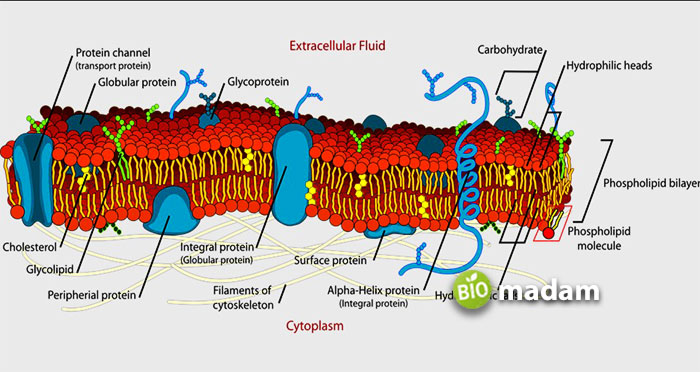
Vascular plants, non-vascular plants, and animal cells have cell membranes, but it is still not the latter’s most external layer. In plants, a cell wall is the primary support, whereas, a cell membrane is under it. On the contrary, a cell membrane in an animal cell is its ultimate support. It helps as a protective boundary for the inner material from the outside atmosphere. Furthermore, this membrane runs a key role during cell division in cytokinesis.
Explain Plasma Membrane
People often confuse the plasma membrane with the well-known cell membrane, although these are quite different terms. A plasma membrane is any layer wrapping up the cellular content or parts. The cell membrane is one type of plasma membrane surrounding a plant or animal cell. Such membranes can perform several functions, depending on their covering structure. A plasma membrane can either bind to a mitochondrion or a chloroplast.
It can even surround a nucleus, particularly called the nuclear membrane. Hence, the function of this membrane depends entirely on its location. It can differ with the difference in organelles’ location.
A plasma membrane holds great significance in the phosphorylation process, whether its substrate-level or oxidative phosphorylation. Moreover, these layers help in guarding the internal structures of a cell. If this membrane encloses an organelle, it must be partially permeable for selective substances to enter and exit. Besides, the plasma membranes will be variable, with different organelles performing different functions. Let this discussion end with a simple example. A mitochondrion’s plasma membrane allows pyruvate inside for the process of cellular respiration. Similarly, a chloroplast performs photosynthesis when its plasma membrane lets carbon dioxide enter it.

Let’s check the key differences between the two terms below to understand more about them.
Grab the Differences Between Cell Membrane and Plasma Membrane
Definition
Cell Membrane
It is defined as a membrane that promotes cell security surrounding it.
Plasma Membrane
On the contrary, it is defined as all those membranes covering a specific cell’s internal contents, including mitochondria, chloroplast, and rough and smooth ER.
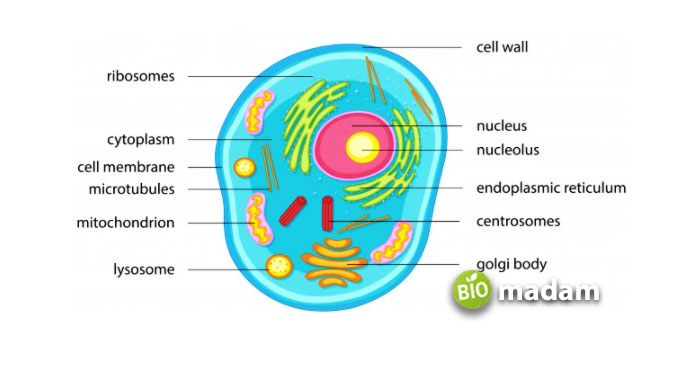
Location
Cell Membrane
This structure covers an entire cell, ultimately protecting its content inside.
Plasma Membrane
In contrast, one can find this structure enclosing different organelles inside a cell.
Cell Composition
Cell Membrane
It is generally composed of phospholipid layers containing large proteins and cholesterol molecules.
Plasma Membrane
The constitution of the plasma membrane diversifies with variations in organelles. For example, the plasma membrane of a mitochondrion will be different from that of a chloroplast.
Modifications
Cell Membrane
This membrane can transform itself as per a cell’s need. For example, some microorganisms require cilia for their movement. Hence, these hair-like projections (cilia) are modified on the cell membrane.
Plasma Membrane
Comparatively, there are no such modifications seen on the plasma membrane, as these are inside a cell.
Supporting Cell Structure
Cell Membrane
It plays a pivotal role in the tonicity of a cell.
Plasma Membrane
On the contrary, the plasma membrane has no role in managing the entire cell structure.
Role in Signal Transductions
Cell Membrane
Cell membranes are the first to deal with external signal transductions because of their peripheral structures in most cells.
Plasma Membrane
These structures can never receive receptor signals for the first time. However, plasma membranes can still play a crucial role in the transduction process.
The Function of Antimicrobial Agents

Cell Membrane
Most antimicrobials (medicines) are made to destroy the cell membranes of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It eventually kills that microorganism.
Plasma Membrane
In contrast, no antimicrobials are mainly observed to destroy any plasma membrane.
Summary
Now that we elaborated on all possible differences between the cell membrane and plasma membrane, we envy clear all of them. Do not ever confuse these two terms. A plasma membrane can never be a cell membrane unless not surrounding a cell. The composition may vary in cellular compartments, but these membranes are generally phospholipid bilayers. Last but not least, these membranes help in transporting essential content in and out of the cell.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.