The endoplasmic reticulum is present in all animal and plants eukaryotic cells. It is a series of flattened sacs found in the cell’s cytoplasm and is involved in multiple functions. Endoplasmic Reticulum is typically the site of the production of different types of proteins that help in body processes. Let’s look at Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) and its function in detail.
What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
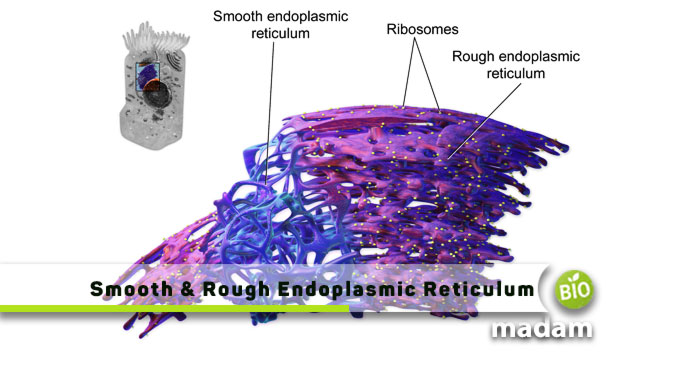
The sac-like layered structure of the endoplasmic reticulum is primarily involved in producing and transporting fats, proteins, hormones, and other molecules needed for cell function. The endoplasmic reticulum is of two types.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Both these are distinguished mainly based on their structure. The smooth ER has a soft, slippery surface, whereas the rough ER has rough layers due to ribosomes on them. They are involved in different functions.
Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum
While the Smooth and Rough endoplasmic reticulum has their distinct functions, some of the collective functions of the ER include:
- The endoplasmic reticulum helps in cell membrane biogenesis through the build-up of proteins and lipids produced by smooth and rough ER.
- The surface area of the endoplasmic reticulum allows the exchange of cell materials through active transport, and passive transport.
- It is a storage site for calcium.
- It offers mechanical support to the cell.
- The endoplasmic reticulum also forms some organelles within the cell, such as lysosomes, helping in digesting waste material.
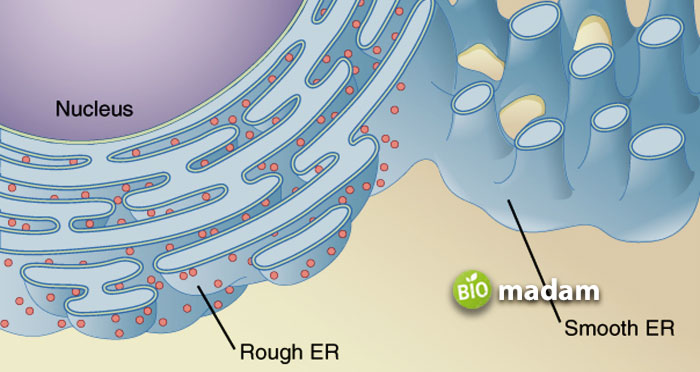
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The rough endoplasmic reticulum may develop from the nuclear envelope in the form of cisternae and a few tubules. It has ribosomes attached to it that help produce proteins and certain enzymes. Rough ER has ribophorins that enable the ribosomes to attach to the endoplasmic reticulum. They are transmembrane glycoproteins attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane and involved in ribosome binding.
Functions of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in producing various materials within the cell, like proteins. The functions of the Rough ER are:
- It helps in the formation of lysosomes.
- It manufactures lipids and proteins that are further transported through the Golgi apparatus.
- The rough endoplasmic reticulum is majorly involved in enzyme and protein synthesis.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the other form of endoplasmic reticulum in the body. It is different from rough ER as it does not have ribosomes attached to the surface. The structure and function of smooth ER vary significantly from rough ER.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum forms from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It is formed as an extension of the rough ER towards the periphery of the cell. Contrary to rough ER, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is not made of cisternae. It is composed of vesicles and tubules that do not have ribophorins. They provide vesicles for the cis-face of the Golgi apparatus. Smooth ER is less extensive than rough ER, and both are interconnected.
Functions of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
While the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is not involved in protein production, it synthesizes other nutrients necessary for cell function, like
- It gives rise to Spherosomes.
- The smooth ER is responsible for the production of lipids and glycogen.
- It also produces steroids essential for several body functions.
FAQs
What are Spherosomes?
Spherosomes (also known as Oleosomes) are tiny single-membrane-bound organelles that help synthesize and store lipids.
Why are spherosomes called plant lysosomes?
Spherosomes in plants are also known as plant lysosomes as they have more than one hydrolytic enzyme and are involved in lipid synthesis in plants.
How does Endoplasmic Reticulum contribute to mechanical support?
The endoplasmic reticulum enables the skeletal muscle fibers to contract. If the endoplasmic reticulum is not present, your body will be deprived of these mechanical functions.
Which cells do not have endoplasmic reticulum?
The ER is an essential part of the eukaryotic cell, however, it is absent in prokaryotic cells. It is because they do not have membrane-bound organelles.
The Final Words
The Endoplasmic reticulum is vital for many cellular functions, and the lack of an ER can affect the mechanical functions of the cell. The rough ER has ribosomes attached to it that help in protein synthesis, while smooth ER lacks ribosomes and has a smooth surface. SER and RER perform different functions, including cell membrane biogenesis, protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and storage of macro and micronutrients, like lipids, calcium, etc.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.